- Author Jason Gerald gerald@how-what-advice.com.
- Public 2024-01-19 22:11.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 12:04.
Violence against children is a serious situation that unfortunately still colors the lives of millions of children around the world. Ironically, violence against children is actually more prone to happen to toddlers, especially because they do not have the ability to fight back, ask for help, or tell the situation in detail; their helplessness is a wetland for perpetrators of violence. If you suspect that there is violence against children around you, make sure you really identify the signs before reporting it to the authorities.
Step
Method 1 of 4: Observing Behavior

Step 1. Watch out if they seem scared of a certain appearance
Toddlers who are victims of violence will usually show a sudden fear of a particular location, gender, or physical appearance (e.g., women with brown hair, men with beards, etc.). They may cry when escorted to daycare or display discomfort around certain adults. In addition, they will also show extreme fear if their parents leave when the perpetrator is there.

Step 2. Observe their discomfort while changing clothes
Victims of sexual assault are usually afraid of having to undress before taking a shower, or show strange signs of discomfort when going to the doctor. They may also show signs of deterioration, such as still urinating despite being taught to pee in the toilet, sucking their thumb, or experiencing speech delays.

Step 3. Watch out for sleep disturbances
Toddlers who are victims of violence often experience sleep disturbances or nightmares.

Step 4. Be aware of increased sexual interest or knowledge in minors

Step 5. Be aware of their behavioral gaps with their peers
Toddlers who are victims of violence usually have difficulty playing and interacting normally with their peers.
Method 2 of 4: Recognizing Emotional Symptoms

Step 1. Observe drastic and sudden changes in behavior
If a child who was once very active suddenly becomes passive and quiet (and vice versa), it's a sign that you should be wary. Another symptom to watch out for is when the child has a sudden speech disorder (such as stuttering).

Step 2. Beware of aggressiveness and irritability
Toddlers who are victims of violence are prone to vent their trauma by acting aggressively towards their peers, adults, or even the animals around them.
Method 3 of 4: Recognizing Physical Symptoms
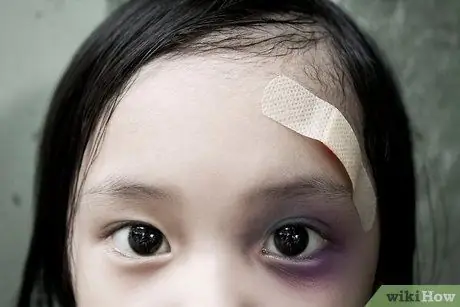
Step 1. Observe external symptoms of physical violence such as burns, bruises, bruises, scratches, and other physical injuries
If the injuries are on their knees, elbows, and foreheads, they are more likely to get these injuries while playing or being exposed to a physical environment. However, if the sores appear in unusual locations such as the face, head, chest, back, arms, or genitals, this is a sign that you should be wary.

Step 2. Observe the wounds produced by sexual violence
Victims of sexual violence may experience sores, bleeding, or itching around the genitals. Most likely, they will also have difficulty walking and standing, and have a urinary tract infection.
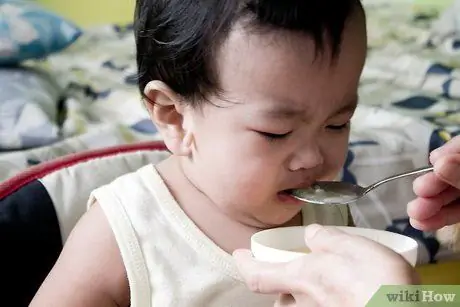
Step 3. Watch out if they start refusing food
Toddlers who are victims of violence often experience decreased appetite, lose interest in food, often vomit or choke for no reason, and show other symptoms related to their emotional disturbance.
Method 4 of 4: Taking Action

Step 1. Try talking to the caregiver (or parent) of the victim
Find out if they are feeling frustrated with the victim and/or ask why the child is acting differently than usual. Be aware of the tension that might follow.
Step 2. Contact the police or other authorities
In many cases, reporting allegations of violence does not need to be accompanied by complete evidence. Usually the authorities will respond to your report by carrying out the relevant investigative process. Remember, determining the real situation is not your job, it's theirs. This step is very important because children (especially toddlers) do not have the ability to fight for themselves and are very dependent on the help of others.
Tips
- Determining the cause of the slow process of child development is very difficult, especially because the development process of each child varies naturally. So if a child you know is experiencing a slow development process, you shouldn't jump to conclusions as a result of violence.
- Shaken Baby Syndrome (SBS) is a form of violence that often afflicts toddlers. SBS is one type of trauma experienced by babies because they are shaken too hard or harshly. Be careful, the trauma can cause long-term disability or even death. Although very dependent on the duration and intensity, in general the symptoms of SBS include retinal damage, tremors, vomiting, irritability, convulsions, decreased appetite, difficulty lifting the head, and difficulty breathing.






