- Author Jason Gerald gerald@how-what-advice.com.
- Public 2024-01-19 22:11.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 12:04.
There are two forms of energy: potential and kinetic energy. Potential energy is the relative energy that one object has with respect to the position of another object. For example, if you are at the top of a hill, you have more potential energy than if you were at the foot of a hill. Kinetic energy is the energy an object has when it is in motion. Kinetic energy can be generated due to vibration, rotation, or translation (movement from one place to another). The kinetic energy of any object can be easily found by an equation that uses the mass and velocity of that object.
Step
Part 1 of 3: Understanding Kinetic Energy

Step 1. Know the formula for calculating kinetic energy
The formula for calculating kinetic energy (EK) is EK = 0.5 x mv2. In this equation, m represents mass, which is the amount of matter in an object, and v represents the object's velocity or the rate at which the object changes position.
Your answer should always be written in joules (J), which is the standard unit of measurement for kinetic energy. Joule is equivalent to 1 kg * m2/s2.

Step 2. Determine the mass of the object
If you solve a problem for which the mass is unknown, you must determine the mass yourself. The value of mass can be determined by weighing an object on a scale and finding its mass in kilograms (kg).
- Take the scales. Before you weigh your objects, you must turn the scales down. Zeroing the scales is called a tower.
- Place your object on the scale. Slowly place the object on the scale and record its mass in kilograms.
- If necessary, convert grams to kilograms. For the final calculation, the mass must be in kilograms.
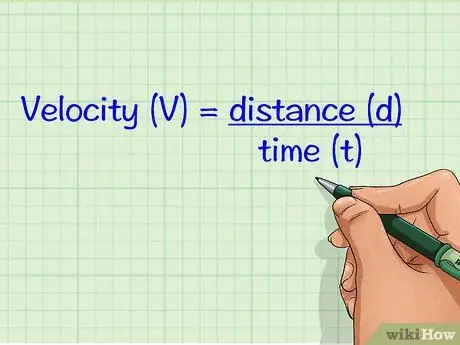
Step 3. Calculate the object's velocity
Often times, the problem will give the object's velocity. If not, you can find its velocity by using the distance the object travels and the time it takes the object to travel that distance. The unit for speed is meters per second (m/s).
- Velocity is defined according to the equation as displacement divided by time: V = d/t. Velocity is a vector quantity, i.e. it has both magnitude and direction. Magnitude is a numerical value that represents speed, while direction is the direction in which the speed is traveling.
- For example, the speed of an object can be 80 m/s or -80 m/s, depending on the direction in which it is moving.
- To calculate speed, simply divide the distance an object has traveled by the time it took the object to cover that distance.
Part 2 of 3: Calculating Kinetic Energy

Step 1. Write down the equation
The formula for calculating kinetic energy (EK) is EK = 0.5 x mv2. In this equation, m represents mass, which is the amount of matter in an object, and v represents the object's velocity or the rate at which the object changes position.
Your answer should always be written in joules (J), which is the standard unit of measurement for kinetic energy. Joule is equivalent to 1 kg * m2/s2.

Step 2. Plug the mass and velocity into the equation
If you don't know the mass or velocity of the object, then you have to calculate it. Suppose you know the magnitude of the two variables and are trying to solve the following problem: Determine the kinetic energy of a 55 kg woman who is running at a speed of 3.87 m/s. Since you know the woman's mass and velocity, you can plug the values into the equation:
- EK = 0.5 x mv2
- EK = 0.5 x 55 x (3, 87)2
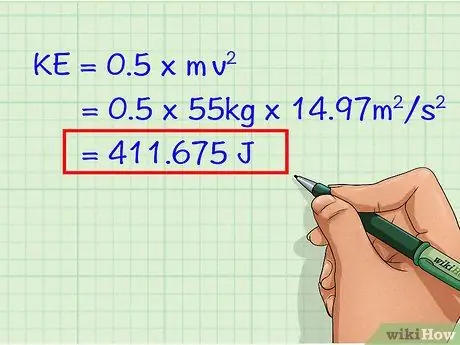
Step 3. Solve the equation
Once you enter the mass and velocity, you can find the kinetic energy (EK). Square the velocity and multiply all the variables. Remember to write your answer in joules (J).
- EK = 0.5 x 55 x (3, 87)2
- EK = 0.5 x 55 x 14.97
- EK = 411,675 J
Part 3 of 3: Using Kinetic Energy to Find Velocity or Mass

Step 1. Write down the equation
The formula for calculating kinetic energy (EK) is EK = 0.5 x mv2. In this equation, m represents mass, which is the amount of matter in an object, and v represents the object's velocity or the rate at which the object changes position.
Your answer should always be written in joules (J), which is the standard unit of measurement for kinetic energy. Joule is equivalent to 1 kg * m2/s2.

Step 2. Enter the known variables
In some problems, you may know the kinetic energy and mass or the kinetic energy and velocity. The first step to solving this problem is to enter all the known variables.
-
Example 1: What is the velocity of an object of mass 30 kg with kinetic energy of 500 J?
- EK = 0.5 x mv2
- 500 J = 0.5 x 30 x v2
-
Example 2: What is the mass of an object that has a kinetic energy of 100 J and a speed of 5 m/s?
- EK = 0.5 x mv2
- 100 J = 0.5 x m x 52

Step 3. Rearrange the equation to solve the unknown variable
Using algebra, you can find the value of an unknown variable by rearranging all the known variables to one side of the equation.
-
Example 1: What is the velocity of an object of mass 30 kg with kinetic energy of 500 J?
- EK = 0.5 x mv2
- 500 J = 0.5 x 30 x v2
- Multiply the mass by 0.5: 0.5 x 30 = 15
- Divide the kinetic energy by the product: 500/15 = 33, 33
- Square root to find the velocity: 5.77 m/s
-
Example 2: What is the mass of an object that has a kinetic energy of 100 J and a speed of 5 m/s?
- EK = 0.5 x mv2
- 100 J = 0.5 x m x 52
- Square the speed: 52 = 25
- Multiply by 0.5: 0.5 x 25 = 12, 5
- Divide the kinetic energy by the product: 100/12, 5 = 8 kg






