- Author Jason Gerald gerald@how-what-advice.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 10:50.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 12:04.
Microsoft Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) is the standard language for writing function automation programs in Microsoft Office. Learn how to protect your VBA code from being stolen or sabotaged by others.
Step
Method 1 of 3: Password Protecting the Code
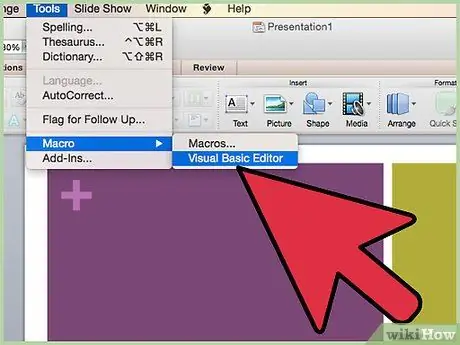
Step 1. Open the Visual Basic Editor, which is usually in the "Tools" > "Macro" menu
If you're using Access, you may need to open the database window first, depending on your computer settings.
-
Select "Project Properties" on the "Tools" menu in the Visual Basic Editor.

Protect VBA Code Step 1Bullet1
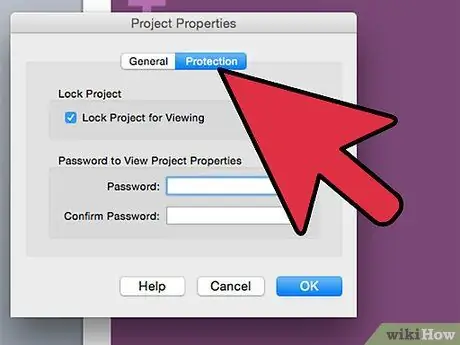
Step 2. Go to the "Protection" tab
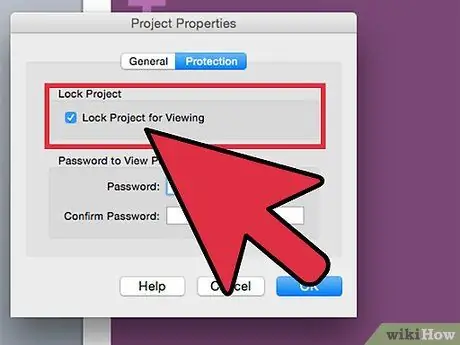
Step 3. Check the "Lock Project for Viewing" option to hide the code
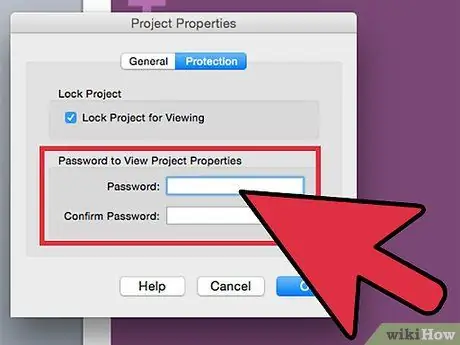
Step 4. Enter the password twice in the box provided to create and confirm a password
Step 5. Save, close, and reopen the file to save the changes
If you are using Excel 2007 and later, you may need to save the file as an XLSM file for the code to work.)
Method 2 of 3: Hiding VBA Code in Access 2007 Files Read-only
Step 1. Go to the "Database Tools" tab
Step 2. Locate the "Database Tools" group
Step 3. Select Make ACCDE. "
Step 4. Save the ACCDE file with a different name
ACCDE files are read-only files so you will still need to keep the original files to make changes.
Method 3 of 3: Protecting VBA Code by Creating Add-ins
Step 1. Create a blank Office file according to the code you want to create
For example, if your code is designed for Excel, create a new Excel file.
Step 2. Copy the VBA code into the Visual Basic Editor in an empty file
Step 3. Open the "Macros" window, which is generally under "Tools. "
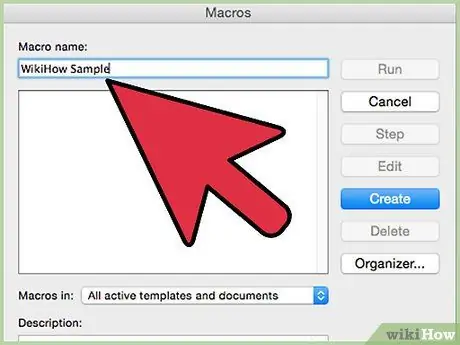
Step 4. Test your code, and "debug"
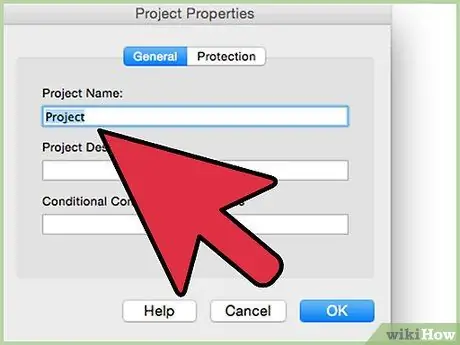
Step 5. Delete the contents of the file added by the macro
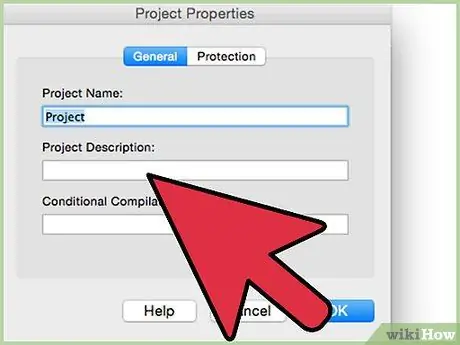
Step 6. Add a description of the macro to be run
To add a description, you may need to click "Options" in the macro window.
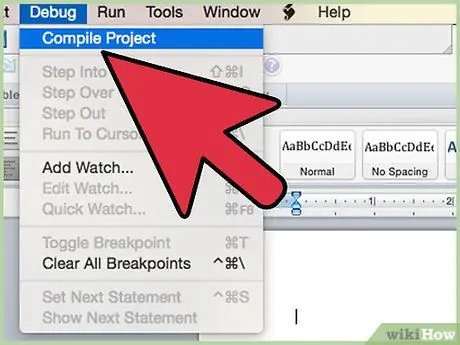
Step 7. Compile the code
In the Visual Basic Editor, find the "Debug" menu, and select "Compile VBA Project."
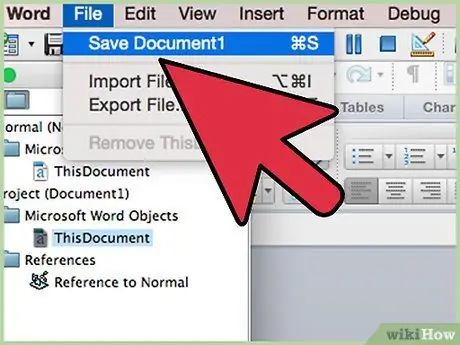
Step 8. Save a copy of the file in the standard format
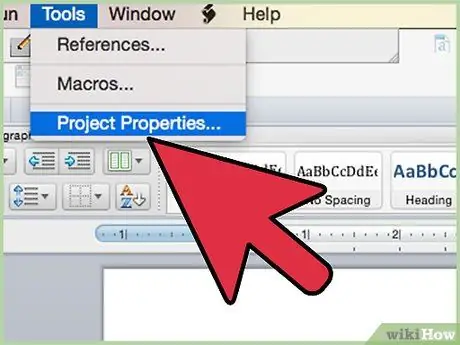
Step 9. Click "Tools" in the Visual Basic Editor, then select "Project Properties. "
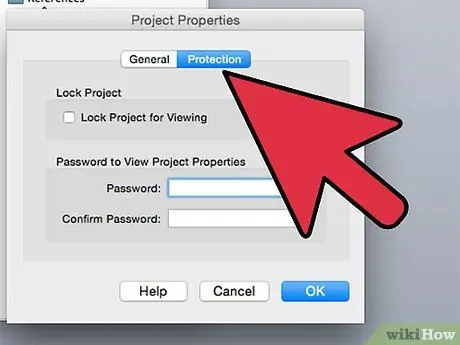
Step 10. Click the "Protection" tab
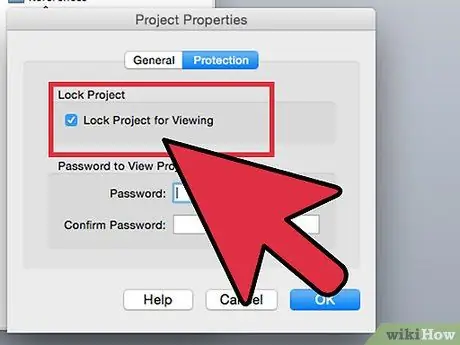
Step 11. Check the "Lock Project for Viewing" checkbox
You may need to set a password, depending on the type of file you are using and your Office/computer settings.
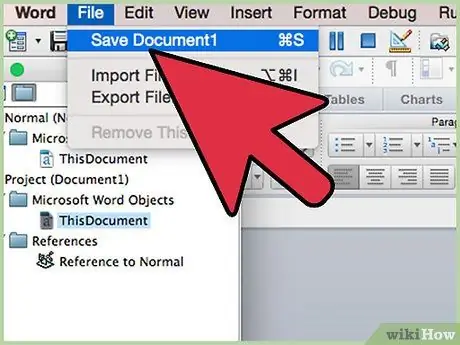
Step 12. Open the "Save As …" or "Save a Copy".
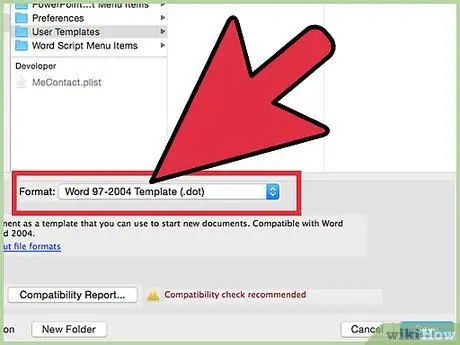
Step 13. Access the drop-down menu, then change the file type according to the add-in you created
- Save Microsoft Word add-ins as DOT or templates. If you want the add-in to run when you open Word, save the file in Word's "Startup" folder.
- Save the Microsoft Excel add-in as an XLA.
- Save the Microsoft Access add-in in MDE format. This format will protect the VBA code. Excel macro files can also be saved in MDA format, but the code will not be hidden.
- Save the Microsoft PowerPoint add-in as a PPA. This way, the VBA code will be locked, and no one else can access or edit it.
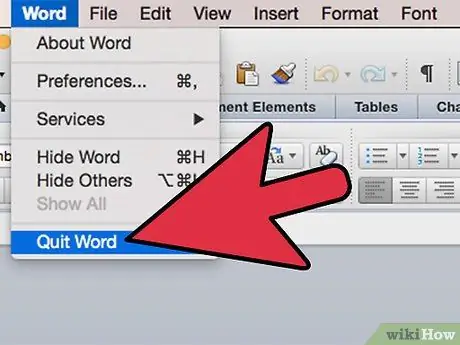
Step 14. Close and reopen Microsoft Office
Your add-in will be usable.
Tips
- If you can't find the VBA Editor or Add-in Manager, make sure the program is installed on your computer. If the program is not installed, you may need to use the Office installation CD to install the necessary files.
- Your Microsoft Office settings may affect the location of functions in individual programs. If you can't find a specific function, look for it in the "Help" menu.






