- Author Jason Gerald gerald@how-what-advice.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 10:50.
- Last modified 2025-06-01 06:05.
Avocados - a smooth, soft, nutrient-dense fruit essential for cooking such as guacamole, can be grown from the seeds that remain after the fruit is eaten. Although avocado trees grown from seed take a long time to bear fruit (sometimes as long as 7-15 years), growing avocado trees is fun and profitable and gives you a tree that looks great. Once the tree has grown, you can wait for the avocado to start developing or speed up the process by grafting or grafting it for your tree. Whichever method you choose, learn how to grow your own avocado from scratch by starting with Step 1 below!
Step
Part 1 of 3: Choosing Good Cultivation Conditions

Step 1. Find a warm planting spot with some sun
As a subtropical plant, avocado loves the sun. Native to Central America, Mexico and the West Indies, avocados evolved to thrive in warm, humid environments. Even though avocados have been bred to grow in places as far away as California, they always need sunlight to grow well. However, young avocado plants can be damaged by excessive direct sunlight (especially before they have time to develop broad leaves). Therefore, if you are growing an avocado plant from a seed, you should choose a planting site that has good access to the sun from time to time but not all the time in direct sunlight.
A sunny windowsill is a good growing place for avocados. In addition to ensuring that the avocado only receives a certain amount of sunlight, an indoor window sill also allows you to control the temperature and humidity of the environment around the plant

Step 2. Avoid cold temperatures, wind and ice
Most avocado plants do not grow well in bad weather. Snow, cold winds, and drastic drops in temperature that are harmful to even tougher plants, can kill avocado plants right away. If you live in a tropical or subtropical climate with fairly mild winters, you may be able to put your avocado plant outside all year round. However, if you live in an area where winter temperatures are likely to drop below freezing, you should be prepared to move the plant indoors in winter to protect it from the elements that inhibit growth.
-
Different types of avocado have different tolerances for cold temperatures. In general, the common avocado types listed below will spoil by freezing at the listed temperatures:
- West Indian - -2.2-1.7o C
- Guatemalan - -2.8-1.7o C
- Hass - -3.9-1.7o C
- Mexican - -6.1-2.8o C

Step 3. Use fertile soil with good drainage
Like many common garden plants, avocados thrive best in rich, loose soil. This type of soil provides a good nutrient content to help plants grow strong while also reducing the danger of excess water and allowing for great aeration. For best results, try to prepare a supply of this type of soil (such as soil rich in humus and organic matter) to use as potting media once your avocado roots and stems are strong.
To be clear, you don't need to prepare the soil for pots from the start because at the beginning of planting avocado seeds grow in water before being transferred to the ground
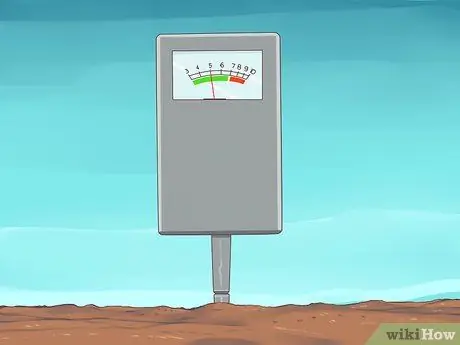
Step 4. Use soil with a fairly low pH
Like many garden plants, avocados grow better in soils that have a low pH (in other words, soils that are acidic, not alkaline). For best results, try to grow your avocado in soil with a pH of 5-7. At higher pH levels, the avocado plant's ability to absorb essential nutrients such as iron and zinc can decrease significantly and inhibit their growth.
If the soil pH is too high, consider using techniques to lower the pH such as adding organic matter or growing alkaline tolerant plants in your garden. You can also achieve good results with soil additives such as aluminum sulfate or sulfur. For more tricks, see How to Lower Soil pH
Part 2 of 3: Start Growing Avocado
Starting from Seeds

Step 1. Take and wash the avocado seeds
Extracting seeds from ripe avocados is very easy. Use a knife to slice the avocado down the middle lengthwise on both sides, then hold and twist the avocado to separate the two halves. Take the seeds attached to the half of the fruit. Then, wash the remaining avocado sticking to the seeds until it is completely clean and smooth.
Don't throw away the avocado - try making guacamole (a traditional Mexican dish made from avocado, topped with lemon and salt), spreading it on bread, or eating it raw as a tasty and nutritious snack

Step 2. Soak the seeds in water
Avocado seeds should not be planted directly into the ground - instead, they should be placed in water until enough roots and stems have grown to support the plant. An easy way to soak avocado seeds in water is to stick three toothpicks next to the seeds so the avocado seeds can sit on the edge of a large cup or bowl. Don't worry - it doesn't hurt the plant. Fill a cup or bowl with water until the bottom of the avocado seed is submerged.
Make sure that the avocado seed is sitting in the water with the correct side up. The top of the avocado seed should be slightly rounded or pointed (like the top of an egg), while the bottom, which is in the water, should be slightly flat and may have an even discoloration compared to the rest of the avocado seed

Step 3. Place it near a sunny window and refill water when needed
Next, place the avocado seed and a container of water in a place where it will receive occasional (but not direct) sunlight, such as a window that only receives a few hours of sunlight per day. Monitor your plants occasionally and add fresh water whenever the water level drops below the bottom of the avocado seed. In a few weeks to about a month and a half, you will see roots starting to emerge from the bottom of the seed and a small stem starting to emerge from the top.
The initial stage of inactivity can last about two to six weeks. Your avocado seed may not change, but be patient - eventually, you'll see the beginnings of the plant's roots and stems emerging

Step 4. Cut the stems when they reach about six inches in length
As the avocado roots and stems begin to grow, you should continue to monitor progress and change the water as needed. When the stem reaches a length of about 15 cm, cut it back so that it reaches a length of about 7.5 cm. Within a few weeks, this will lead to the development of new roots and cause the stems to eventually grow to be more extensive and complete.

Step 5. Plant your avocado seeds
A few weeks after the first pruning, when the avocado plant's roots are thick and developed and the stem has sprouted new leaves, you should transplant it into a pot. Remove the toothpick and place the seeds root-down in soil rich in organic matter with good drainage. For best results, use a pot with a diameter of about 25 - 30 cm. A small pot can cause the plant's roots to become tied up and stunt its growth if you don't move it to a new pot.
Don't bury the whole seed - bury the roots, but leave some of the top

Step 6. Water the avocado plant frequently
As soon as the avocado plant is transplanted into the pot, you will need to water it a lot. Wet the soil slowly and thoroughly. After that, add enough water so the soil is slightly damp, but not too wet or muddy.

Step 7. Accustom the plant to the natural outdoor temperature
If you want to move plants outdoors, it's a good idea to introduce outdoor conditions gradually first. Start by placing the pot in a place that gets indirect sunlight throughout the day. After that, gradually, move the potted plant to a brighter area again. Eventually, your plant will be ready to grow in a place that gets constant direct sunlight.

Step 8. Remove the foliage of each avocado plant growing to a height of 30 cm
Once your plant has been transplanted into the ground, continue the care by providing frequent watering and strong sunlight. Periodically, monitor the progress of plant growth with a ruler or measuring tape. When the plant stems reach a height of about 30 cm, cut off the new leaves by hand. As the avocado grows, cut off a series of new leaves each time the stem grows 15 cm long.
This encourages the plant to grow new shoots, which makes for a fuller and healthier tree in the long run. Don't worry this will hurt your plants - avocados are hardy enough to be able to recover from this regular pruning without a problem
Grafting

Step 1. Grow the seedlings to about 0.6-1 meters
As mentioned above, growing an avocado tree from seed does not mean that the tree will be able to bear fruit in the short term. Some avocado trees take several years to start producing fruit, while others may take longer or may not even produce good fruit. To speed up this process and ensure your tree produces large fruit, use a technique professional growers use - grafting. To do this, you will need an avocado tree that is already producing good fruit and avocado seedlings that are at least 60 to 75 cm tall.
If you can, try to find a "producing" tree that is strong and disease-free and produces good fruit. A successful grafting is combining two of your plants together, so you will have to use the healthiest plants to avoid problems with their health

Step 2. Start getting ready to plant avocados at the end of the dry season
Avocado should be planted early in the rainy season when the weather is not too dry. So, start preparing avocado seeds at the end of the dry season so that they can be planted at the beginning of the rainy season.
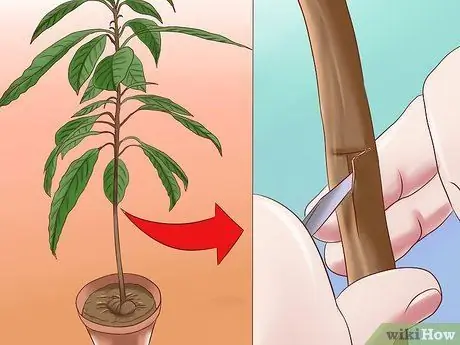
Step 3. Make a “T” shaped cut in the seed
Use a sharp knife and make T-shaped cuts in the stems 20 to 30 cm from the ground. Cut horizontally through about a third of the thickness of the stem, then turn the knife and cut the stem about 2.5 cm toward the ground. Use a knife to peel the skin off the stem.
Of course, you should avoid cutting too far into the stem. Your goal is to "open" the bark along the sides of the stem so you can join it with new limbs instead of damaging the seedlings

Step 4. Cut the shoots from the “producing” tree
Next, find healthy-looking shoots on the fruit-bearing tree you've chosen. Remove it from the tree by making a diagonal cut that starts about 1.5 cm below the shoot and ends about 2.5 cm below it. If the shoot is in the “middle” part of the branch or twig, not at the tip, make a 2.5 cm cut above the shoot as well to release it,

Step 5. Merge the shoots with the seedlings
Next, slide the shoot you removed from the producing tree onto the T-shaped cut in the seedling. You should make the green material under the skin of each plant touch each other - otherwise grafting may fail. Once the shoot has been placed in the cut in the seedling, secure it in place using a rubber band or grafting rubber (special tools available at gardening stores).

Step 6. Wait for the shoots to grow
If your grafting attempt is successful, the shoots and seedlings will heal together, forming one smooth plant. In spring, this can happen in a month or less, but in other months it may grow more slowly, it may take up to two months. Once the plant is fully healed, you can remove the rubber band or grafting rubber. If desired, you can also carefully cut the stems of the original plant 2, 5 or 5 cm above the new branch to create a new main branch.
Keep in mind that avocados grown from seed can take 5-13 years to flower and bear fruit
Part 3 of 3: Caring for Avocado Plants

Step 1. Water often, but don't overdo it
Compared to other plants in your garden, avocado plants may require a lot of water. However, it is important to remember that over-watering is a potential problem for almost any plant, including avocados. Try to avoid watering so frequently or thoroughly that the avocado tree soil looks runny or muddy. Use soil with good drainage (soil rich in organic matter is usually a good choice). If your tree is in a pot, make sure that the pot contains drainage holes at the bottom to allow water to drain out. Follow these simple tips, and your plants will be free from the dangers of overwatering.
If your plant's leaves turn yellow despite frequent watering, it may be a sign that your plant is receiving too much water. Stop watering immediately and start again when the soil is dry

Step 2. Fertilize your plants only occasionally
You may not need fertilizer at all to grow a healthy, strong avocado tree. However, if used wisely, fertilizers can promote the growth of young plants. Once the tree is strong enough, add a balanced citrus fertilizer to the soil during the growing season according to the directions provided. Don't overdo it - when using commercial fertilizers, it's usually better to be a bit conservative. Always water the plant after fertilization to ensure the fertilizer is absorbed into the soil and delivered directly to the plant roots.
Like many plants, avocados are generally not fertilized when they are very young, as they can be very susceptible to "burning" that results from overuse of fertilizers. Try to wait at least a year before fertilizing
Step 3. Watch for signs of salt buildup
Compared to other crops, avocados can be very susceptible to salt buildup in the soil. Avocado plants that suffer from high salt content will have slightly wilted leaves with tips that look brown and slightly burnt, where excess salt accumulates. To lower the salinity (saltiness level) of your soil, change your watering method. At least once a month, try to water abundantly, thus soaking the soil. The large flow of water will carry the salts that have accumulated deep into the soil, below the roots where they will be less harmful to plants.
Step 4. Learn how to beat common avocado pests and diseases
Like agricultural crops, avocado plants can suffer from various pests and diseases that can threaten the quality of the fruit or even harm the entire plant. Knowing how to recognize and solve these problems is critical to maintaining a healthy and productive avocado tree. Here are some of the most common avocado pests and diseases - for more information, contact botanical sources:
- Cancer - sunken sores on the plant that can secrete sap. Cut the cankers from the affected branches. Cankers on tree trunks can kill plants.
- Root rot - Usually caused by excess water. Causes leaves to turn yellow, wilt, and eventually rot even when all conditions for growth have been met. Stop watering immediately and, if it gets too severe, dig up the roots to provide air. Sometimes fatal to plants.
- Wilt and blight - 'dead' fields on the tree. The fruits and leaves in this field wither and die. Remove the affected area from the tree immediately and wash the utensil you used to do this before reuse.
- Weevil lace bugs or tingidae - Causes yellow spots on leaves that dry quickly. Damaged leaves can die and fall. Use commercial pesticides or natural pesticides such as pyrethrins.
- Weevils - hollow trees, making small holes through which sap can be released. Prevention is the best medicine - keeping the tree healthy and maintained makes the tree less affected. If weevils are present, remove affected branches to reduce their spread.
Tips
There is a special fertilizer for avocados. If used as directed, these fertilizers almost always help. Other fertilizers can also be useful, especially if your overall soil is less than optimal for avocado growth. Since you will be eating the produce, consider buying an organic fertilizer instead of a synthetic one
Warning
- While it's true that you can grow a tree from avocado seed, keep in mind that a tree grown from seed will be very different from the parent type and can take 7-15 years to start producing fruit. Fruits from trees grown from seed tend to have different taste characteristics from the parent type.
- If the leaves turn brown and burn at the tips it means that too much salt has accumulated in the soil. Let the water run freely into the pot and run it for a few minutes.






