- Author Jason Gerald gerald@how-what-advice.com.
- Public 2024-01-19 22:11.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 12:04.
Chlamydia, especially chlamydia trachomatis, is a type of sexually transmitted disease (STD) that is commonly experienced by both men and women and although it can be treated, the disease is actually dangerous and prone to triggering various health complications, including infertility. Unfortunately, chlamydia is often difficult to detect unless complications occur. In particular, chlamydia symptoms are only shown by about 14% of men. Fortunately, the symptoms of chlamydia are not difficult to identify and treat until they are completely cured.
Step
Method 1 of 3: Recognizing Specific Symptoms in the Genital Area
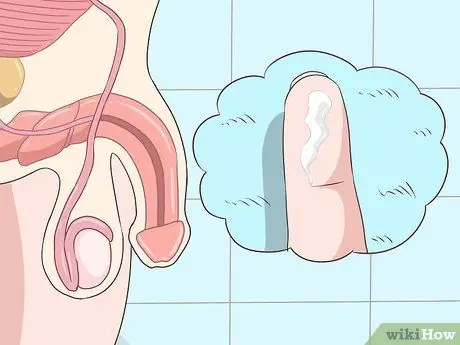
Step 1. Watch for abnormal discharge from the penis
The fluid may appear liquid and clear, milky white, opaque, or yellowish like pus. However, the discharge will generally appear clear and will only appear when the urethra is being "expressed".

Step 2. Watch for a burning sensation when urinating
This is another common symptom that indicates a chlamydia infection in your body.
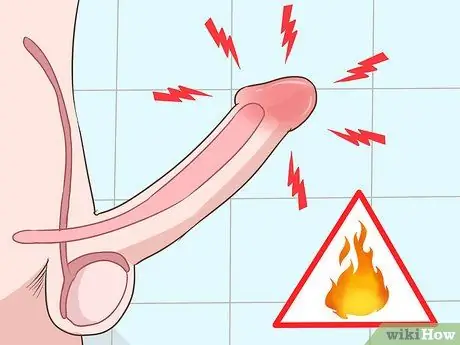
Step 3. Watch for burning or itching around or at the opening of the penis
You can definitely feel the uncomfortable sensation. In fact, very intense sensations can make it difficult for you to sleep at night, you know!.
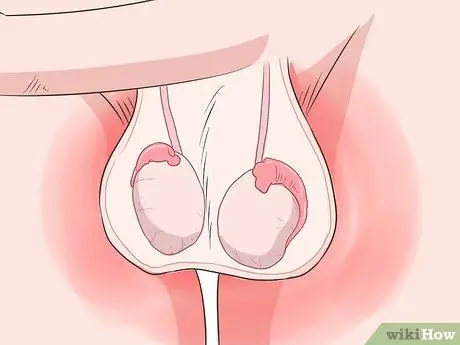
Step 4. Identify pain or swelling in one or both testicles, as well as in the scrotal area
Be careful, you may also feel the pain around, not directly in, the testicle.

Step 5. Consult the doctor for pain, bleeding, or discharge from the rectum
Rectum pain and discharge can also be associated with chlamydia. If you experience this condition, chances are the infection is in the rectum or has spread to the penis.

Step 6. Watch for symptoms of epididymitis
In fact, this is a symptom of chlamydia that may appear and risk infecting the epididymis and making it inflamed. As a result, your testicles will swell and feel painful because of it. Therefore, do not hesitate to see a doctor if you experience pain in the testicles.
Method 2 of 3: Recognizing the Physical Symptoms of Chlamydia
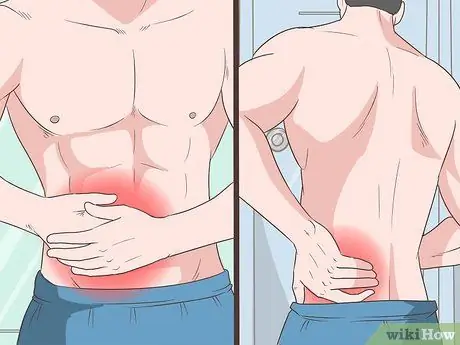
Step 1. Watch for symptoms of pain in the back, abdomen, and pelvis
All three, known as reactive arthritis, can indicate a chlamydia infection in your body. In fact, about 1% of men with urethral inflammation will also develop reactive arthritis, and about a third have the complete reactive arthritis triad (RAT) previously known as Reiter's syndrome (arthritis, uveitis, and urethritis).
Pain and swelling in the scrotum (testicles) are the most common symptoms. If not treated immediately, chlamydia that gets worse will trigger a feeling of fullness or bloating in the abdomen due to infection in the epididymis. As a result, the lower body area will feel pain

Step 2. Watch for sore throat symptoms
If you have a sore throat after having oral sex, chances are that you have contracted chlamydia from your partner, even if your partner doesn't show any symptoms.
Chlamydia transmission may occur through vaginal, anal, and oral sex from the penis to the mouth

Step 3. Watch for symptoms of nausea or fever
Men with chlamydia will generally experience fever and nausea, especially if the infection has spread to the ureters (inner urinary tract).
Body temperature when you have a fever will generally exceed 37.3 degrees Celsius
Method 3 of 3: Understanding Chlamydia

Step 1. Understand your risk factors
In particular, chlamydia is at risk of infecting you who are sexually active, have unprotected sex, and/or have sex with several people at the same time. Chlamydia itself is caused by a bacteria called "chlamydia trachomatis" which can be transmitted when the bacteria come into contact with mucous membranes during vaginal, oral, or anal sex. That's why all sexually active people should have a sexually transmitted disease, including chlamydia, checked regularly.
- The risk of chlamydia is even greater for those of you who have unprotected sex with people with chlamydia or people with other sexually transmitted diseases. Therefore, always use latex condoms or dental dams when having sex to overcome these risks!
- The risk of chlamydia is higher in people who are sexually active at a young age.
- The risk of chlamydia will increase in sexual intercourse between men.
- The risk of chlamydia will also increase in those of you who have other sexually transmitted diseases.
- Oral sex has a lower risk of transmission than anal or vaginal sex. In particular, oral-to-vaginal or mouth-to-anal transmission is less common than oral-to-penis transmission and vice versa.

Step 2. Don't wait for symptoms to appear
Remember, anyone may have a latent infection and not be aware of it. That's why it's important to have regular checkups, especially if you've had unprotected sex.
- Untreated chlamydia in men can progress to nongonococcal urethritis (NGU) or infection of the urinary tract (urethra). In addition, the condition may also develop into epididymitis, which is an infection of the epididymis or the channel that serves as a place for sperm to be transported.
- Chlamydia can still damage a woman's body even though it doesn't cause symptoms. In particular, untreated infections can lead to inflammation of the pelvic bones, which sooner or later can injure the area and lead to infertility. That's why regular checks are so important.
- Symptoms of chlamydia will usually appear within 1-3 weeks after the occurrence of infection.
- Even if you don't experience symptoms and take treatment for it, get checked out immediately if your partner claims to have chlamydia.

Step 3. Do the check
Contact the nearest clinic or hospital, your personal doctor, sexual health clinic, or any other place that provides sexually transmitted disease screening. The costs that need to be spent generally vary so it is necessary to check directly at the place concerned.
Generally, the inspection will be carried out in two ways. The first way, the doctor will take a sample of mucus from the infected genital area for analysis in the laboratory. For men, the doctor will usually insert a cotton swab into the tip of the penis or into the rectum. Meanwhile, the second way is to take a sample of the patient's urine. This method is actually more often used because it has a higher level of effectiveness than the mucus sample test

Step 4. Immediate treatment
If the test results show that you are positive for chlamydia, your doctor will most likely prescribe oral antibiotics, especially azithromycin or doxycycline. If the antibiotics are taken as directed by your doctor, the infection should clear up within a week or two. To treat more severe chlamydia, your doctor may need to administer antibiotics with the help of an IV line.
- If you have chlamydia, your partner should also be examined and treated to prevent re-infection in the future. In addition, both of you should also stop having sex during treatment.
- Generally, people with chlamydia also have gonorrhea and receive treatment for both conditions, especially since the cost of treating gonorrhea is usually less than the cost of the examination.






