- Author Jason Gerald gerald@how-what-advice.com.
- Public 2024-01-19 22:11.
- Last modified 2025-06-01 06:05.
Usually, obesity is a lifestyle disease although it may be associated with a medical condition. Obesity is most common in adults, but it can also occur in the elderly, teenagers, and even children. Obesity is not just a cosmetic problem, its effects can increase the risk of diseases such as heart disease, stroke, high blood pressure, diabetes, cancer, back pain, sleep apnea, mental health problems, and others. In many cases, obesity can be overcome. If you want to tackle obesity or help people who are obese, consider working with a professional and making changes to your diet, activity level, and lifestyle choices.
Step
Part 1 of 4: Working with Professionals

Step 1. Create a program with the doctor
The majority of obesity cases are caused by diet and lifestyle. You will gain weight if you take in more calories than you burn through daily activities due to a sedentary lifestyle, unhealthy diet, or both. Your doctor can help with obesity by educating you about diet and lifestyle changes, helping you make an appropriate eating or exercise plan, and referring you to a professional who can help. You and your doctor can work together as a team to tackle obesity.
- You should also see your doctor regularly to monitor and treat other health conditions that are affected by obesity, such as diabetes, high cholesterol, and high blood pressure.
- Ask your doctor if the medications you are taking are making it difficult to lose weight. Some medications, such as antidepressants, antipsychotics, anticonvulsants, steroids, and beta blockers (a type of heart medication) can cause weight gain.
- Consult a doctor before starting any major changes in diet or exercise. Discuss health conditions and medications you take regularly so you can reach your goals safely and effectively.

Step 2. Collaboration with nutritionists
Nutritionists and dietitians are professionals who can help you eat healthily in the best way for you. Make a meal plan with them, and make sure you get all the vitamins and minerals you need while eating to lose weight.
Usually, your doctor can refer you to a nutritionist or dietitian. Tell the doctor, “I need some extra help putting together a healthy diet. Do you have any recommendations for people who can help?”

Step 3. Find a personal trainer
Consider paying for a personal trainer if you can afford it. A personal trainer can teach you how to exercise the right and safe way, and provide motivation. A trainer can teach you the right poses and help you come up with a consistent plan with gradually increasing difficulty.
If a personal trainer is out of budget, consider joining a gym. You may not receive individual attention, but you will still have friends and support from other members

Step 4. Work with a dedicated team
Sometimes, the best way to deal with obesity is with a team. Depending on your needs and situation, your doctor may advise you to work with a mental health professional or obesity specialist. Remember that obesity is a disorder that can be treated and treated with the right help.

Step 5. Discuss weight loss medication with a medical professional
Weight loss medications do not replace a healthy diet and exercise, but in some situations they can help. The requirement for using weight loss drugs is a BMI above 30, or above 27 with related health problems. Not everyone feels the results, and there is a risk of gaining weight again after the drug is stopped, but the doctor will tell if there is a suitable drug. The following weight loss drugs are often used:
-
Orlistat (Xenical), phentermine and topiramate (Qsymia), lorcaserin (Belviq), liraglutide (Saxenda), and buproprion/naltrexone (Contrave).
Take all medications as directed by the doctor
Step 6. Consider weight loss surgery
Also called bariatric surgery, this procedure limits the food you can eat and/or how you digest and absorb food. You can get good results, but there are also risks. Surgery affects how the body absorbs the vitamins and minerals it needs. So, continue to work closely with your health care professional after surgery. There are several types of surgery to consider, and your doctor can help you choose the right one. The following criteria must be met for surgery:
- You've tried other methods, but it doesn't work
- Your BMI is 40 or more, or 35-39.9 with other health problems
- You are committed to changing your diet and lifestyle during and after taking the drug

Step 7. Treat medical problems that cause obesity
There are very few cases of obesity caused by medical problems or genetic conditions. Discuss your medical and family history with your doctor to find out if there is a medical cause behind your weight problem. Talk about whether you need to be screened if there is a family history of any of the following conditions or if you have any of the following signs or symptoms (although this list is not comprehensive):
- Hypothyroidism (low thyroid function): common symptoms include fatigue, frequent chills, dry skin, weight gain, changes in the menstrual cycle, and depression.
- Cushing's syndrome (too much cortisol in the body): symptoms include fat bulges between the shoulder blades, menstrual cycle changes, round face, and purplish stretch marks.
- Prader-Willi syndrome: people born with the disorder always feel hungry and have to eat constantly.
Part 2 of 4: Eat to Lose Weight
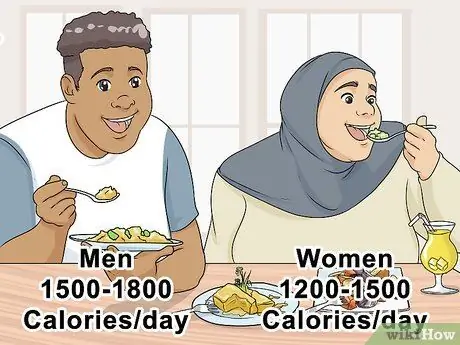
Step 1. Reduce the calories you eat
You and your doctor should discuss the amount of calorie intake per day. The average goal is 1,200 to 1,500 calories per day for women, and 1,500 to 1,800 calories per day for men. The goal is to burn more calories than you eat, which is the only safe and effective way to lose weight naturally.
It's best to keep a food journal. Record what you eat, how many calories you take in from food, and how many portions you eat. Remember that if a food label lists 100 calories as an ingredient, but you eat three times the serving size, you are eating 300 calories in total
Step 2. Eat smaller portions
If possible, try to eat five to six small, healthy meals instead of three heavy meals a day. You will feel fuller and will not overeat. If your schedule doesn't allow it, focus on limiting portion sizes at meals. Use small plates and fill 2/3 of the plate with vegetables, fruit, or whole grains.

Step 3. Choose foods with low energy density
Limit calories without missing out on nutritional value by choosing the right foods to keep you full even if you eat a little. Some foods, such as cakes and junk food, have a high energy density, so they contain a lot of calories in small portions. Meanwhile, foods with low energy density such as fruits and vegetables contain fewer calories, but can be eaten in larger portions.
Step 4. Prioritize fruit, vegetables, and whole grains
Fresh fruits and vegetables are low in fat and calories and also contain lots of nutrients. Choose fresh or frozen, not canned, because canned fruits and vegetables contain a lot of gases and preservatives. The staples of the diet are whole grains, choose whole grain breads, rice, pasta, oats, and quinoa.
- Avoid white bread and refined sugar.
- Eat a variety of vegetables, such as green leafy vegetables, red and yellow vegetables, beans and legumes, as well as starchy vegetables. Try to eat 5-9 servings of fruits and vegetables every day.
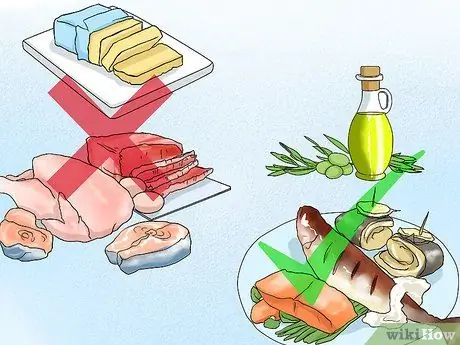
Step 5. Replace bad fats with good fats
Bad fats are saturated fats found in red meat, butter, lard, and bacon. Trans fats are solid at room temperature, and can increase blood cholesterol. Limit trans fats as much as possible.
- Use olive oil for cooking, don't use butter. Olive oil contains good fats that are better for you.
- Replace red meats such as beef and pork with poultry and fish. Healthy options are fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and herring.
- Choose low-fat or fat-free dairy products.
- Get protein from nuts, seeds, and unsalted soybeans.

Step 6. Avoid junk food
Junk foods like chips, pastries, soda, and other packaged foods from the snack aisle are high in fat and sugar which increase calorie intake quickly without realizing it. Limit these foods as much as possible. Try replacing high-fat sweets with fresh fruit or fruit popsicles. Replace salty snacks with vegetables, hummus, or nuts.
Limit the frequency of ordering food out or fast food, a maximum of once a week

Step 7. Cut down on sugary foods
Sugar increases the calories in the daily diet and contributes to health problems such as diabetes. Try not to eat a lot of cakes or sweets. Avoid sugary drinks like soda, energy drinks, sweetened coffee and tea, as well as flavored water.
Flavor plain water with natural flavors such as orange slices, mint leaves, or cucumber
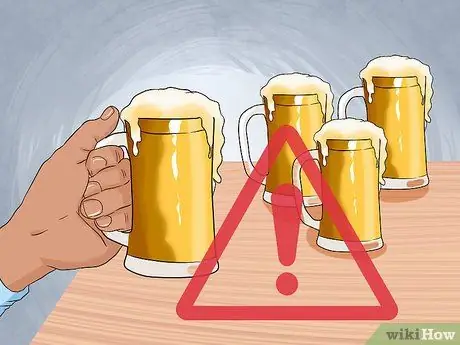
Step 8. Limit alcohol intake
Alcohol contains a lot of sugar and extra calories. Besides having a negative impact on health, alcohol consumption also makes weight loss efforts difficult. If you drink, limit it to one drink a day for women and two for men.
If you're not used to drinking, don't start

Step 9. Avoid extreme diets
Diets that promise rapid or drastic weight loss are usually unhealthy, unrealistic, or both. Most extreme diets can help you lose weight fast, but you're guaranteed to gain weight again, and in the process, your body suffers. The best way is to improve your health gradually and consistently, and lose weight at a steady pace.
Part 3 of 4: Adopting an Active Lifestyle

Step 1. Start slowly
Walking 10 minutes every day can improve health. If you usually don't move much or are overweight, it's best to start slowly. Set small goals and increase them gradually, such as “I'm going to be walking 15 minutes every day this week,” and “I'm going to increase activity to 30 minutes, 5 days per week by the end of this month.” Once you start to be consistent, exercise will become a habit, making it easier to do.

Step 2. Aim for at least 150 minutes of aerobic exercise per week
In order to lose weight, obese people should do at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise each week. Try creating an exercise schedule that requires you to move for 30 minutes a day, at least 5 days a week. Just start with a low frequency and slowly increase until the goal is achieved.
- For extreme results, aim for 300 minutes of exercise per week.
- There are many types of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise and you may need to get creative. Try brisk walking (fast enough to sweat), cycling, swimming, playing tennis, dancing, exercise with videos at home, and anything that increases your heart rate, breath, and sweat.
- Consult a professional about the sport that is right for you, especially if you have a medical condition or are over 40 (women) or 50 (men).

Step 3. Keep moving your body to burn extra calories
In addition to setting specific times for exercise, there are easy ways to burn calories throughout the day. Choose to walk anywhere, park far from your destination, garden, take your pet or neighbor's dog for regular walks, move energetically while listening to music while cleaning the house, or choose to take the stairs instead of the elevator.
People who watch less than 2 hours of TV a day tend to be thinner than those who watch TV more often. Instead of sitting in front of the TV after dinner, take a walk outside. If you can't miss your favorite TV show, do some light exercise while watching, like squats, crunches, or jogging in place
Part 4 of 4: Forming Healthy Habits
Step 1. Set realistic goals
The great thing about weight loss is that even the smallest changes can improve overall health. The normal initial goal for treating obesity is “moderate weight loss”, usually 3-5% of total body weight. For example, if you weigh 100 kg, set a goal to lose 3-5 kg to improve health.
- Even a 5% reduction can reduce the risk of diabetes, and improve liver function.
- The more weight you lose, the greater the health benefits. However, set goals small and easily achievable so that you can stay positive and dedicated to achieving them.

Step 2. Reward yourself when you succeed
You don't have to be perfect, it's okay to indulge once in a while. If you succeed in achieving your weight loss or exercise goals, reward yourself. Ideally, do something fun like watching a movie at the cinema or a weekend getaway, but if you're craving certain foods, go ahead. One fattening meal will not derail success and is important as a reward for effort.

Step 3. Record BMI
Body Mass Index, or BMI, is determined by comparing weight in kg to height in meters. Usually, BMI is an indication of body fat. BMI 18-25 is normal, and obesity is characterized by very high numbers. Know your BMI and consult your doctor to monitor progress and set health conscious goals. BMI is divided as follows:
- 40 and over: extreme/abnormal obesity (class III obesity)
- 35-39, 9: Obesity class II
- 30-34, 9: Obesity class I
- 25-29, 9: Overweight
- 18, 5-24, 9: Normal/healthy

Step 4. Sleep 8 hours every night
When you don't get enough sleep or get too much sleep, your body releases hormones that affect your appetite and trigger a craving for carbohydrates. Have a healthy and consistent sleep schedule, 7-9 hours each night. Try the following methods:
- Set bedtime and wake up.
- Avoid naps.
- The bedroom is only for sleeping. Don't watch TV or do other activities in bed.
- Sleep in a cool and dark room.
- Avoid caffeine after 4 PM or earlier if you are sensitive to caffeine.
- Create a calming ritual before bed, such as a hot bath or a cup of tea (decaffeinated).

Step 5. Find support
Surround yourself with friends and family who support the goals of tackling obesity and maintaining a healthy weight. Invite others to cook healthy meals with you. Find "exercise buddies" and motivate each other to exercise regularly.
Tips
- It's normal to gain weight again after a lot has been lost. The best way to maintain weight is to move your body for 60 minutes per day.
- Because muscle weighs more than fat, a very muscular person may be considered "obese" if judged by their BMI even though they are at a healthy weight for their body type. Discuss any BMI-related issues with your doctor.
- Be an example for the children. Demonstrate healthy eating habits and serve healthy, balanced meals. In the United States, childhood obesity is considered an epidemic. One-third of children in the US are overweight or obese. These children usually grow up to be obese adults.






