- Author Jason Gerald gerald@how-what-advice.com.
- Public 2024-02-01 14:11.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 12:04.
If your computer is starting to run slowly, it may be time to defragment your computer's hard disk (aka hard drive). Fragmentation can slow down a computer and take up available free space. Follow this guide to defragment your hard drive with a Windows XP system.
Step
Method 1 of 3: Understanding Defragmentation
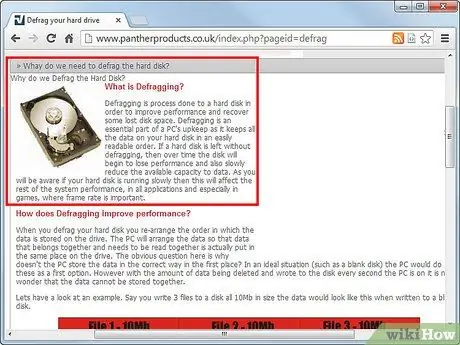
Step 1. First understand why the hard drive is fragmented
Step 2. Learn how fragmentation can affect performance
As the number of fragments increases in the drive, the performance will continue to deteriorate. The drive takes longer to find the file, and the free space on the drive will be reported incorrectly.
Step 3. Know how to prevent fragmentation
Many modern file systems are built to limit the amount of fragmentation that occurs. If you feel that your computer is starting to slow down, defragmenting it can increase the read speed of its hard drive.
Solid state drives (flash memory) do not require defragmentation, as they do not have a mechanical read mechanism. Defragmenting the solid state drive will actually cause the drive to crash more quickly, as only a certain amount of data can be written to
Method 2 of 3: Defragment Windows XP
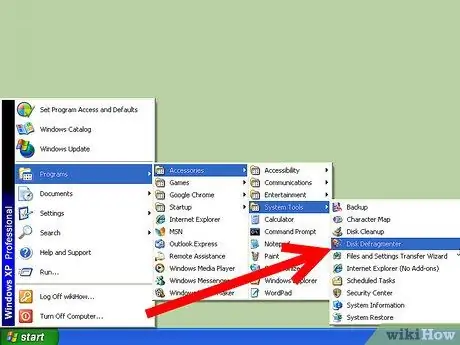
Step 1. Open the Disk Defragmenter utility
You can find this by clicking the Start menu, selecting All Programs, Accessories, then System Tools. Select Disk Defragmenter from the list. You must have administrator access to run the Disk Defragmenter utility.
You can also open the Disk Defragmenter utility by clicking Start then Search. Type "Disk Defragmenter" in the field then click Search
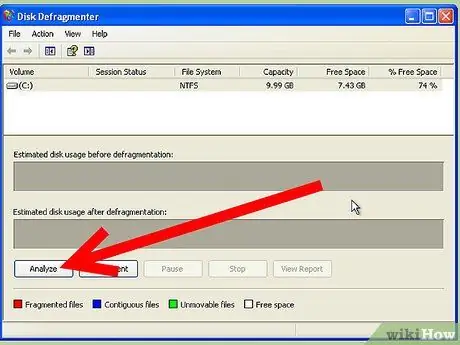
Step 2. Select your mover
There will be a list of drivers installed on the computer. Select the drive you want to defragment, usually the C: or D: drive. Click the Analyze button to see if the drive needs to be defragmented.
-
You can compare the graphs below the list of drives to see how defragmenting a drive will affect its space allocation. If there are many red lines, it means that there is a large amount of file fragmentation.

Defragment a Windows XP Computer Step 5Bullet1 - The drive must have at least 15% free space for defragmentation. Files will be moved around to optimize the drive, so the system needs a place to put files that are being organized.
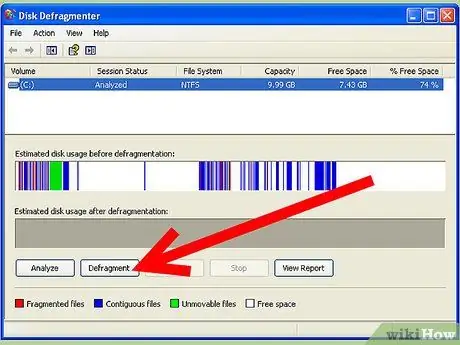
Step 3. Defragment the drive
Select the driver then click Defragment. Confirm that you want to start the process in the pop-up window. Once the process is complete, you will receive the report in a new window. This report will tell you which files were moved and which could not be moved, as well as the new free space reading.
- Avoid using the computer during the drive defragmentation process. If you change files, the defragmentation application may have to start from scratch.
- You can watch the process by following the status bar at the bottom of the window. This will show you how far along the process is, as well as what files are currently being moved. The after defragmentation graph will also adjust as the process progresses.
Method 3 of 3: Defragmenting Via Command Line
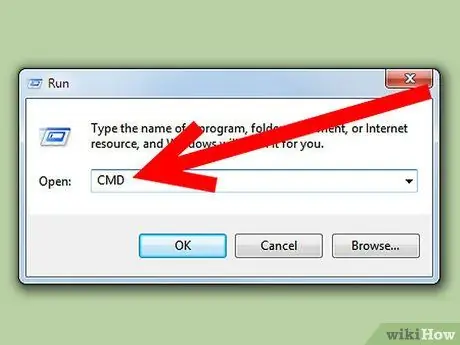
Step 1. Open the command line
Click the Start menu and Select Run. In the new window, type "cmd" into the field and press Enter. This will open a command line interface.
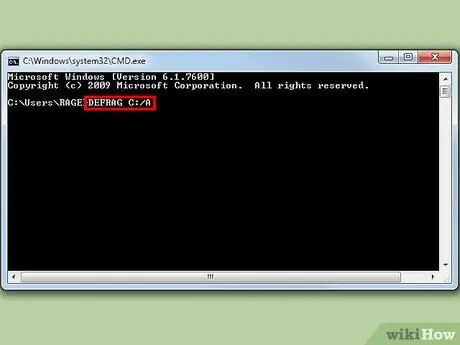
Step 2. Driver analysis
To see if the drive needs to be defragmented, enter the following command into the command line. Replace "C" with the drive you want to analyze:
defrag C: /a
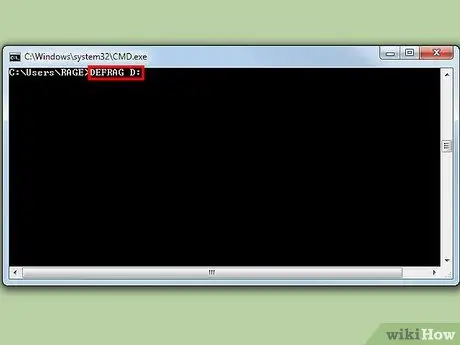
Step 3. Defragment the drive
To start the defragmentation process, enter the following command on the command line. Replace "C": with the driver you want to analyze:
defrag C:
- You can force defragmentation by adding the /f parameter at the end of the defragmentation command.
-
While the defragmentation process is working, the system will display a blinking cursor. The report will be displayed after the process is complete. You can write the report to a text file by starting the defragmentation process with the following command:
defrag C: /v >filename.txt..
- You can stop the defragmentation process by pressing Ctrl+C.






