- Author Jason Gerald [email protected].
- Public 2024-01-19 22:11.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 12:04.
When you have a bacterial infection in your eye, or if your doctor wants to prevent it from happening, you will need to use the antibiotics your doctor has prescribed to treat it. One of the most commonly prescribed antibiotics to treat eye infections is erythromycin. Erythromycin ointment can help kill bacteria that cause eye infections. Several brands of erythromycin eye ointment available include Ilotycin, Romycin, PremierPro RX Erythromycin, and Diomycin. To ensure the effectiveness of using erythromycin, you need to understand how to use it properly.
Step
Part 1 of 2: Preparation for Using Erythromycin
Step 1. Understand the possible side effects
Side effects that may arise from the use of erythromycin are burning, redness, or stinging in the eyes, and blurred vision. If these symptoms persist for a long time and your condition does not improve, stop using erythromycin and inform your doctor immediately. Erythromycin can also cause severe allergic reactions, and you should stop using it immediately if you experience any of the following symptoms:
- Rash
- Bidur
- Swollen
- Redness
- Tightness in the chest
- Difficulty breathing or wheezing
- Dizzy or giddy

Step 2. Consider your medical status and history
Know the contraindications for erythromycin, or special conditions and factors that prevent you from using this drug. Always tell your doctor if you are pregnant or have certain allergies, or are taking any other medications. There are a number of conditions and situations that do not allow you to use erythromycin, including:
- Breast-feed. Do not use erythromycin ointment while breastfeeding. Erythromycin ointment is a category B drug according to the FDA (US Food and Drug Administration) and is less likely to harm the fetus. However, this drug can enter the bloodstream of a nursing mother and enter the baby's body through breast milk.
- Allergy. Avoid using erythromycin if you are allergic to it. Tell your doctor about any allergic reactions you have after taking erythromycin. Your doctor may lower the dose of erythromycin or change it to another drug. Hypersensitivity to erythromycin ointment may be similar to allergies, but milder.
- certain drugs. The use of drugs such as warfarin or coumadin can cause interactions with erythromycin ointment. Tell your doctor if you are taking any of these medicines.
Step 3. Prepare to use the drug
Remove contact lenses and remove all eye makeup. Make sure there's a mirror in front of you to see what you're doing, or ask friends or family for help with medication.

Step 4. Wash your hands
Always make sure your hands are clean before applying the ointment by washing them with soapy water. Washing your hands before touching your face and eyes can help prevent the infection from getting worse.
- Be sure to wash your hands thoroughly for at least 20 seconds, especially the areas between your fingers and under your nails.
- Use warm running water and soap.
Part 2 of 2: Using the Ointment

Step 1. Tilt your head back
Lean your head back slightly, then with the fingers of your dominant hand (or whichever hand is comfortable for you), draw in your lower eyelid. That way, a small gap will be formed to enter the drug.

Step 2. Position the ointment tube
Take the tube of ointment and place the tip as close as possible to the slit of the lower eyelid. During this step, you will need to roll your eyes upwards, as far from the end of the ointment tube as possible. This will reduce the chances of your eyes getting injured.
- Do not touch the tip of the ointment tube with your eyes. This is very important to prevent contamination of the tube tip. If the tip is contaminated, the bacteria causing the infection will spread more easily, potentially infecting other parts of your body or causing a new secondary infection to your eye.
- If the tip of the ointment tube is accidentally contaminated, rinse it with sterile water and antibacterial soap. Press the ointment tube or remove the surface of the ointment that has come into contact with the tip.
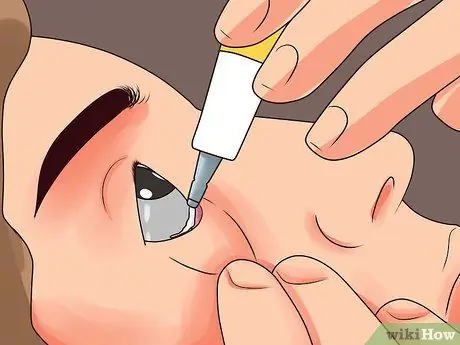
Step 3. Add the ointment
Insert about 1.2 cm of ointment (or as directed by your doctor in a prescription) into the crevice of your lower eyelid.
During this step, make sure not to touch the tip of the ointment tube to the surface of your eye

Step 4. Look down and close your eyes
As soon as you put the ointment in your eye, look down and close your eyes.
- Turn the eyeball closed to spread the ointment evenly.
- Close your eyes for another 1 to 2 minutes. Thus, the eye has sufficient time to absorb the drug.

Step 5. Open your eyes
Use a mirror to make sure the ointment actually gets into the eye. Wipe off the remaining ointment with a clean tissue.
- Your vision may be slightly blurry from the ointment. So, avoid driving or wearing contact lenses as long as your vision is temporarily impaired. Basically, you should avoid any activity that requires good eyesight. Once your vision returns to normal, you can resume such activities.
- Your vision should be back to normal in a few minutes.
- Never rub your eyes as long as your vision is blurry. Rubbing your eyes will only make blurry vision worse or injure your eyes.

Step 6. Attach and tighten the ointment cap
Store the ointment at room temperature, no more than 30 degrees Celsius.
Step 7. Follow the recommended dosage
Understand and follow the recommended frequency of use of the drug. Most people should use this ointment 4 to 6 times a day.
- Set alarms or reminders throughout the day to make sure all the ointment doses are met.
- If you miss a dose of the ointment, use the ointment as soon as you remember. However, if it is near the time of your next drug use, skip the missed dose and return to the original schedule. Never add ointment to make up for a missed dose.

Step 8. Use the medication within the recommended timeframe
The duration of use of erythromycin varies from a few weeks to 6 months. Always finish taking erythromycin as directed by your doctor. Antibiotics should be used until treatment is complete. Even though your eye infection may have cleared up, it could reoccur if you don't continue taking the medication within the time frame recommended in the prescription.
- Recurrent infections are potentially more severe than the initial infection.
- In addition, not completing the entire dose of an antibiotic carries the risk of developing bacterial resistance which is an increasing problem in diseases requiring antibiotic treatment.

Step 9. Visit a doctor for a follow-up examination
After using erythromycin for the recommended time, you can go back to see your doctor for a follow-up examination. If you experience any side effects, such as watery and itchy eyes, you may have an allergy and should rinse your eyes immediately with sterile water. Get someone to take you to the ER or call 118.
Tell your doctor if the infection persists after taking erythromycin as directed. Your doctor may recommend using the ointment longer or switching to another medication
Tips
- Erythromycin is an antibiotic that belongs to the macrolide group. Erythromycin is bacteriostatic which means it is able to inhibit the growth or division of bacteria.
- Erythromycin can also be used in newborns to treat infections such as "chlamydia trachomatis", which is passed from mother to baby during delivery.
- People who are allergic to pencilin can use erythromycin as an alternative treatment.
- Generally, doctors will give ointments to newborns immediately after birth.






