- Author Jason Gerald gerald@how-what-advice.com.
- Public 2024-02-01 14:11.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 12:04.
You've equipped your computer with the best sound card, plugged it in with great speakers and now it sounds great. But how do you record the sounds you hear on the internet or create your own? Here are a few ways to do it.
Step
Method 1 of 3: Recording to Computer from Sound Card

Step 1. This is probably the most difficult way, because manufacturers are trying to reduce copyright infringement, most operating systems and sound programs for consumers today always prevent the ability to record
You can download older versions of drivers, but this can cause problems when running with the latest software or operating systems
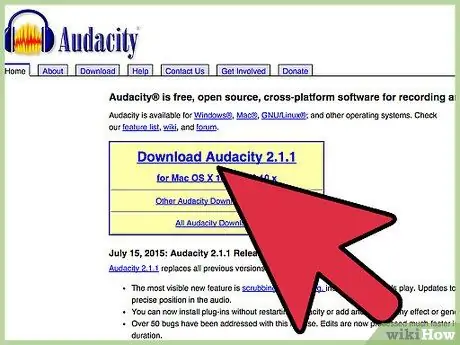
Step 2. For this material, we used an open source recording program called Audacity
Other voice recorders usually offer the same principles and features..
Method 2 of 3: Using Windows Software
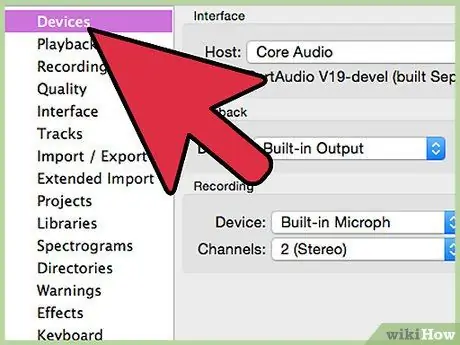
Step 1. Select your input source
You can find this on the Device Toolbar, or in Device Preferences. If it is not found, you may need to enable it from the sound card control panel as illustrated below.
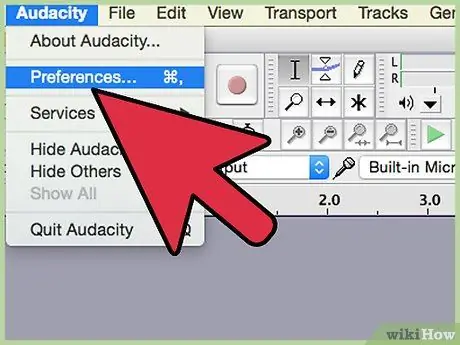
Step 2. Show hidden tools
Right-click on the Recording tab and select Show disabled devices.
Right-click again and tick Show Disconnected Devices.
Step 3. Plug in the required labels
If your Sound Card has a physical input line such as a microphone or line in, connect it to the required cable according to the instructions in the manual.
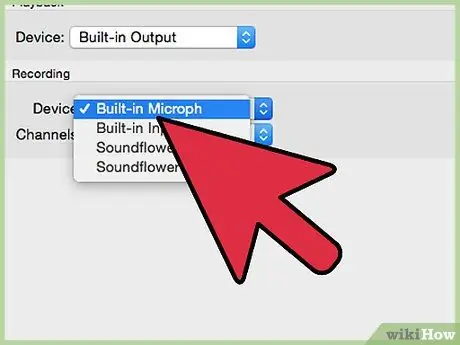
Step 4. Activate your input device
Right-click the input device you want to use for recording and select Enable.
- Right-click again on your input device and select Set as Default Device.
- Right-click again on your input device, and select Properties, then tab Levels and make sure the volume on the slider is turned up.
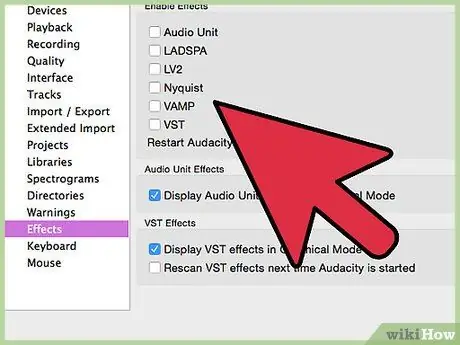
Step 5. Turn off all VolP boosts
Also turn off any other sound effects, unless they are essential to your sound card usage.
- Right-click on Microphone and select Properties then look for tab Enhancements so you can click Disable all sound effects.
- In Windows 7, click the tab Communications. Under When Windows detects communications activity:, choose Do nothing.
-
If you make frequent internet calls, right-click on the microphone and select Set as Default Communication Device.
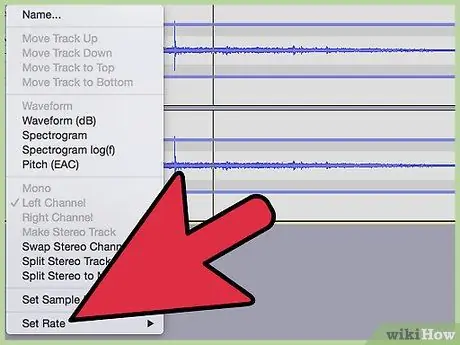
Step 6. Adjust the sample rate
Right-click the input device, select Properties, then click tab Advanced and verification Default format which matches both of your project rates (at the bottom left of the Audacity screen), and with the record channel number in the tab Devices Audacity preferences. Click OK.
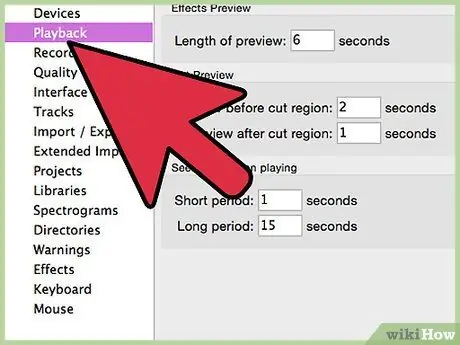
Step 7. Set your default tool
In the voice control panel, click Playback, right-click on the speaker or headphones for your sound card and set it to Default Device or Default Communication Device.
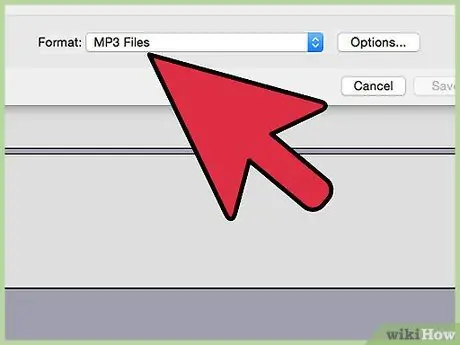
Step 8. Match the formats
Right click and click Properties then tab Advanced, and set Default Format to match the settings in step 7 above.
Method 3 of 3: Using Windows Hardware
Step 1. Connect the cables
Connect the cable with a mini-plug from your Sound Card line out (green hole) to line in (blue hole).
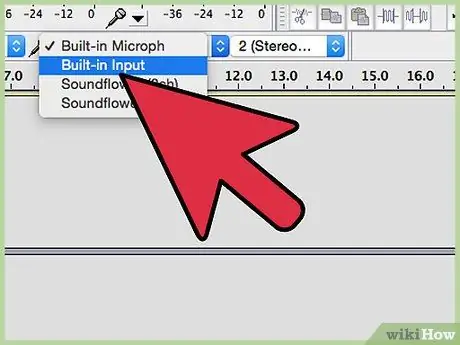
Step 2. Select Line In as the recording source
- Note that all sounds from your computer will be recorded, including system sounds such as beeps, alarms, and alerts. You must turn off the sounds before you start recording.
- Use a single-to-double stereo adapter on the output connector, then plug a single-to-single stereo cable from one side of the adapter into the input port, and a pair of headphones into the second side of the adapter, so you can monitor what's being recorded.
Using Macintosh
-
Install Soundflower. [Soundflower] is a free and open source system for Mac OS X (10.2 onwards) that allows applications to pass sounds to other applications.

Record Sound Produced by Your Sound Card Step 13 -
Click button Free Download. You will be directed to the download page. Choose the version that is suitable for your hardware and OS configuration.

Record Sound Produced by Your Sound Card Step 14 After the download is complete, install the software to the folder Applications.
-
Run Soundflowerbed. This program is in your Soundflower folder, and when launched it will appear in the right-hand menu bar with a flower-shaped icon.

Record Sound Produced by Your Sound Card Step 15 -
Open control panel Sound. From Apple Menu, choose Sound Preferences…

Record Sound Produced by Your Sound Card Step 16 -
Set the output. Click tab Output, then select Soundflower (2ch) from the output list.

Record Sound Produced by Your Sound Card Step 17 -
Redirect your sound system. Click tab Sound Effects, and from the drop-down menu Play alerts and sound effects through:, choose line out or Internal Speakers, which is most suitable for your setup, then close the window.

Record Sound Produced by Your Sound Card Step 18 -
Set Soundflower and Audio preferences. Click on the Soundflower icon in the menu bar, and select Built-in Line Output in the Soundflower (2ch) section. Make sure Soundflower (16ch) is set to None(Off).

Record Sound Produced by Your Sound Card Step 19 -
Go to Audio MIDI settings. From the menu Soundflower, choose Audio Setup… and from the resulting Audio MIDI Setup menu bar select Window > Show Audio Window.

Record Sound Produced by Your Sound Card Step 20 -
Set the input. From the output list on the left, select an option Soundflower(2ch). Click button Input.

Record Sound Produced by Your Sound Card Step 21 - Set Format to the sample rate you want. Standard sample rate is 44100Hz (CD quality)
- Set the Master volume and channels 1 and 2 to a value of 1.
-
Set Output. Click button Output and adjust the settings as follows.

Record Sound Produced by Your Sound Card Step 22 - Set Format to match the input value. The default value is 44100Hz.
- Set the master volume and channels 1 and 2 to a value of 1.
-
Open Audacity, and from the Device toolbar, select Soundflower (2ch) as your input tool.

Record Sound Produced by Your Sound Card Step 23 -
Hit the red record button when you're ready to capture sound!

Record Sound Produced by Your Sound Card Step 24 Recording to Other Devices
-
Use computer output. If recording to an internal sound card is not possible, there is a way to capture your computer's audio using an external device plugged into your computer's output.

Record Sound Produced by Your Sound Card Step 25 -
plug. Connect a stereo cable (usually a stereo mini-plug) to your computer's sound card output line (green port), and the input of an external device. This includes:

Record Sound Produced by Your Sound Card Step 26 - MP3 recorder.
- Smartphones like iPhone or Android.
- Professional recording system.
- You can even use a second computer.
-
Record with an external device, and capture your voice.

Record Sound Produced by Your Sound Card Step 27 Like the Hardware Method described above, all sounds from your computer will be recorded, including system sounds such as beeps, alarms, and alerts. You may want to mute the sounds before you start recording
Tips
- If your software allows, turn off all play through functions as uncontrolled echoes can be created which can damage speakers, ears, and connections with neighbors.
- To monitor the sound you recorded with the hardware method above, use a single-to-double adapter on the output channel, then plug a single-to-single stereo cable from one side of the adapter to the input channel, and a pair of headphones into the second side of the adapter, so You can monitor recordings.
- Microsoft Sound Recorder will only record 60 seconds of sound due to the RIAA's role.
- The sound quality will be better if you import the audio from a CD or DVD.
- Windows standard recorder will only record 60 seconds of audio.
- If using Audacity, check and make sure the slide-bar Volume Input (which is next to the microphone icon) is set to a value greater than 0.
- If after trying everything written here but no sound is recorded, make sure you have an unmuted Mono Mix or Stereo Mix. You can check this by right-clicking the speaker in the menu, clicking Open Volume Control, clicking Properties, selecting your input device, and checking all the checkboxes. Then un-mute the Stereo/Mono mix and you're ready to record.
Warning
- Do not use this method to violate copyright laws by stealing music from the internet or extracting music from DVDs to create a soundtrack that you want to distribute to the public.
- Copyright or network restrictions may prevent you from recording or distributing sound material. Check first.
- https://manual.audacityteam.org/help/manual/man/tutorial_recording_computer_playback_on_windows.html
- https://cycling74.com/products/soundflower/
-






