- Author Jason Gerald gerald@how-what-advice.com.
- Public 2024-01-19 22:11.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 12:04.
Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted disease that affects both men and women. In women, gonorrhea occurs in the uterus, cervix, and fallopian tubes, as well as the urethra for both sexes. Gonorrhea also infects the throat, eyes, mouth and anus. Gonorrhea can be treated and cured with proper medical help.
Step
Method 1 of 2: Identifying Gonorrhea

Step 1. Gonorrhea can affect anyone who is sexually active
If you've had sex recently, there's a good chance you're infected. In the United States, gonorrhea most commonly affects sexually active adolescents and young people.

Step 2. Know the symptoms of gonorrhea in men
Symptoms include a burning sensation when urinating, blood in the urine, other fluid in the urine (white, yellow or green in color), swelling of the testicles, the tip of the penis being swollen and red and painful. Frequent urination and sore throat are also symptoms of gonorrhea.

Step 3. Know the symptoms of gonorrhea in women
The symptoms of gonorrhea in women are difficult to identify. Usually people mistake the symptoms of gonorrhea with other diseases. The only ways to be sure are serological tests (detection of certain antibodies) and culture tests (researchers take a sample from the infected area and see what organisms develop from that sample).
Symptoms in women include: vaginal discharge (sometimes smelling of yeast), pain/burning when urinating, frequent urination, sore throat, vaginal pain during intercourse, and fever. If the infection spreads to the fallopian tube, there will be severe pain in the lower abdomen

Step 4. Look for the symptoms of gonorrhea
Symptoms of gonorrhea appear within 2-10 days after infection, or 30 days in men. Most cases of gonorrhea are asymptomatic. About 20% of men and 80% of women are affected by gonorrhea, the symptoms do not appear. Symptoms and signs are also often non-specific. If you think you have gonorrhea, see your doctor immediately.

Step 5. Gonorrhea should be treated medically
If not treated, other diseases will come, such as chronic pain and infertility in men and women. In addition, gonorrhea will spread to the blood and joints, thus endangering the life of the sufferer.
On the other hand, gonorrhea can be cured with antibiotics and the symptoms will go away
Method 2 of 2: Treating Gonorrhea

Step 1. Don't ignore the symptoms of gonorrhea and just ignore it
Without treatment, gonorrhea can cause a variety of serious illnesses. Both men and women can develop a condition called disseminated gonorrhea, where the bacteria has entered the bloodstream and spread to the skin and joints. As a result, the body has a fever, maculopapular skin rash (nodules around the neck down), and the joints are very painful.
- Complications of gonorrhea in women include inflammation of the fallopian tubes, which can lead to pelvic inflammatory disease (severe pain in the lower abdomen). Furthermore, this inflammation can cause pregnancy complications and infertility. In addition, untreated pelvic inflammation can lead to an ectopic pregnancy (pregnancy outside the uterus).
- In men, a symptom called epididymitis can cause pain behind the testicles and lead to infertility.
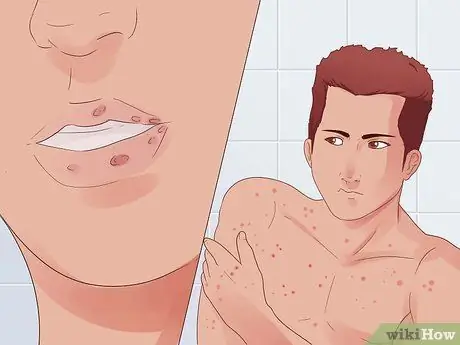
Step 2. Untreated gonorrhea increases the risk of getting HIV infection
Gonorrhea contains a protein that makes HIV multiply faster so that the virus is more easily transmitted. Patients with untreated gonorrhea have a 5-fold increased risk of contracting HIV.
Do not have sex until the symptoms of gonorrhea are completely healed. There is a risk that you will pass it on to others. Advise your partner to do the detection and treatment of gonorrhea because the symptoms often go undetected

Step 3. Visit your doctor's clinic
Explain your history and complaints to your doctor. You may be asked the following questions: When was the last time you had sex? Do you have oral, anal or vaginal sex? How many sexual partners do you have? Do you use condoms? Gonorrhea is a disease that is transmitted through sexual activity. The more active the sexual partner, the higher the risk.
- Drink water before seeing the doctor. The doctor will ask for a urine sample to detect white blood cells (cells of the immune system), blood, or other signs of infection from the urine.
- For women, a urine pregnancy test will be performed.
- You will always be given a confirmation test. In America, this test is required by law and is reported to the Department of Health and the CDC.

Step 4. Follow the doctor's instructions
If you are diagnosed with gonorrhea, your doctor will assume you also have chlamydia. These two bacteria are often sexually transmitted and have similar symptoms. Your doctor will prescribe treatments for both diseases.
- You will be prescribed 250 mg of cetriaxone and it is usually injected into the shoulder muscle to treat gonorrhea. This drug is part of the cephalosporin class of antibiotics and prevents the development of gonorrhea cell walls.
- In addition, you may be prescribed 1 g of Azithromycin or 100 mg of Doxycycline 2 x 7 days to treat chlamydia. Both of these drugs interfere with protein synthesis thereby preventing the production of important enzymes and the formation of the structural components of gonorrhea.






