- Author Jason Gerald gerald@how-what-advice.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 10:50.
- Last modified 2025-06-01 06:05.
Fundamental first aid refers to the initial process of assessing and serving the needs of someone who is injured or under physiological stress due to choking, heart attack, allergic reaction, medication or other medical emergency situation. Basic first aid allows you to quickly determine a person's physical condition and the appropriate course of treatment. You should always seek professional medical help as soon as possible, but applying the right first aid procedures can be life-or-death. Follow our entire tutorial, or find the specific advice you need by checking out the sections listed above.
Step
Method 1 of 4: Performing Triple P. Relief
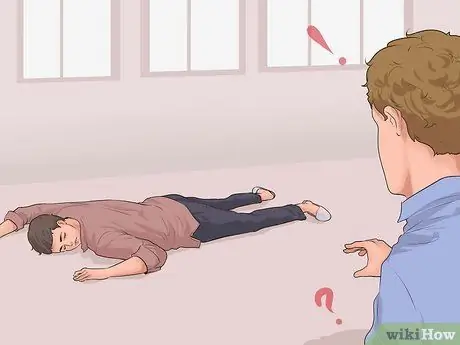
Step 1. Check the surroundings
Evaluate the existing situation. Are there things that can harm you? Are you or the victim threatened by fire, smoke or toxic gases, unstable buildings, moving power lines or other hazardous scenarios? Do not rush into a situation that will make you a victim yourself.
If approaching a victim is potentially life-threatening, seek professional help immediately; they have a higher level of training and know how to handle these situations. First aid is useless if you can't do it without hurting yourself

Step 2. Call for help
Call the authorities or emergency services immediately if you believe someone is seriously injured. If you are the only person there, try to give the patient rescue breaths before seeking help. Do not leave the victim alone for very long periods of time.

Step 3. Provide assistance to the victim
Helping someone who has recently been seriously traumatized includes physical care and emotional support. Remember to stay calm and calm; let the victim know that help is coming soon and that everything will be okay.
Method 2 of 4: Treating a Fainted Person

Step 1. Determine the response rate
If someone is unconscious or unconscious, try to wake them up by gently tickling their hands and feet, or talking to them. If the victim does not respond to actions, sounds, touch, or other stimuli, immediately check to see if he or she is still breathing.

Step 2. Check the victim's breathing and pulse
If the victim is unconscious or unconscious, check to see if he or she is still breathing: “see” if the chest is rising and falling; "listen" to the sound of the breath coming in and out; “feel” the presence of air by using the side of your face. If there are still no obvious signs of breathing, check for a pulse.

Step 3. If the victim remains unresponsive, prepare to perform CPR (Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation)
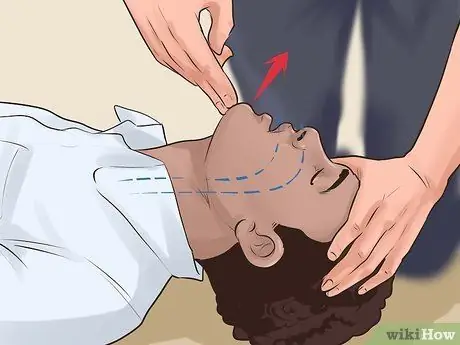
Unless you suspect a spinal cord injury, gently lean back and open the airway. If you suspect a spinal cord injury, leave the victim as is, as long as they are still breathing. If the victim begins to vomit, turn her on her side so she doesn't suffocate.
- Keep the head and neck aligned.
- Be careful to lay down the victim's body while guarding and supporting his head.
- Open the victim's airway by lifting the chin.

Step 4. Perform 30 chest compressions and two exhales as part of CPR
In the center of the victim's chest, just below the imaginary line that bisects the nipples, cup your hands together and press down on the victim's chest to about 5.1cm at a rate of 100 compressions per minute. After 30 compressions, give two rescue breaths and check vital signs. If breathing is obstructed, correct the victim's airway. Make sure the head is tilted back slightly and the tongue is not in the way. Continue this cycle of 30 chest compressions and two rescue breaths until someone replaces you.
Step 5. Remember the JPS RPJ
JPS RPJ refers to three critical things that you should pay attention to. Check these three things as often as possible while providing RPJ assistance to victims.
- Breathing Path. Is the victim's airway blocked?
- Respiration. Is the victim breathing?
- Circulation. Whether the victim shows signs of pulsation at the main points. (wrist, carotid artery, groin)?
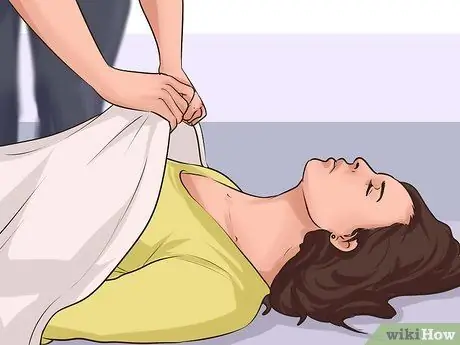
Step 6. Keep the victim warm while you wait for medical help
Cover the body with a towel or blanket, if available. That is if you don't take off part of the clothes you are wearing (jacket or coat) and use it as a cover for the victim's body until medical help arrives. However, if the victim is exposed to heat, do not cover or warm the body. In this case, keep the body cool by fanning and moisturizing.

Step 7. Pay attention to all the do's and don'ts
When providing first aid, make sure you know all the "don'ts" to do, such as:
- Do not feed and/or drink an unconscious person. This will cause him to choke and potentially suffocate.
- Do not leave the victim alone. Unless you really have to go for help. Accompany the victim until help or medical personnel arrive.
- Don't support an unconscious person's head with a pillow.
- Do not slap or splash water on an unconscious person's face. It's just a movie trick.
Method 3 of 4: Treating Common Problems in First Aid Scenarios

Step 1. Protect yourself from blood-borne pathogens
Blood-borne pathogens can threaten your health and well-being in the form of disease. If you have a first aid kit, first sanitize both hands and put on sterile gloves. If sterile gloves and sanitizing equipment are not available, cover hands with gauze or cotton. Avoid direct contact with the victim's blood. If you touch or come into contact with it, clean it as soon as possible. Remove all remaining sources of contamination.
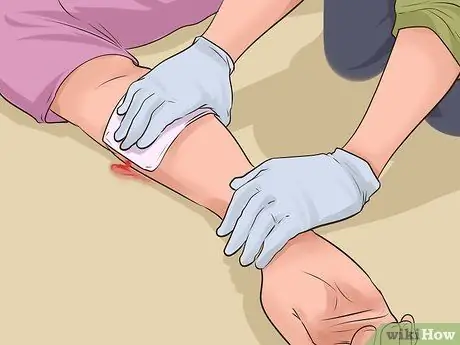
Step 2. Stop the bleeding first
After successfully confirming that the victim is still breathing and has a pulse, the next priority is to control the bleeding. Controlling the bleeding is one of the most important things you can do to save the victim's life. Apply direct pressure over the wound before trying other ways to manage the bleeding. Read the related article for details on the steps you can take.
Treat gunshot wounds. This wound is a serious and unexpected wound. Read more about special considerations when caring for victims of gun fire

Step 3. Next is to treat the victim in shock
Shock, usually from blood loss, often accompanies physical and psychological trauma. Shock victims often have cold, clammy skin, a restless attitude or altered mental state. The skin is also pale around the face and lips. If not treated immediately, shock can be fatal. Everyone who suffers a serious injury or a life-threatening situation is at risk of developing shock.

Step 4. Provide first aid for fractures
Severe bone loss, although common, can be treated in the following steps:
- Make sure the area of the fractured bone remains stationary. The part and region of the broken bone must not move or support any part of the body.
- Get rid of the pain. Often, this can be done with an ice pack wrapped in a towel.
- Make a bandage. A roll of newspaper and strong tape is enough to make this. A broken finger, for example, can also use the finger next to it that is still normal, as a bandage.
- Make clothespins, if necessary. Tie a t-shirt or filter pillow around the broken arm and secure it and hang it around the shoulder.

Step 5. Assist a choking victim
Choking can lead to death or permanent brain damage within minutes. Read this article to find out how to help a choking victim. This article tells how to help children and adults with choking victims.
One method to help a choking victim is the Heimlich maneuver. This maneuver is performed by straddling the victim from behind and then hugging them like a bear with your hands locked above the navel, below the breastbone. Press up to expel air from the lungs. Repeat until you have cleared the object blocking the victim's airway

Step 6. Learn how to treat burns
Treat first- and second-degree burns by immersing or splashing the area with cold (no ice) water. Don't use other creams, butters or ointments, and don't squeeze the blisters (such as popping a pimple). Third degree burns can be covered with a damp cloth. Remove clothing and jewelry from the burn, but do not remove charred clothing that is stuck to the wound.

Step 7. Watch for impact injuries
If the victim has suffered a blow to the head, look for signs. The most common symptoms include:
- Loss of consciousness after being hit
- Disorientation or poor memory
- Vertigo
- Nauseous
- Weak.
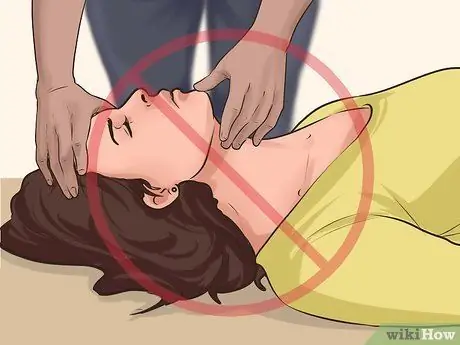
Step 8. Treat the victim with a spinal injury
If you suspect that the victim has a spinal cord injury, you should absolutely not move or reposition the victim's head, neck or back “unless the victim is in danger”. You should also be very careful when performing rescue breathing or CPR. Read this article to know what to do.
Method 4 of 4: Handling Rare Cases in First Aid Scenarios

Step 1. Help the person who has a seizure
Seizures can be very scary for people who have never experienced them before. Fortunately, helping people with seizures is fairly easy.
- Clean the surrounding area so that the victim is not injured.
- Activate emergency medical services if the seizure lasts more than 5 minutes or if the victim is not breathing after the seizure
- After the episode ends, help the victim lie on the floor and place a soft or flat mat under the head. Tilt the victim's body to make it easier for him to breathe, but "don't" hold or force the victim to stop the movement.
- Be friendly and reassuring when the victim's consciousness recovers. Do not offer food or drink until they are fully aware.

Step 2. Help someone survive a heart attack
It helps to know the symptoms of a heart attack, such as a rapid heartbeat, pressure or pain in the chest, and unexplained nausea. Immediately take the victim to the hospital while being given aspirin or nitroglycerin, and this drug must be chewed by the victim.

Step 3. Recognize the symptoms of people who have had a stroke
Again, knowing the symptoms of a stroke is very important. Symptoms of a stroke include temporary speech paralysis or difficulty understanding other people's speech; confusion; loss of balance or dizziness; also a severe headache without starting any signs. Get the person you suspect has had a stroke to a hospital emergency room as soon as possible.
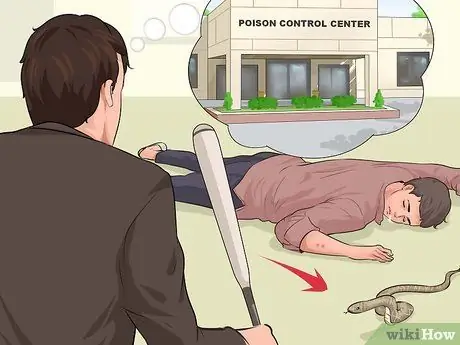
Step 4. Handle poisoning cases
Poisoning can result from a natural toxin (eg snakebite) or a combination of chemicals. If the poisoning was caused by an animal, try to kill the animal (safely), put it in a bag and take it to a poison control center.
Tips
- If possible, use latex gloves or other barriers to protect you from other people's bodily fluids.
- If someone is stabbed by an object, do not pick it up unless it is blocking the airway. Lifting the object has the potential to widen the wound and increase the severity of bleeding. Do not move the victim. If it is "forced" to move, try shortening and securing the object.
- As much information as there is in this article, what you can learn from reading these action steps remains limited. Therefore, “try to seek first aid and/or CPR training services as much as possible” - this will give you, the reader, the ability to learn exactly and firsthand how to actually bind a fractured or loose bone, bandage moderate to severe wounds, and even perform CPR, and you will be much better prepared to care for those in need after the exercise. In addition, this certification also protects you from lawsuits - while the Good Samaritan or Generous laws will protect you from these types of cases, having a certificate of first aid training and CPR will be very supportive.
Warning
- Moving a person with a spinal cord injury increases the chances of the victim becoming paralyzed or dying
- Never risk your own life! Even if it doesn't sound sympathetic, remember that being a hero, in this case, would be pointless if it ended in your own death.
- Do not move the victim. Because it can hurt more; unless the victim is in real danger and must be moved immediately. Wait for the ambulance to arrive and take over the care of the victim.
- If you're not sure what to do, let the professionals do the work. If the wound is not life threatening, the wrong action will actually endanger the victim. Take a look at the notes on training above, before this tip.
- Do not touch a victim who has been shocked by an electric shock. Turn off the power source or use a non-conducting object (eg wood, dry rope, dry cloth) to separate the victim from the power source before touching it.
- Giving aspirin to anyone under the age of 16 is extremely dangerous, because aspirin has the potential to cause severe damage to the brain and liver when a person is not old enough.
- Never try to reattach a broken or loose bone. Keep in mind that what you are doing here is “first aid”, so if you dare to do so, it is the same as preparing the patient to be transported and taken to the hospital. Unless you're 110% sure of what you're doing, reinserting a fractured, broken or loose bone carries a high risk of making the injury worse.
- Before touching the victim or providing “any” assistance, make sure you have permission to handle or care for the victim! Check local laws and regulations. Providing assistance without permission can result in lawsuits. If someone clings to the "Don't wake up" command, respect it (only if you see the evidence for yourself). If someone is unconscious and is at risk of death or injury, without being known to be attached to the "Don't wake up" command, please help and treat on the basis of implied consent. If the unconscious status is not confirmed, touch the victim on the shoulder while calling out, "Sir/Madam, are you all right? I can help you." Before continuing to help.






