- Author Jason Gerald gerald@how-what-advice.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 10:50.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 12:04.
Skin is the largest organ of the body. Because it protects the body from pathogens and water loss, the skin is affected by a variety of factors, including what we eat and what elements come into contact with the skin. The most common cause of skin redness is rosacea, a chronic skin disease that can be caused by a variety of things, such as exposure to heat, sunlight, certain foods, or alcohol. The skin may also become reddish due to symptoms of psoriasis, eczema, or overexposure to the sun or dry weather. Use the following remedies to treat some of the problems that cause the skin to turn red.
Step
Method 1 of 5: Heal Dry and Reddish Skin
Step 1. Keep skin hydrated
The redness of dry skin can be greatly reduced if the body is properly hydrated. Drink at least 8 240 ml glasses of water every day.

Step 2. Prevent skin redness by using sunscreen lotion
Buy a sunscreen that blocks both UVA and UVB rays. Apply the lotion on the skin every day.

Step 3. Apply moisturizer on the skin several times a day
Use a moisturizer after bathing or washing your hands. For people with very dry skin, apply moisturizer every time interval. Make sure you buy a moisturizer that contains the following ingredients:
- Ceramide: helps water retention and relieves redness.
- Dimethicone and glycerol: draw water closer to the skin.
- Hyaluronic acid: just like ceramides, hyaluronic acid helps with water retention.
- Lanolin, mineral oil, and petroleum jelly (petrolatum): help skin retain moisture lost in bathing.

Step 4. For the time being, don't take long hot showers
Prolonged exposure to warm water can absorb essential oils and moisture from the skin, resulting in dry, flaky, and red skin. Limit the duration of a warm bath to no more than 10 minutes.
Soak with oatmeal. Oatmeal helps relieve skin irritation and has also been shown to treat redness caused by poison oak and chickenpox. Use edible oatmeal or commercial bath oatmeal-whichever is easily available
Step 5. Use unscented organic soap
Throw away all colored and scented soaps that can cause dry and irritated skin. Instead, buy a superfat soap that's made primarily of shea and cocoa butter.

Step 6. Avoid exposure to chemicals
Chemicals, such as bleach, hair dye, or other chemical solvents, can cause the skin to turn red when touched.
Step 7. Use common sense
Ask yourself a few questions before consulting your doctor. A recent history-taking can be useful:
- Have you just started using a new product? For example, if you have just started acne treatment, specifically retinoids, it may cause your skin to turn red.
- Are you rubbing or irritating the skin? Are you exfoliating your skin too much? As a general rule, the less contact your skin has with dust, dirt, and oil, the better.

Step 8. Use gels and creams that have healing properties
Many gels and creams available in stores claim to help relieve redness. However, only two have long been recognized and tested:
- Hydrocortisone cream. Usually used 1-4 times a day, hydrocortisone has been shown to treat dry, itchy, and red skin.
- Aloe vera gel. Aloe vera gel is often used in a topical form to help soothe redness by fighting inflammation. In addition, aloe vera gel can also relieve skin irritation.
Method 2 of 5: Treating Rosacea

Step 1. Start by using a topical medication
The symptoms of rosacea, which usually appear on the face, can include constant red patches, intermittent blushing, and small red blood vessels or bumps. If you suspect you have rosacea, talk to your doctor about the following topical medications:
- Topical antibiotic medications, including products containing metronidazole (Metrocream, Metrogel)
- Topical tretinoin (Atraline, Renova)
- Topical exfoliants, including products containing benzoyl peroxide and azelaic acid (Azelex, Finacea)

Step 2. Talk to your doctor about taking oral antibiotics
Oral antibiotics are used to treat rosacea because they relieve inflammation and redness of the skin more quickly than topical antibiotics. Oral antibiotics include tetracycline, minocycline, and erythromycin. However, these medications can cause serious side effects, such as diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting.
Step 3. If none of the above treatments work, talk to your doctor about isotretinoin (Accutane)
Isotretinoin is a strong oral medication used to treat acne and rosacea that doesn't work with other medications. Because isotretinoin is very strong and is associated with depression, skin rashes, and joint pain, patients taking this drug should be closely monitored by a doctor.

Step 4. Take various measures to prevent rosacea
Although it's usually chronic, there are a variety of actions you can take to prevent rosacea from appearing. Some common causes of rosacea to avoid include sun and wind exposure, emotional stress, strenuous exercise, hot or cold weather, and alcohol consumption.
Method 3 of 5: Treating Psoriasis

Step 1. Apply topical creams and ointments to treat psoriasis
Although chronic like rosacea, psoriasis can be treated by applying creams and other topical medications. Topical creams and ointments can greatly reduce the appearance of psoriasis.
- Use salicylic acid. This acid works by triggering the exfoliation of psoriasis scales. However, using too much salicylic acid over too large an area can cause severe side effects.
- Use steroid ointment. Steroid ointments are very effective at reducing inflammation, relieving itching, and inhibiting the production of psoriasis cells. This ointment is a good standard psoriasis treatment.
- Use calcipotriene. Calcipotriene, in association with vitamin D, is also effective in treating psoriasis, particularly when combined with corticosteroids. However, don't overuse it.
- Use retinoids. Retinoids contain artificial vitamin A, but are overall less effective and slower than steroid ointments.

Step 2. Talk to your doctor about light therapy (phototherapy)
Light therapy, combined with a topical ointment, provides a glow to skin experiencing psoriasis symptoms. Patients usually undergo light therapy 3 times a week for 3 months. This combination method has been shown to be effective and preferred by patients in various studies, despite increasing the risk of skin cancer.
Step 3. Use certain oral medications
Oral medications can be used in conjunction with topical medications to inhibit the overproduction of skin cells, which is a problem with psoriasis. These oral medications include:
- Methotrexate. Although it is a chemotherapy drug, methotrexate has been shown to be very effective in psoriasis patients. Since this drug can cause serious side effects, patients need to have regular blood tests and consult the results with their doctor.
- Oral retinoids. Oral retinoids, like topical ones, contain artificial vitamin A. However, for female patients, this drug must be combined with other birth control methods for 3 years after the first use because it can cause birth defects.
Step 4. Use natural remedies
While scientifically tested medications are often the most effective psoriasis treatments, natural remedies can also provide certain benefits. Try these natural remedies:
- Aloe vera. In medical trials examining various psoriasis treatments, aloe vera was only slightly more effective than a placebo.
- Fish oil. Taken orally, fish oil supplements can slightly relieve psoriasis symptoms.
- Bath solution. Epsom salt, dead sea salt, bath oatmeal, and mineral oil can be mixed into bath water as a whole body treatment.
- Cayenne red chili. Capsaicin, which causes chili peppers to taste hot, is also used in various analgesic drugs. Capsaicin applied to the skin can help relieve itching and skin damage caused by psoriasis.
Method 4 of 5: Treating Eczema

Step 1. Reduce stress
Like acne, the appearance of eczema is usually caused by stress. Reduce overall stress levels and find ways to vent stress in a healthy way.

Step 2. Use hydrocortisone cream and steroids
Used most often to treat mild eczema, over-the-counter hydrocortisone creams are effective at relieving redness and itching in some people. For more severe cases, steroid creams may need to be used.
Step 3. Try one of several oral medications
Oral medications currently used by doctors to treat more severe eczema include:
- Oral antihistamines. Many antihistamine drugs, such as Benadryl, can be purchased without a prescription.
- Corticosteroids. Consumed especially if other treatments have not worked, the use of corticosteroids should be under the close supervision of a doctor. Always follow the instructions exactly when taking this type of medication.

Step 4. Try light therapy
Light therapy can help treat more severe eczema. In this therapy, doctors use ultraviolet light to slow down the production of skin cells so that redness is reduced.
Method 5 of 5: Treating Sun Burns
Step 1. Cool the sunburnt area to reduce redness
Place the cold washcloth on the skin and let sit until the cold temperature of the washcloth is gone. Repeat if necessary.
Step 2. Shower/bath with cold water frequently
Soaking in cold water can help relieve redness and pain from sunburns.

Step 3. Apply aloe vera and/or hydrocortisone
Use pure aloe vera topically, or lotions containing aloe, as needed. Hydrocortisone 1% cream can also be used topically. Do not use other types of lotions because they can contain ingredients that trap heat in the skin so that the skin continues to experience redness.
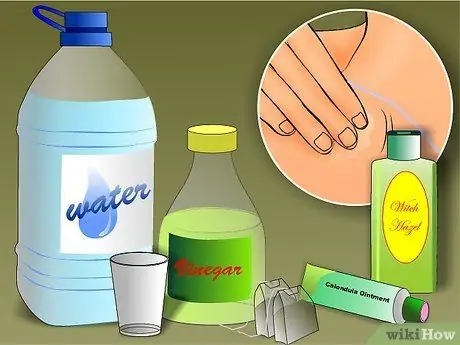
Step 4. Try one of the few untested home remedies
Treating redness from sunburn takes time (and aloe vera). However, the following untested home remedies may also help:
- witch hazel
- Vinegar (mix with water in equal proportions)
- Calendula ointment
- Wet tea bag
Tips
- Keeping skin moisturized can prevent dry skin. Buy a good moisturizer with all-natural ingredients. Do not use moisturizers that contain chemicals.
- Rosacea is a chronic skin disease that can recur frequently. However, undergoing medical treatment for more than 2 years can eliminate the appearance of skin redness in many patients.
Warning
- To prevent allergic reactions, do not use hydrocortisone cream on children under 2 years of age, unless instructed otherwise by a doctor.
- Do not apply hydrocortisone cream to the rectal or vaginal area.






