- Author Jason Gerald gerald@how-what-advice.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 10:50.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 12:04.
This wikiHow teaches you how to recover a damaged Ubuntu system. If the system is not running properly, there are some simple fixes you can do via Terminal. If that doesn't work, load Ubuntu in recovery mode and repair the broken package. If the system still crashes, you may need to reinstall Ubuntu.
Step
Method 1 of 2: Using Terminal
Step 1. Open Terminal
This application is marked by a black screen icon with a command line in the upper left corner.
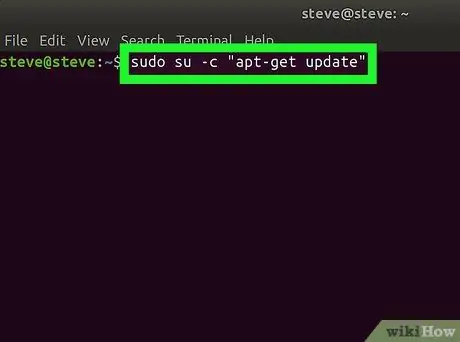
Step 2. Type the following command into the Terminal window and press Enter key
Enter the command sudo su -c "apt-get update". This command works to check for updates from the package repository.
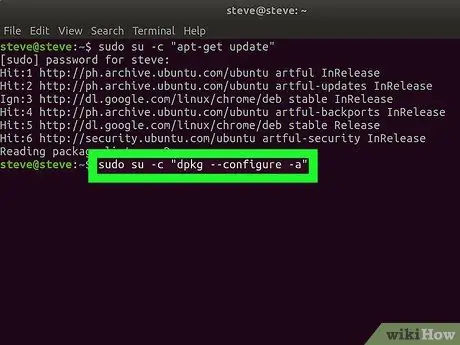
Step 3. Type the next command in the Terminal window and press Enter key
Enter the command sudo su -c "dpkg --configure -a". This command fixes the problem with “dpkg”.
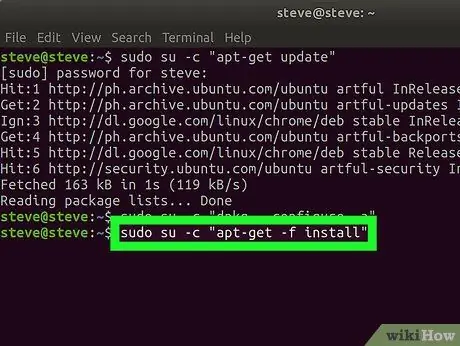
Step 4. Enter the next command and press the Enter key
Type in sudo su -c "apt-get -f install". This command serves to fix failed or problematic dependencies on the system.
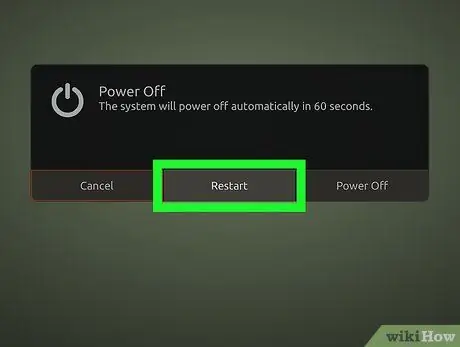
Step 5. Restart Ubuntu
After running the above commands via Terminal, restart Ubuntu and check if the issues were resolved successfully. If not, move on to the next method.
Method 2 of 2: Using Recovery Mode
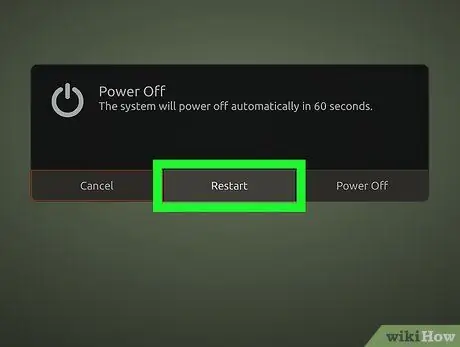
Step 1. Restart Ubuntu
To load the GRUB menu on Ubuntu, you need to restart the system. Click the gear icon in the top right corner of the screen and select " Shut Down ".
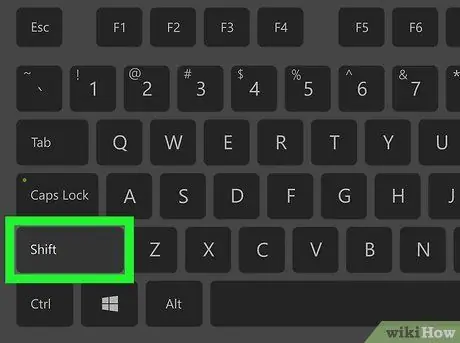
Step 2. Press and hold the Shift key while the computer restarts
The initial GRUB loading page (boot splash screen) will appear after that.
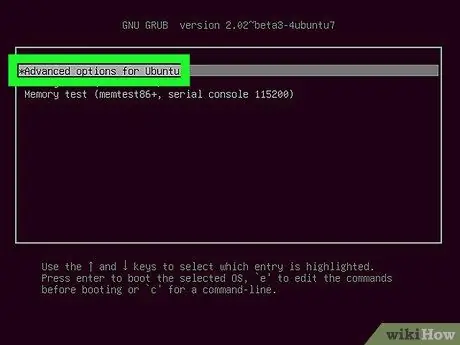
Step 3. Select Advanced Options for Ubuntu
This option is the second option on the GRUB initial load page.
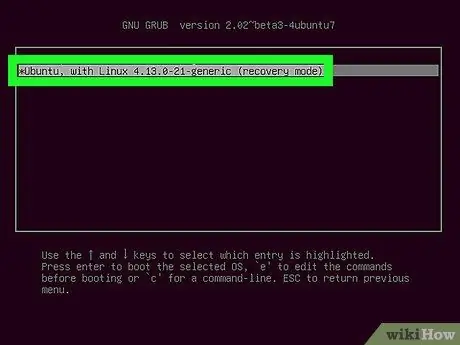
Step 4. Select Ubuntu, with Linux x.xx.x 32 generic (recovery mode)
After that, Ubuntu will load in recovery mode.
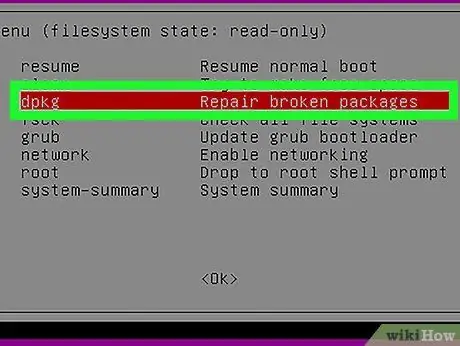
Step 5. Select dpkg Repair broken packages
This option is the third option in the recovery menu. With this option, the problematic packages on the system will be fixed. This option will also scan for errors or damage to the hard drive. Look for the drive check output containing the blocks. If the error is detected successfully, there may be a problem with the computer's hard drive. If the error is not found, but the problem is not resolved, you may need to reinstall the Ubuntu system.






