- Author Jason Gerald gerald@how-what-advice.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 10:50.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 12:04.
You can restrict access to the web for users on Internet Explorer or Microsoft Edge by modifying family settings ("Family"). This can be “good news” for Windows users who want to protect students, children, and employees from certain web content. Protect Internet Explorer users by blocking dirty or annoying websites on all the latest versions of Windows. Keep in mind that these methods only work to restrict browsing through Internet Explorer, not other web browsers!
Step
Method 1 of 3: Windows 10
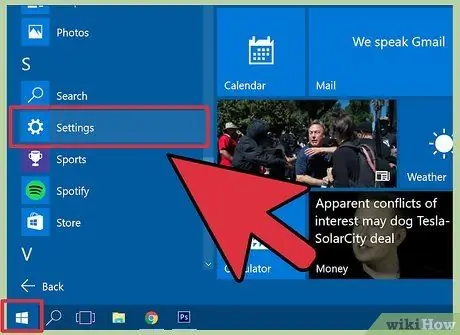
Step 1. Open the “Start” menu and click “Settings”
To restrict web traffic on Internet Explorer, you need to create a new Windows user account with restricted access. Such accounts are referred to as "child" accounts.
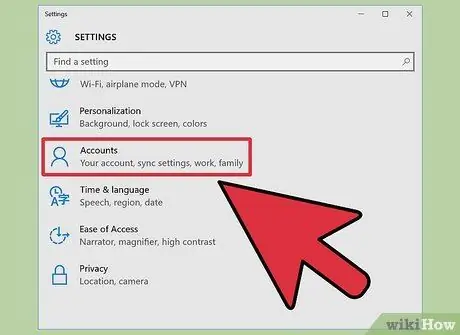
Step 2. Click “Accounts”, then select “Family & other users”
The “Family & other users” page will display a list of user accounts stored on the computer.
If the user already has a “child” account, you don't need to create a new account. Instead, edit the web restrictions on the child account at account.microsoft.com/family. You can learn how later in this method
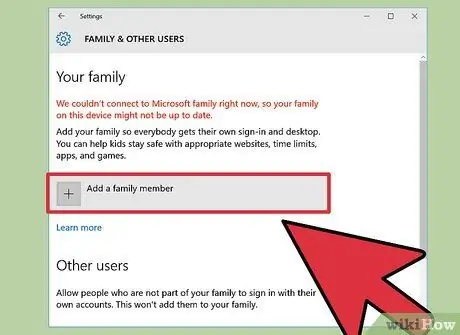
Step 3. Click “Add a family member”, then select “Add a child”
Adult or “Adult” accounts have no restrictions so don't select that option.
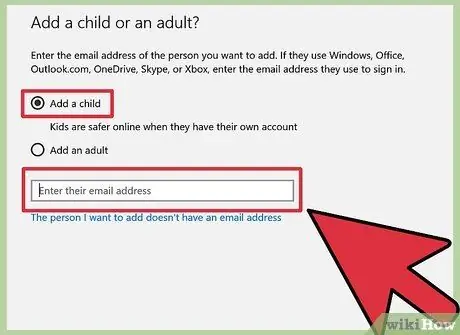
Step 4. Enter the new Microsoft email address for the new child account
The new child account must have an email address that ends in the domain @outlook.com, @hotmail.com, or @live.com.
- If your child has a Microsoft email account, type the address into the blank, click “OK”, and select “Confirm”.
- If your child doesn't have a Microsoft email account, click "The person I want to add doesn't have an email address". Type in the new email address and password for the child's account, then click “Next”.
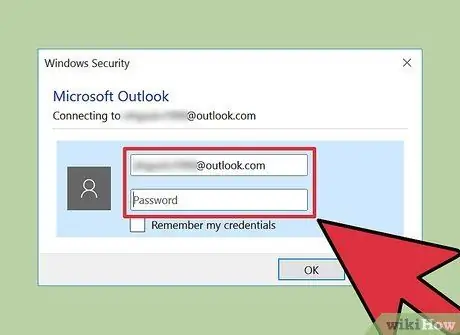
Step 5. Log into Outlook to read the confirmation message from Microsoft
When logging in, you will need the child's account username and password. You can see a message in your inbox that says “You need a parent's permission”.
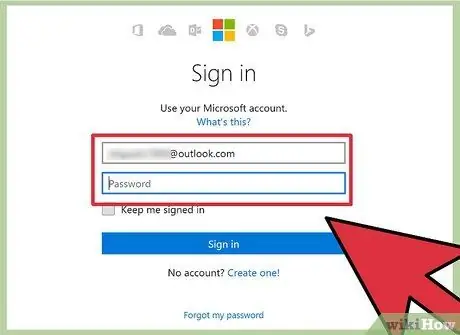
Step 6. Click “Have a parent sign in”
Enter YOUR Microsoft account username and password, then click “sign in”.
This is the username and password combination you use to sign in to Windows 10
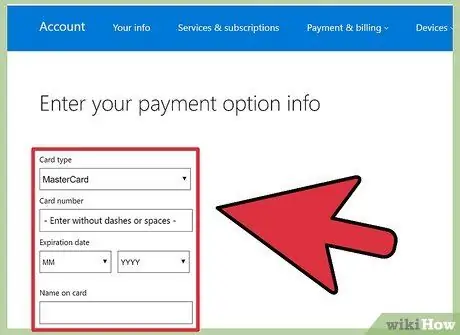
Step 7. Enter your credit card information when prompted to prove that you are an adult
Your card will be charged 0.5 US dollars by Microsoft. There is no way to get around this move. Enter the credit card information, click “Next”, then select “Confirm”.
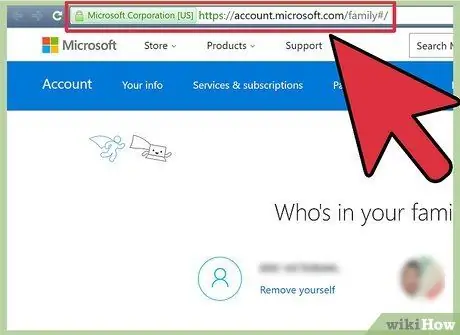
Step 8. Navigate your browser to account.microsoft.com/family to view family settings (“Family settings”)
You can see a list of accounts linked to your “family” on the right side of the screen.
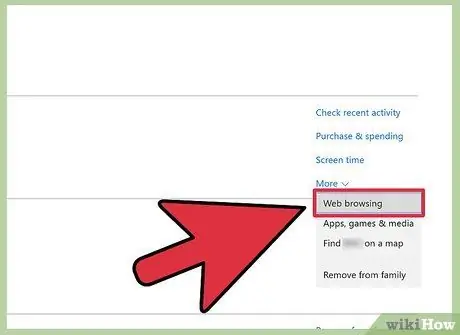
Step 9. Click the arrow next to the child's account name to access their web browsing settings
When the new menu appears, select “Web browsing” from the list.
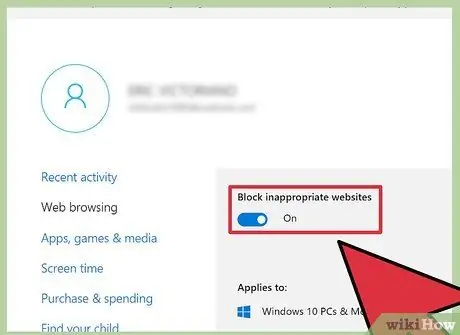
Step 10. Block unsafe websites
In the “Web browsing” menu, click the switch next to the text “Block inappropriate websites” to the on position (“On”). After that, adult content will be blocked and the SafeSearch feature will be activated to filter children's search results.
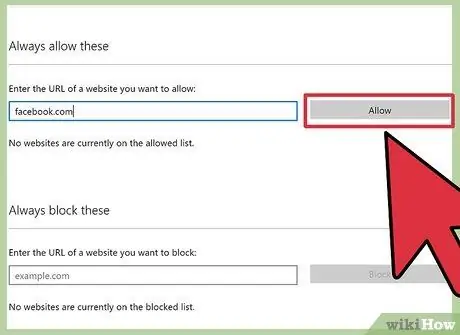
Step 11. (Optional step) Allow some specific websites through the filter
Some websites, such as sites that address gender or medical issues, may be inadvertently blocked by filters. If you know a site that your child is allowed to access, regardless of the active filter, type the website's address into the box below the “Always allow these” message. Click “Allow” to add the site to the permissions list.
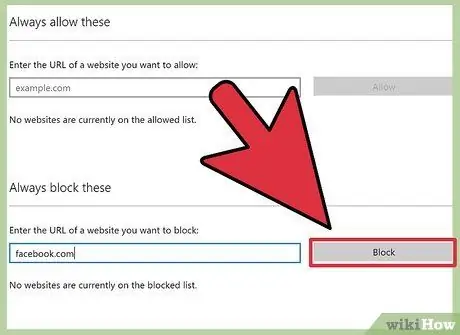
Step 12. Block the site
If you want to block access to a specific website (e.g. Facebook), type the website address under the “Always block these” text. Click the “Block” button to add it to the block list.
Step 13. Make sure the user is ONLY logged into the computer using the child account
Your little one will only be protected by web browsing filters when using the computer through the child's account. If he accesses the internet from a different account (including yours), he can bypass the filter.
Method 2 of 3: Windows 8
Step 1. Press the key combination Win+X and select “Control Panel”
You can filter Internet Explorer traffic for a specific user by creating a “child” account for that user.
Step 2. Select the “Users” menu, then click “Add a user”
The “Add a user” option is in the lower-right corner of the screen.
If your child already has a limited local account on the computer, you don't need to create a new account. Instead, select the created child account from the list of users on the “Family Safety” settings page when prompted for this method

Step 3. Click “Sign in without a Microsoft account”
Since you only need to restrict internet access to certain users on the computer, you need to create a local account.
Step 4. Click “Local accounts”
This option is selected to confirm the previous selection.
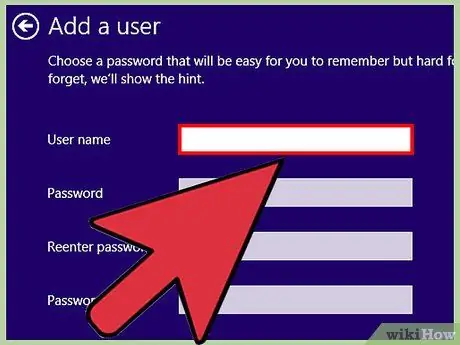
Step 5. Enter the new username and password for the child account, then click “Next”
When your child uses the computer, this is the account information he or she needs to use.
- The use of simple usernames such as “children” or the child's first name is sufficient.
- If you do not want to set a password for this new account, leave the password field blank.
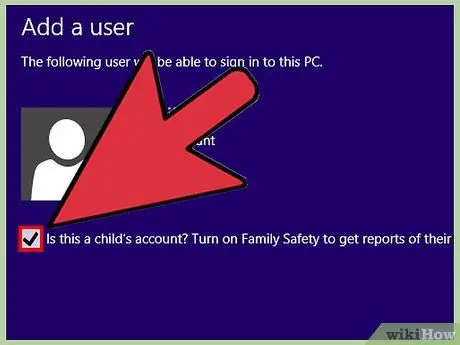
Step 6. Check the box next to the “Is this a child's account? ” and click “Finish”. The child's account is now active.
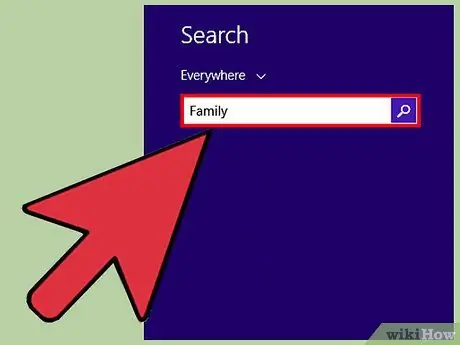
Step 7. Access "Family Safety" settings
Press the Win+S key combination to launch the search box, then type
"family"
. Click “Set up Family Safety for any user” in the search results.
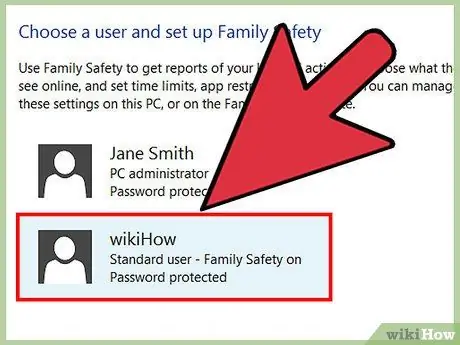
Step 8. Select the child account from the list of users
After that, the “Family Settings” panel for that user account will be opened.

Step 9. Click “Web filtering”
The default setting set by the computer is “(User) can use all websites”.

Step 10. Enable the “(Users) can only use the websites I allow” feature
It should be noted that if you wish to disable the filter at this stage, you can return to this page and restore it to the default settings.

Step 11. Click “Set web filtering level” to select an option from the list of restriction options
- The “Allow list only” option only allows the child to view the websites that you add to the access list.
- The “Designed for children” option includes the above options, but also includes websites rated for children.
- The “General interest” option includes all of the options above, including additional options from the “general interest” category (non-adult sites that are educational or offer safe entertainment, but NOT social media).
- The “Online Communication” option offers all of the above options, including social media and access to chat and email.
- The “Warn on Adult” option includes all of the options above AND an adult site. However, a warning message will be displayed before the adult site is opened.
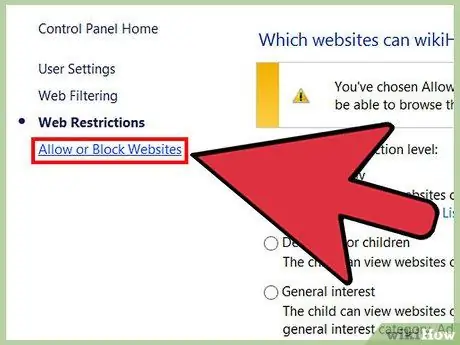
Step 12. Add the website to the list of permissions ("Allow") and block it ("Block")
Click the “Allow or Block Websites” link on the left side of the screen. To add a website to the block list (users cannot access the site), type the URL in the provided field and click the “Block” button. You can also add site URLs that passed the filter (regardless of the filter you selected earlier). Type the URL into the field, then click the “Allow” button. Close the window when finished.
Sites like YouTube can be blocked by filters, but your child may need to use them for school purposes

Step 13. Make sure the child only accesses the computer using the child's account
It will not be protected by web restrictions when using an account other than a child's account. He can click on his username, then enter his account password when prompted.
Method 3 of 3: Windows 7 and Vista
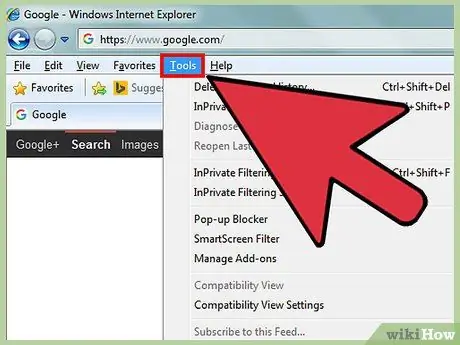
Step 1. Open Internet Explorer and access the “Tools” menu > “Internet Options”
You can enable web filters for Internet Explorer (IE) by enabling and configuring “Content Advisor”. If IE doesn't have a standard toolbar display, the “Tools” button looks like a gear and appears in the upper right corner of the window.
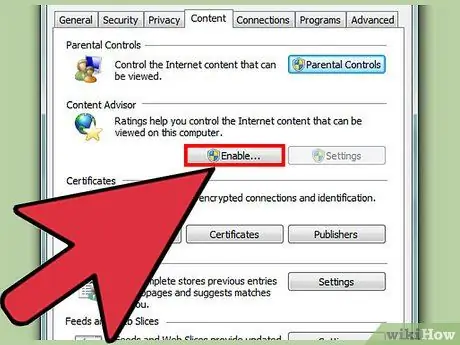
Step 2. Access general settings “Content Advisor”
Click “Enable” and enter the administrator password if necessary. Now, click on “Settings”.
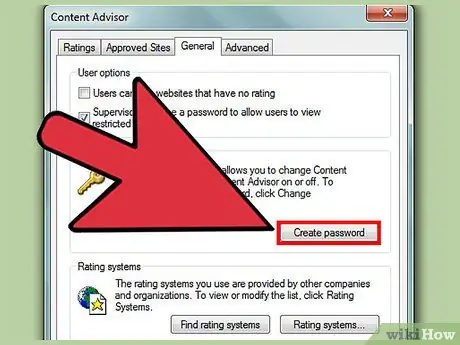
Step 3. Create a supervisor password (“supervisor password”)
To enable website restrictions, you need to set a password. Otherwise, other users can clear the settings with just a few clicks. Click the “General” tab, then click “Create Password”. Enter and confirm the password, then click “OK”. Now, when you enter the “Content Advisor” settings, you will be asked to enter the password.
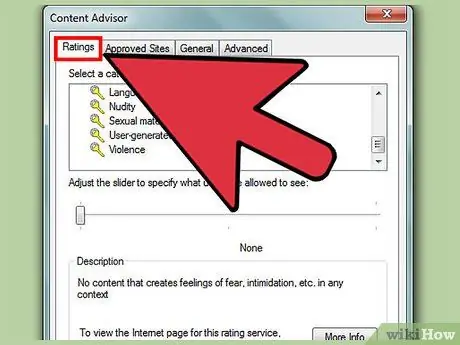
Step 4. Select an allowed rating level
Click the “Ratings” tab and review the list of categories available (language (“language”), nudity (“nudity”), sex (“sex”), and violence (“violence”). click on a topic with the mouse, then drag the slider to the far left. The further the slider is moved to the left, the higher the web browsing protection for users against that type of content. Meanwhile, when shifted to the right, more content will escape from filtering.
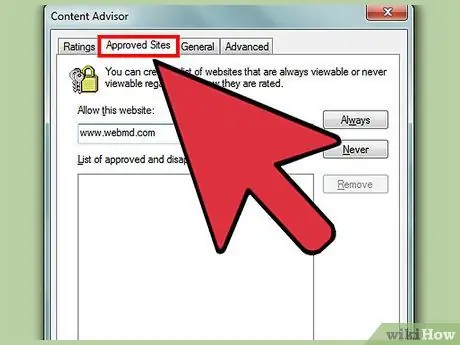
Step 5. Allow or block certain sites
Click the “Approved Sites” tab. On this page, you can type in the specific websites that you want to exclude from the added filter. For example, some medical websites may be filtered into the nudity or violence category. If you know that users need to access a site like WebMD, enter the URL www.webmd.com in the field, then click “Always”.
- If you find a particular site that is moderately annoying, but not necessarily vulgar (e.g. Facebook), type in www.facebook.com and click “Never.” Click "Apply" after that.
- Blocking sites like Google or YouTube can make it difficult for users to complete actual tasks. You need to consider the possibilities before blocking sites like this.
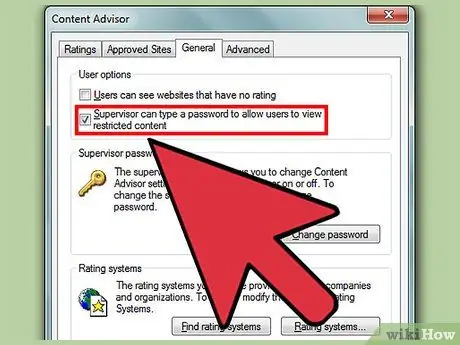
Step 6. Decide how to bypass the filter
On the “General” tab, check the box with the text “Supervisor can type a password to allow users to view restricted content”. This option allows (only) you, the supervisor, to bypass your own filter rules in order to access blocked sites while using a computer.
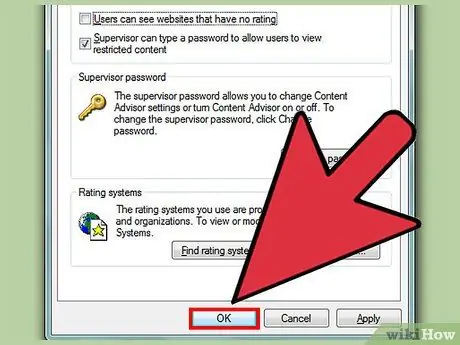
Step 7. Click “OK” to save changes
After enabling “Content Advisor”, data will be limited to all users. If you're browsing and need to open a blocked website, access the website and type in the supervisor password when prompted.
Tips
- Another more effective way to filter browsing is to block websites in all web browsers or install a protection program like K9 or Net Nanny.
- Free proxy service websites (try searching "free web proxy" through Google) can hide browsing web pages from parental control. Most parental control programs will automatically block access to these sites, but try checking your browsing history for “trials” of access, and talking to your child to agree on allowed site browsing.
- Internet Explorer is no longer developed by Microsoft so it's a good idea to switch to Microsoft Edge, Google Chrome, or Mozilla Firefox.
Warning
- If you have a router/modem that always provides internet access, parental control programs (and, of course, Windows itself) can be bypassed by loading the modified operating system from a removable disk.
- Try installing a physical proxy that controls all web requests at the access level. This step may include installing a more expensive router/firewall with additional features (unless you already have/use one).
- This setting change on all versions of Windows will only affect users using Internet Explorer or Microsoft Edge. If you have Chrome installed on your computer, try locking the browser with a password.






