- Author Jason Gerald gerald@how-what-advice.com.
- Public 2024-01-15 08:07.
- Last modified 2025-06-01 06:05.
The normal force is the magnitude of the force required to negate the other forces in any scenario. The best way to find it depends on the condition of the object and the variables you have. Keep reading to learn more.
Step
Method 1 of 5: Normal Style At Rest
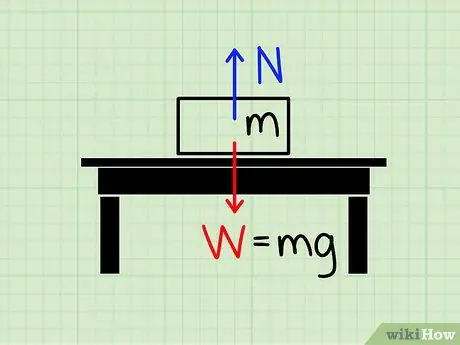
Step 1. Understand the meaning of normal force
The normal force refers to the magnitude of the force used to negate the gravitational force.
Imagine a block at rest on a table. The force of gravity pulls the block toward the earth, but clearly, there is a force acting, preventing the block from crushing the table and falling to the ground. The force that acts to stop this block despite the force of gravity is called normal style.
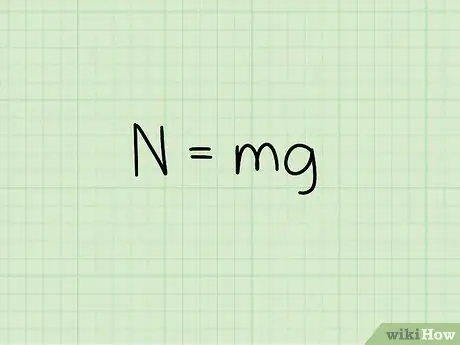
Step 2. Know the equation for the normal force on an object at rest
When calculating the normal force of an object when it is at rest on a flat surface, use the formula: N = m * g
- In this equation, N symbolizes normal style, m represents the mass of the object, and g represents the acceleration due to gravity.
- For an object that is at rest on a flat surface, without an external force acting, the normal force is equal to the weight of the object. To keep an object at rest, the normal force must equal the gravitational force acting on the object. The gravitational force acting on an object is the weight of the object, or the mass of the object times the acceleration due to gravity.
- Example: Find the normal force of a block with a mass of 4.2 kg.
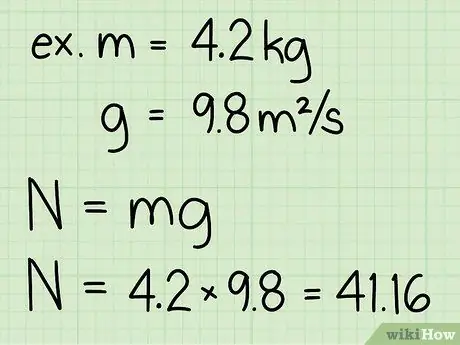
Step 3. Multiply the mass of the object and the acceleration due to gravity
This multiplication will produce the weight of the object, which of course is equal to the normal force of the object at rest.
- Note that the acceleration due to gravity on the Earth's surface is always constant: g = 9.8 m/s2
- Example: weight = m * g = 4, 2 * 9, 8 = 41, 16

Step 4. Write down your answers
The previous step will solve the problem, giving you your answer.
Example: The normal force is 41, 16 N
Method 2 of 5: Normal Force on an inclined plane
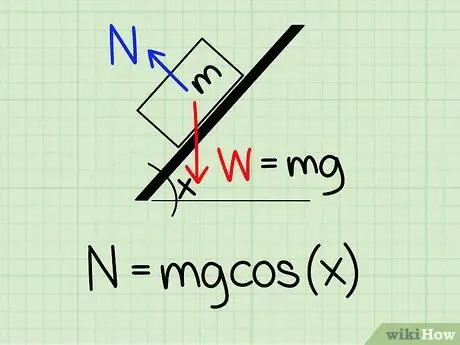
Step 1. Use the correct equation
To calculate the normal force on an object tilted at a certain angle, you need to use the formula: N = m * g * cos(x)
- For this equation, N symbolize normal style, m represents the mass of the object g represents the acceleration due to gravity, and x represents the oblique angle.
- Example: Find the normal force of a block with a mass of 4.2 kg, which rests on an inclined plane with an inclination of 45 degrees.

Step 2. Find the cosine of the angle
The cosine of the angle is equal to the sine of the complementary angle, or the adjacent side divided by the hypotenuse of the triangle formed by the slope.
- This value is often determined with a calculator because the cosine of any angle is always constant, but you can also calculate it manually.
- Example: cos(45) = 0.71
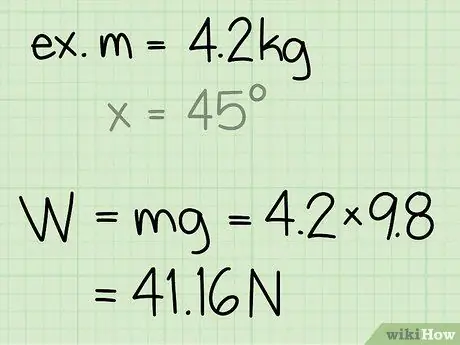
Step 3. Find the weight of the object
The weight of an object is equal to the mass of the object times the acceleration due to gravity.
- Note that the acceleration due to gravity on the Earth's surface is always constant: g = 9.8 m/s2
- Example: weight = m * g = 4, 2 * 9, 8 = 41, 16
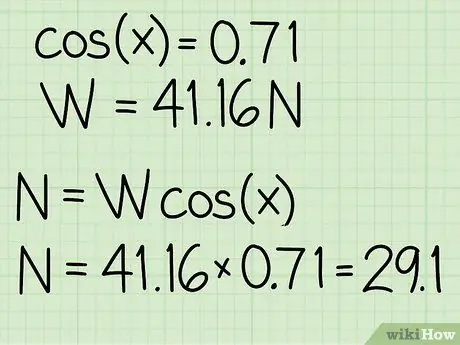
Step 4. Multiply the two values
To find the normal force, you must multiply the weight of the object by the cosine of the angle of inclination.
Example: N = m * g * cos(x) = 41, 16 * 0, 71 = 29, 1
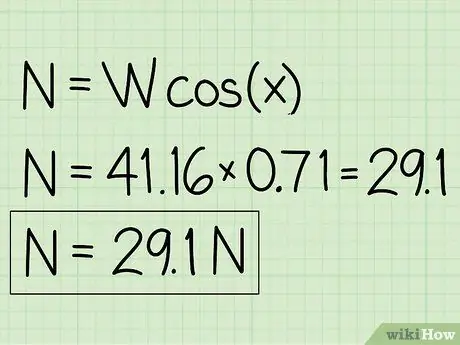
Step 5. Write down your answers
The previous step will solve the problem and provide your answer.
- Note that when an object is at rest on an incline, the normal force will be less than the object's weight.
- Example: The normal force is 29.1 N.
Method 3 of 5: Normal Style with Outer Down Style
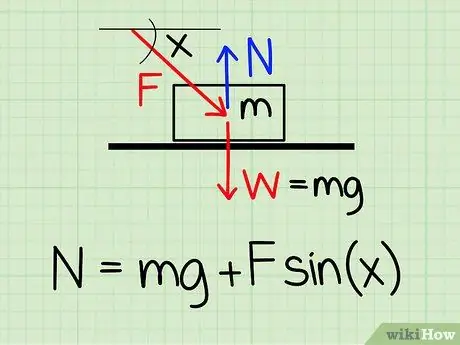
Step 1. Use the correct equation
To calculate the normal force on an object at rest if there is an external downward force on the object, use the equation: N = m * g + F * sin(x)'
- N symbolizes normal style, m represents the mass of the object g represents the acceleration due to gravity, F symbolizes external style, and x represents the angle between the object and the direction of the external force.
- Example: Find the normal force of an object with a mass of 4.2 kg if the object is pushed by a person at an angle of 30 degrees and a force of 20.9 N.
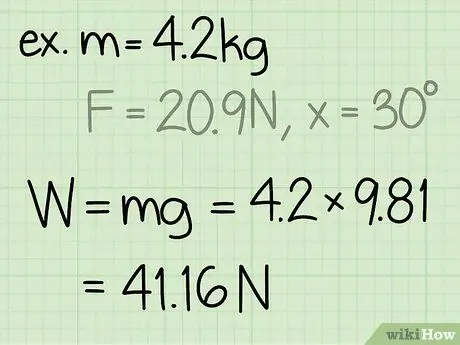
Step 2. Find the weight of the object
The weight of an object is equal to the mass of the object times the acceleration due to gravity.
- Note that the acceleration due to gravity on the earth's surface is always constant: g = 9.8 m/s2
- Example: weight = m * g = 4, 2 * 9, 8 = 41, 16
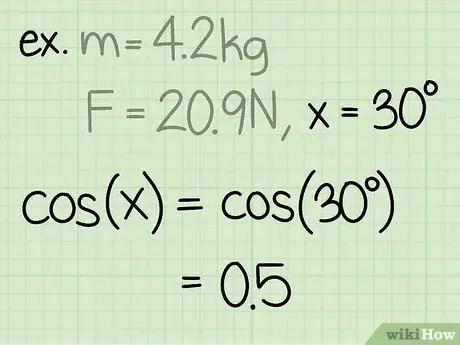
Step 3. Find the sine of the angle
The sine of an angle is calculated by dividing the side of the triangle opposite the angle, by the hypotenuse of the angle.
Example: sin(30) = 0.5

Step 4. Multiply the sine by the external force
External force, in this example, refers to the downward force hitting the object.
Example: 0, 5 * 20, 9 = 10, 45
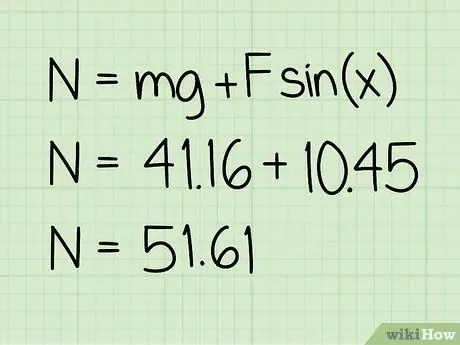
Step 5. Add this value to the weight
This sum will give the magnitude of the normal force acting.
Example: 10, 45 + 41, 16 = 51, 61
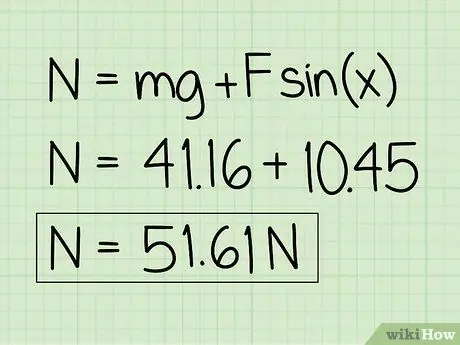
Step 6. Write down your answers
Note that for an object at rest which is affected by an external downward force, the normal force will be greater than the object's weight.
Example: The normal force is 51.61 N
Method 4 of 5: Normal Style with Outer Force Up
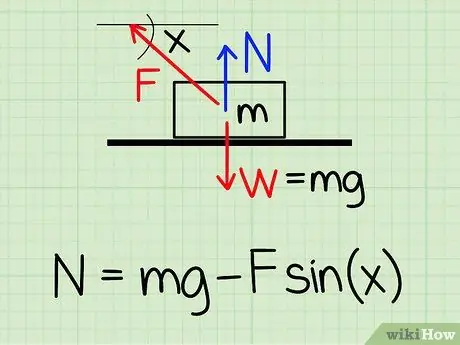
Step 1. Use the correct equation
To calculate the normal force on an object at rest if there is an external upward force on the object, use the equation: N = m * g - F * sin(x)'
- N symbolize normal style, m represents the mass of the object g represents the acceleration due to gravity, F symbolizes external style, and x represents the angle between the object and the direction of the external force.
- Example: Find the normal force of a block with a mass of 4.2 kg, if someone pulls the block up at an angle of 50 degrees and a force of 20.9 N.

Step 2. Find the weight of the object
The weight of an object is equal to the mass of the object times the acceleration due to gravity.
- Note that the acceleration due to gravity on the earth's surface is always constant: g = 9.8 m/s2
- Example: weight = m * g = 4, 2 * 9, 8 = 41, 16
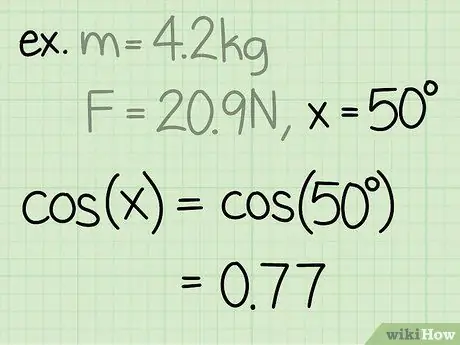
Step 3. Find the sine of the angle
The sine of an angle is calculated by dividing the side of the triangle opposite the angle, by the hypotenuse of the angle.
Example: sin(50) = 0.77

Step 4. Multiply the sine by the external force
External force refers to the upward force hitting the object, in this case.
Example: 0, 77 * 20, 9 = 16, 01
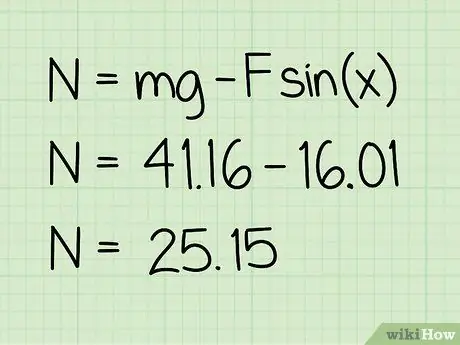
Step 5. Subtract this value from the weight
The subtraction you do will give you the magnitude of the normal force acting on it.
Example: 41, 16 - 16, 01 = 25, 15
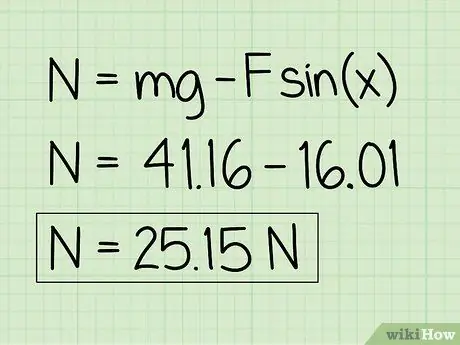
Step 6. Write down your answers
Note that an object at rest is affected by an upward external force, the normal force will be less than the object's weight.
Example: The normal force is 25, 15 N
Method 5 of 5: Normal Force and Friction

Step 1. Know the basic equation for kinetic friction
Kinetic friction, or friction of a moving object, is equal to the coefficient of friction times the normal force of an object. In equation form: f = * N
- In this equation, f symbolize friction, ️ represents the coefficient of friction, and N represents the normal force of the object.
- The "coefficient of friction" is the ratio of the frictional force to the normal force, which compresses two opposing surfaces.
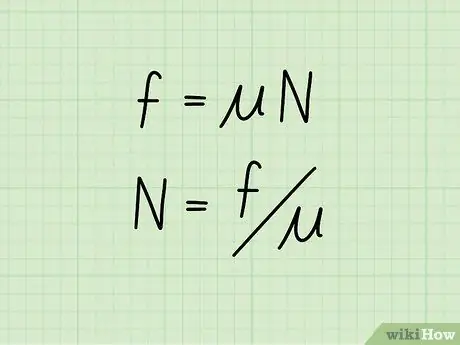
Step 2. Set up the equation to isolate the normal force
If you know the value of an object's kinetic friction, as well as its coefficient of friction, you can calculate the normal force using the formula: N = f /
- Both sides of the original equation are divided by ️, thereby isolating the normal force on one side while calculating the coefficient of friction and kinetic friction on the other.
- Example: Find the normal force of a block if the coefficient of friction is 0.4 and the magnitude of the kinetic friction is 40 N.
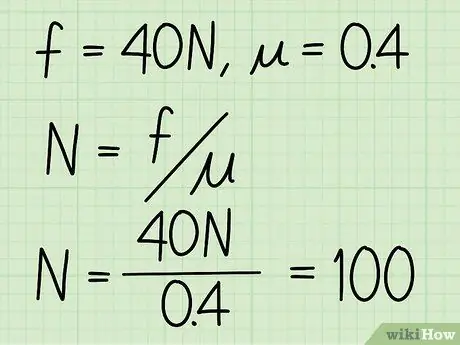
Step 3. Divide the kinetic friction by the coefficient of friction
Basically, this is all you need to do to find the magnitude of the normal force.
Example: N = f / = 40 / 0, 4 = 100
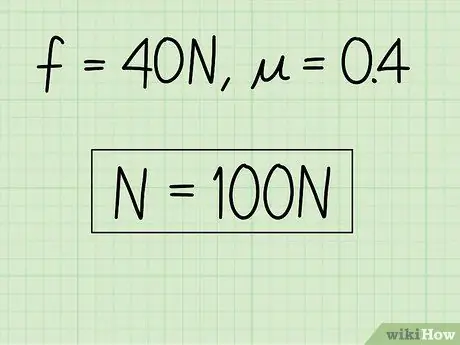
Step 4. Write down your answers
If desired, you can check your answer by plugging it back into the original equation for kinetic friction. If you don't want it, you've solved the problem.






