- Author Jason Gerald gerald@how-what-advice.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 10:50.
- Last modified 2025-06-01 06:05.
VMware is an internet-based (cloud-based) operating system that allows you to run multiple virtual machines from a single computer. Therefore, VMware can act as an interface between hardware and various operating systems. If you run out of disk space on the virtual machine, you will receive a notification every time you turn on the computer. You may also experience a decrease in the speed and efficiency of your computer. To increase the size of the disk space, simply adjust the disk settings and allocate new space for the disk. Before using any of these methods, make sure all snapshots have been deleted and the virtual machine has been shut down.
Step
Method 1 of 2: Enlarging Disk Via VMware Settings
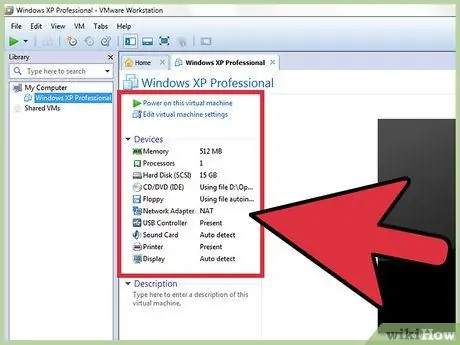
Step 1. Make sure you have met all the prerequisites
To increase disk size in VMware, you need to make sure the existing virtual machine is shut down and has no snapshots. To find out if the machine has a snapshot, check the "Information" section of the virtual machine's "Summary" tab.
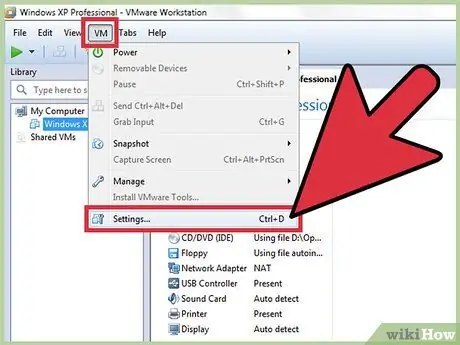
Step 2. Open the "Settings" menu
Access this menu via VMware.
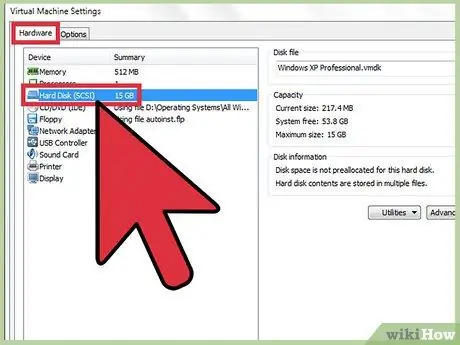
Step 3. Select the hard disk you want to enlarge
You can find the disc in the column titled "Hardware".
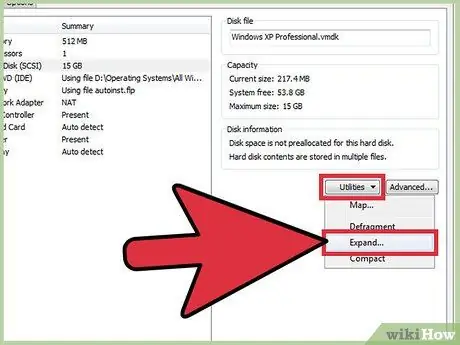
Step 4. Increase the size of the disc
In the " Disk Provisioning " section on the right side of the window, set a new " Provisioned Size " value for the disk. Some layouts have a "Utilities" drop-down menu. From this menu, select “Expand ". In general, disks are 30 to 40 GB in size at this stage. Therefore, try changing the size to 45 to 55 GB first.
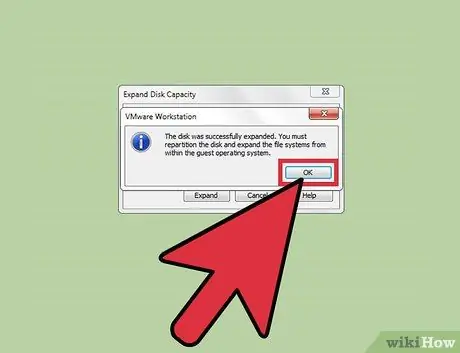
Step 5. Click "OK"
A new maximum size for the virtual disk will be set.
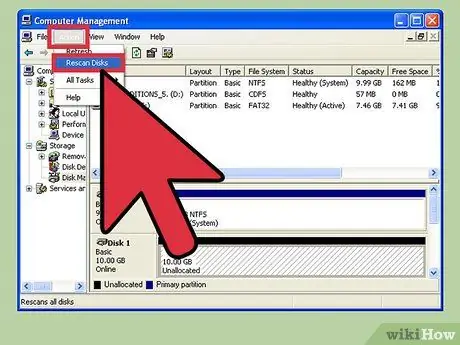
Step 6. Rescan the disc
Even if you have increased the disk size, there are a few additional steps to follow through the operating system. To rescan disks, go to the " Disk Management " menu and select " Rescan Disks ".
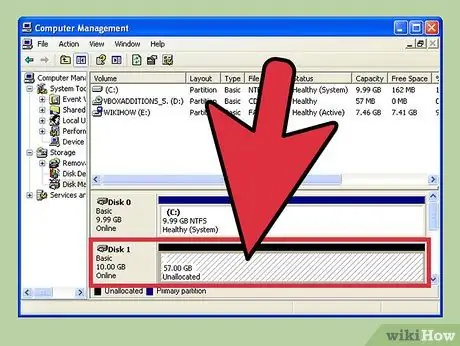
Step 7. Resize the OS drive
After expanding and rescanning the disk, you can see the segment of free space or " Unallocated Space " that was just created. Now, this space needs to be assigned to the operating system drive. To assign it, right-click the remaining free space and select "Expand Volume". After that, a short tutorial will appear that will allow you to define the function of the new disk space. You just need to assign space to the virtual disk.
Method 2 of 2: Enlarge Disk on Workstation, Player, ACE Manager, Server, or GSX
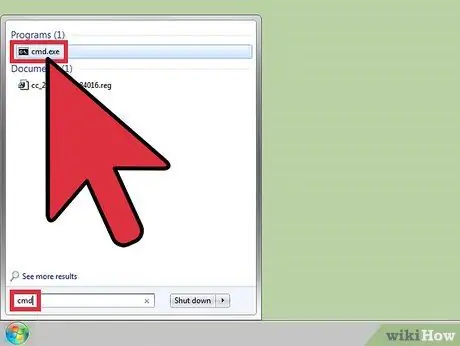
Step 1. Open Command Prompt
If you are using a VMware Workstation, Player, ACE Manager, Server, or GSX product, follow these methods. You can follow this by opening the "Start" menu and typing "cmd" (without the quotes) into the search bar. After that, select "Run".
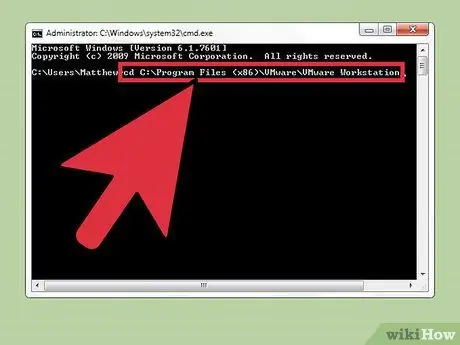
Step 2. Visit the product installation directory
-
For VMware Workstation, enter:
Program Files\VMware\VMware Workstation
on Windows or
:/usr/sbin
- for Linux.
-
For Player and ACE Manager, use the following address:
Program Files\VMware\VMware Player
for Windows or
/usr/sbin
- for Linux.
-
For Servers, use:
Program Files\VMware\VMware Server
on Windows or
/usr/bin
- for Linux.
-
For GSX, use:
Program Files\VMware\VMware GSX Server
on Windows or
/usr/bin
for Linux.

Increase Disk Space in VMware Step 10 Step 3. Enter the following code:
vmware-vdiskmanager -x 100Gb vm.vmdk
and press the “Enter” key. The current disc size will be changed afterwards.
Replace the "vm.vmdk" segment with the full virtual machine disk address and "100GB" with the desired disk size

Increase Disk Space in VMware Step 11 Step 4. Expand the disk partition
Even if you have enlarged the disk volume, you need to notify the operating system of the change. Visit the "Computer Management" menu and select "Disk Management". Right-click the "Volume" option and select "Extend Volume".
Tips
- This step cannot be completed if the virtual machine is still active or all snapshots have not been deleted.
- You may need to create a new disk instead of enlarging the volume of an existing disk and moving data to it.
Warning
- Before enlarging the disc, you need to back up the currently stored data.
- If you want to resize the disc via Lab Manager, you will lose all data. If you need more space on the virtual machine, create a new virtual disk of the desired size, then move the data to the new disk.






