- Author Jason Gerald gerald@how-what-advice.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 10:50.
- Last modified 2025-06-01 06:05.
Ovulation occurs in a woman's menstrual cycle when an egg ready to be fertilized is released from the ovary, enters the fallopian tube, and can be fertilized if it encounters a sperm cell. Because pregnancy can only occur during ovulation, many women use this time of ovulation to plan their pregnancy. This method is not recommended to replace the use of other contraceptives, because of the uncertainty in the estimates, as well as the possibility of sperm to survive for seven days in the female reproductive tract. To get the most accurate results, calculate your ovulation time using more than one method, and record your results over several cycles.
Step
Method 1 of 5: Ovulation Calendar

Step 1. Record your menstrual cycle along with other means
This method is not the most accurate option, but it is easy and useful when combined with other methods. Purchase or create a calendar to keep track of your monthly menstrual cycle. Circle the first day of your cycle, which is the first day of your period. Keep track of the length of your menstrual cycle, usually 28 days on average.
- Record the number of days in each cycle, including the first day your period started. The last day of each cycle is the day before your next period begins.
- Continue to record menstrual cycles in this way for eight to twelve cycles. The more cycles you record, the more accurate this calendar will be.
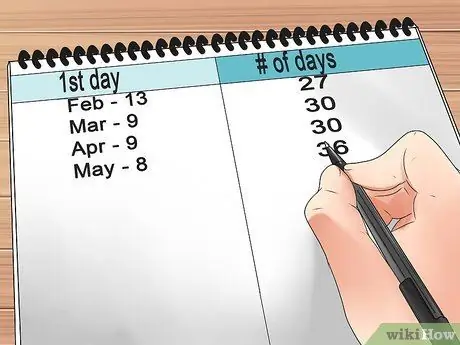
Step 2. Create a cycle duration table
Once you have a record of eight cycles, you can turn the data you get into a table. Write down the day your cycle starts in one month, and the number of days in one cycle in separate columns.
Alternatively, you can also use an online ovulation calculator such as the WebMD Ovulation Calculator. Make sure that you take all of the information mentioned below into account in your calculations, or the estimation results may be inaccurate

Step 3. Use your chart to estimate the fertile period in your cycle
Knowing your exact ovulation time with only this calendar method can be difficult. However, this calendar will be useful for estimating your fertile period, which can vary in length for each woman, as explained below:
- Estimate the first fertile day of your current cycle by finding the shortest cycle in your chart. Divide the total number of days in the cycle by 18. This means the first day in the cycle where pregnancy is possible. For example, if your shortest cycle lasted 26 days, your first fertile day would be the eighth day of each cycle (26-18 = 8), counting the first day of your period as the first day.
- Estimate the last day of the fertile period in your current cycle by finding the longest cycle in your chart. Divide the total number of days in the cycle by 11. For example, if your longest cycle lasted 31 days, then the probability that your last fertile day would be day 20 of your cycle (31-11 = 20).
- Note that the more regular the duration of your cycle, the more effective this method will be.
Method 2 of 5: Cervical Mucus

Step 1. Understand the role of cervical mucus
Cervical mucus, a protective material inside the cervix, will change throughout your cycle. Your body produces more mucus right around ovulation to help fertilize an egg. Once you understand the pattern well, you can use it to predict ovulation.

Step 2. Record the pattern of cervical mucus
Check your cervical mucus every day after your period is over, and watch for changes that occur throughout your cycle. Record changes that occur in the calendar.
- Record the days your period lasts, when cervical mucus is dry, and days when your cervical mucus is sticky, thick, and wet.
- In addition to the texture, pay attention to changes in color and smell. Watch for when cervical mucus is cloudy or clear.
- Make notes as detailed as possible, especially in the first few months when you're just starting out.
- Breastfeeding, infections, certain medications, and other conditions can affect cervical mucus, so be sure to pay attention to these factors as well.
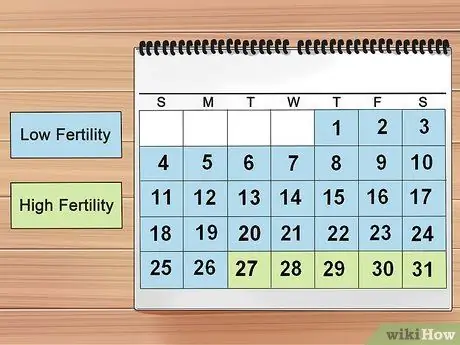
Step 3. Get to know your cervical mucus pattern to determine when to ovulate
Ovulation usually occurs when your mucus is most sticky and thick. The following days, especially when your cervix dries up again, are the days with the lowest fertility rates.
Method 3 of 5: Recording Basal Temperature

Step 1. Purchase a basal temperature thermometer
The time just before ovulation is a woman's most fertile period. Body temperature rises slightly right after ovulation occurs, then remains that way for the rest of the cycle, until the next period. Fertility is at its highest for several days before this increase in temperature occurs. Because the temperature changes that occur from day to day are very small, ordinary thermometers will not give accurate results. A basal temperature thermometer is a digital thermometer available at pharmacies.
The most accurate readings are obtained if the measurement is taken from the vagina or rectum, but there are also basal temperature thermometers that are designed to be taken from the mouth. Use the same measurement method throughout this process, and try to measure from the same depth and angle each time

Step 2. Take your temperature every day
It is important to take your temperature at the same time every day, because your temperature varies throughout the day, take it in the morning after waking up, after sleeping for at least five hours and before getting out of bed. Record your body temperature up to units 1/10 level. Use circles or other markings in your chart to mark when other factors affect the reading, such as illness, poor sleep, and fever-reducing medications such as aspirin, Tylenol, and Motrin.
A woman's average body temperature is 35.6-36.7ºC before ovulation, and 36.1-37.2ºC after ovulation. If you get a reading that differs significantly from this range, consult the thermometer's manual to make sure you are using it correctly
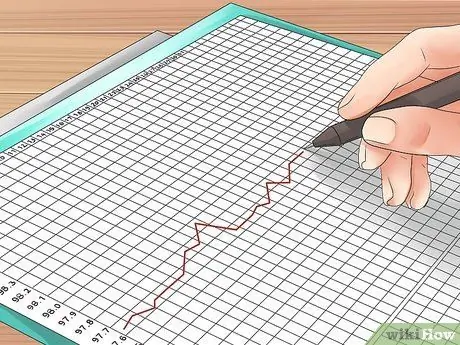
Step 3. Record your body temperature
Record the results of your body temperature measurement in a table that you can make into a graph, to find out how your body temperature changes over time. Check out the Sample Baby Center Table for a table of basal body temperature.
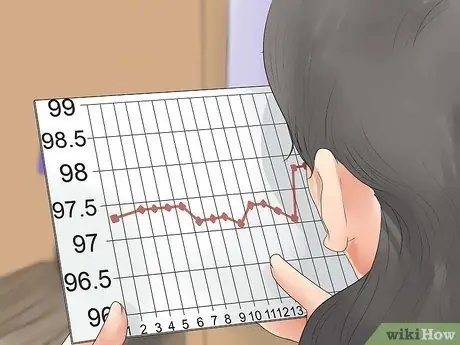
Step 4. Get to know your body temperature pattern
For several months, pay attention to the days when your body temperature rises. Most likely, ovulation has already occurred at this point, so your most fertile period happened right before that. With enough data, you'll know which day your cycle is about to ovulate.
Method 4 of 5: Doing an Ovulation Test
Step 1. Purchase an ovulation test kit
Ovulation test kits, which are sold in pharmacies, can detect levels of luteinizing hormone (LH) in the urine, which will rise a day or two before ovulation. Just like over-the-counter pregnancy tests, these are digital devices with a test stick placed in your urine.
There is another type of test, which examines your dry saliva under a microscope for a "fern" pattern, which often indicates an increase in estrogen levels in the days before ovulation. This test is not as precise as the LH test, especially if you have poor vision

Step 2. Adjust your fluid intake a few hours before the test
Urine that is too concentrated or too dilute will not give the right results. For best results, avoid caffeine and alcohol on the day of your test, avoid dehydration or excessive water consumption, and wait until your bladder is full.

Step 3. Understand your test results
Pour the urine on the test stick, and wait for a line to appear in the results section. The line that is the same color as the control line indicates that you are probably ovulating. While blurred lines are not a good marker.
- An ovulation test can accurately estimate the level of the hormone LH in the urine, but the increase in LH levels only lasts for 24 - 48 hours, so you only have a short time span to detect it. Use several methods at once to track ovulation.
- Some ovulation tests may work differently, so read the guide. For example, you might have to collect your urine in a bowl and dip a test stick into it, or the fertility marker might appear like a smiling face instead of a line.

Step 4. Repeat as needed
Take this test every day for as long as you are likely to be most fertile in your cycle, as shown on your ovulation calendar. If you missed ovulation in a previous cycle, and can afford more test kits, consider taking an ovulation test twice a day.
Method 5 of 5: Detecting Infertility

Step 1. Notice no changes
By measuring your basal temperature, ovulation test kits, or cervical mucus, you may find when there are no changes associated with ovulation and a normal menstrual cycle. Having any of these doesn't mean you're infertile; it may also mean, for example, that you missed an increase in LH levels between two ovulation tests. However, if you are experiencing several irregular cycles, or a short period of conception, you may need to take the following steps.

Step 2. Visit a doctor
Obstetricians can perform a more accurate examination compared to home methods. These tests may include blood tests to measure levels of progesterone or other hormones, or checks for abnormal thyroid function or prolactin levels, if your doctor suspects these conditions may be present. Ultrasound examination can be used to detect structural abnormalities of the reproductive tract that can affect ovulation.

Step 3. Ask your sexual partner to be examined as well
Infertility in men can also be checked. This examination usually begins with a sperm cycle test, and may be followed by an ultrasound examination to detect possible problems in the male reproductive tract.

Step 4. Ask about the treatment
If your doctor suspects that you are infertile due to the absence of ovulation, he or she may suggest a variety of medications, depending on your actual condition. Don't assume that you're not pregnant because you haven't ovulated without a proper diagnosis, as this can have many other causes. Your doctor should also check for blockages in the fallopian tubes, sperm problems, problems with the attachment of the egg to the uterus, and age-related decline in egg quality.
Tips
- The longer you record the cycle, the more accurate the information will be. If you are over the age of 35 and have a narrow window of conception due to other reasons, you may want to consult your doctor when starting the methods in this article.
- If you have recorded your ovulation month, but have not been pregnant for six months or more, see your obstetrician for further examination, especially if you are over 35 years of age. You may experience fertility problems related to sperm, or reproductive tract disorders, such as blockages in the fallopian tubes.
- You can get a rough estimate of ovulation by counting down fourteen days from the last day of your cycle, but this method has an error range of approximately three days.
Warning
- Estimating your ovulation period does not provide protection against sexually transmitted infections.
- Recording ovulation is not a reliable method of contraception. It is impossible to predict your ovulation with precision, besides, sperm can also survive up to seven days after sexual intercourse.






