- Author Jason Gerald gerald@how-what-advice.com.
- Public 2024-01-19 22:11.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 12:04.
Ocular hypertension is one of the most common eye disorders. This disorder occurs when the fluid pressure in the eye (intraocular pressure) is higher than normal. Glaucoma, or even permanent visual impairment can occur if ocular hypertension is ignored, so taking steps to treat it is very important. High intraocular pressure or ocular hypertension does not show any symptoms, so it can only be diagnosed by checking with an ophthalmologist. Eye drops are usually one of the first treatments given to relieve high pressure in the eye, but unfortunately this treatment is not suitable for everyone.
Step
Method 1 of 4: Changing Diet and Lifestyle

Step 1. Lower the insulin levels in your body
People who suffer from various health conditions such as obesity, diabetes, and high blood pressure are often resistant to insulin, as a result of which the body produces more of it. These high insulin levels have been linked to increased pressure in the eyes.
To overcome this problem, patients are advised to avoid certain foods that can trigger a sudden increase in insulin levels. These foods include: sugar, cereals (whole and organic cereals), breads, pastas, rice, cereals, and potatoes

Step 2. Exercise regularly
Regular aerobic exercise, jogging, brisk walking, cycling, and strength training will help lower insulin levels in your body, thereby protecting the eyes from ocular hypertension.
- Insulin is a hormone that helps circulate blood sugar (glucose) into cells as a source of energy. If we use this energy by exercising, blood sugar levels in the body will decrease, followed by a decrease in insulin levels. If insulin levels are low hyperstimulation of the sympathetic nerves of the eye will not occur, thus, there will be no increase in pressure within the eye.
- Try to exercise at least 30 minutes every day, 3 to 5 times a week.
- Avoid movements or positions that turn your head upside down because they can increase intraocular pressure, such as some yoga positions such as the headstand.

Step 3. Increase your intake of omega-3 fatty acids
Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) is a type of omega-3 fatty acid that maintains healthy retinal function and prevents increased pressure inside the eye.
- DHA (and other omega-3 fatty acids are found in cold-water fish such as salmon, tuna, sardines, and herring. To increase your DHA levels, try to eat 2 to 3 servings of these fish each week.
- Alternatively, you can increase your DHA intake by taking fish oil capsules or algae-based DHA supplements. For best results, take a standard 3,000-4,000 mg fish oil capsule daily, or take a 200 mg algae-based DHA supplement daily.

Step 4. Increase your intake of foods containing lutein and zeaxanthin
Lutein and zeaxanthin are carotenoid compounds, which act as antioxidants to protect the body from free radicals. These free radicals can weaken your immune system, resulting in infection and damage to the optic nerve.
- Lutein and zeaxanthin can also help lower eye pressure by protecting them from oxidation. This is very important, because damage to the optic nerve will increase eye pressure.
- Foods that are good sources of lutein and zeaxanthin include kale, spinach, green cabbage, brussels sprouts, broccoli, and raw egg yolks. Try to include at least one of these foods in your diet every day.

Step 5. Avoid trans fats
As described above, omega-3 fatty acids will help lower eye intraocular pressure. However, foods that are high in trans fats will prevent omega-3s from functioning properly, as a result, eye pressure will increase.
Thus, the right step is to limit the intake of foods rich in trans fats. These foods include: processed products, fried foods, microwaved popcorn, ice cream, and ground beef

Step 6. Increase your intake of antioxidants
Dark buni fruits such as blueberries, blackberries, and bilberries can help improve overall eye health by strengthening the capillaries that deliver nutrients to the nerves and muscles of the eye. This is because the dark buni fruit contains antioxidants that can help strengthen blood vessels, so they are not easily broken and damaged.
- Try to eat at least one serving of dark buni fruit every day.
- Alpha lipoic acid (ALA) is an antioxidant, and is used to prevent and treat a number of eye disorders, including glaucoma and increased eye pressure. The dose is usually 75 mg twice daily.
- Bilberry is very commonly used to improve vision and fight degenerative diseases of the eye, including ocular hypertension. One study on a product containing bilberry and pycnogenol (an extract from the trunk of a pine tree) showed clinical results in lowering eye pressure.
- Grape seed extract is an antioxidant that has been used successfully to reduce light-induced eye pressure. Grape seed extract is commonly used to fight signs of aging and improve night vision.

Step 7. Use marijuana (Cannabis), if legal
Marijuana can be used in food, sublingual, tablet, and steamed forms. In a 2006 study, one of the main compounds in marijuana, tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), which has psychoactive effects, was found to temporarily reduce eye pressure when used in doses of 5 mg sublingually. However, another compound, cannabidiol (CBD), which has no psychoactive effect, does not reduce eye pressure.
Method 2 of 4: Undergoing Surgery
Step 1. Understand why surgery is needed
If the pressure in the eye remains high, this can damage the optic nerve, and the result is an eye disease called glaucoma. Over time, glaucoma can lead to blindness. Glaucoma is usually treated with eye drops and oral medications. However, if those treatments don't work, surgery may be needed to lower the pressure inside the eye.
- Surgery for glaucoma will help improve the flow of fluid inside the eye, so the pressure inside the eye will decrease. Sometimes, a single operation will not be enough to lower eye pressure and treat glaucoma. In such a situation, further surgery may be required.
- There are several types of surgery used to treat glaucoma, depending on the severity of the condition.

Step 2. Ask your doctor about implant drainage
Drainage implants are usually used to treat high eye pressure in children and people with severe glaucoma. In this procedure, a small tube is inserted into the eye to allow fluid to flow. Once the fluid can drain, the pressure inside the eye will drop.
Step 3. Consider laser surgery
Trabeculoplasty is a type of laser surgery that uses high-energy beams to open blocked channels in the eye, allowing blocked fluid to drain. After surgery, eye pressure will be checked periodically to ensure the success of the treatment given.
- Another type of laser surgery is iridotomy. This laser surgery is used on people with a very narrow angle of the channel inside the eye. In this surgery, a small hole is made at the top of the iris so that the fluid inside the eye can drain.
- If laser iridotomy still doesn't resolve the eye problem, a peripheral iridotomy may be performed. In this operation, a small part of the iris is removed to improve fluid flow. This kind of surgery is rarely performed.

Step 4. Understand the possibility that you will need a trabeculectomy
This surgery is usually a last resort for treating high eye pressure if eye drops and laser surgery don't work.
- In this operation, the surgeon will make an opening in the sclera (the white part of the eye), and remove a small piece of tissue at the base of the cornea. This will make the fluid flow smoothly from inside the eye, so the pressure will decrease.
- This surgery is performed on one eye first, and continued on the other eye a few weeks later, if necessary. Other treatments may also be needed after surgery, as the gap created may become blocked or closed again.
Method 3 of 4: Practice Relaxation

Step 1. Practice blinking every 3 to 4 seconds
People have a tendency to hold back their blinking while working at the computer, watching TV, or playing video games. This will strain your eyes.
- You can soothe and refresh your eyes by making a conscious effort to blink every 3 to 4 seconds, for 2 minutes. Use your watch to remind you the time if necessary.
- This exercise will relieve strain on the eye, and prepare it to process new information.

Step 2. Cover your eyes with your palms
Covering your eyes with your palms will help calm your eyes and mind, relieve stress, and allow you to blink freely.
- Place your right hand over your left eye, placing your fingers on your forehead and your wrists on your cheeks. Don't press your eyes.
- Keep your hands in this position for 30 seconds to 1 minute, and blink at will during this time. Open your eyes, then use your left hand to close your left eye, and repeat.

Step 3. Move your eyes to form a figure 8
This exercise will help strengthen the eye muscles and improve their flexibility, making them stronger against injury and high pressure.
- Imagine a large number 8 written on the wall in front of you, pay attention to the side. Move your eyes following this number 8 without moving your head. Do this exercise for a minute or two.
- If you have a hard time imagining the side of the number 8, try drawing it on a large piece of paper and attaching it to your wall. You can move your eyes following the image instead.
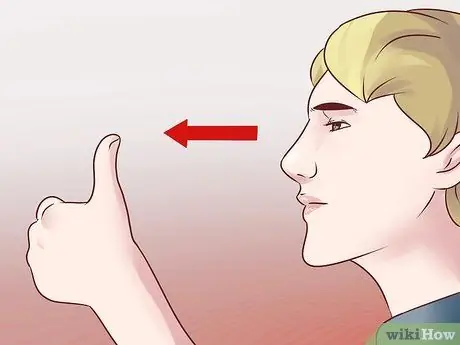
Step 4. Practice focusing your eyes on objects far and near
This exercise will help strengthen your eye muscles and improve your overall vision.
- Find a comfortable place to sit and free from distractions. Place your thumb about 25 cm in front of your face, then focus your gaze on the thumb.
- Focus on your thumb for 5 to 10 seconds, then switch to another object, 3 to 6 m (3 to 6 m) in front of you. Switch the focus of your eyes between your thumb and a distant object repeatedly for a minute or two.
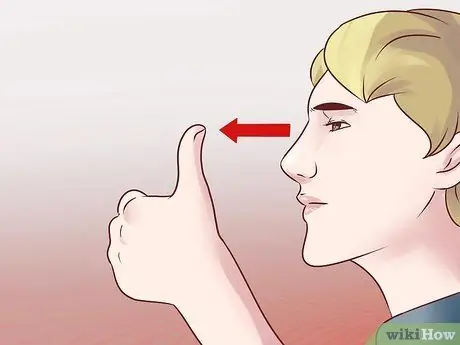
Step 5. Try the zoom exercise
This exercise will improve your ability to focus while strengthening your eye muscles.
- Extend your arms out in front of you, then lift your thumbs up. Focus your eyes on your thumbs, then slowly bring your thumbs closer to you until they are only about 7.5 cm from your face.
- Keep your thumb away from your body again, and keep your gaze. Try to stay focused on your thumb for a minute or two.

Step 6. Find information about biofeedback
This technique can also reduce eye pressure. Biofeedback will teach you how to control normal processes in your body such as heart rate, blood pressure and body temperature. A biofeedback therapist will teach you the correct technique so you can start practicing on your own.
Method 4 of 4: Understanding Ocular Hypertension

Step 1. Understand how to diagnose high eye pressure
High eye pressure (medically referred to as ocular hypertension) is difficult to diagnose, because it does not cause visible symptoms such as eye redness or pain. A diagnosis cannot be made based solely on visual examination, so you should be seen by an ophthalmologist. The ophthalmologist will use several tests to diagnose ocular hypertension.
- Tonometry. This test is used to measure the intraocular pressure inside the eye, and determine whether the pressure is within the normal range or not. Your eye will be sedated, then an orange dye is added to help the eye doctor measure the pressure.
- An eye pressure of 21 mmHg or more usually indicates ocular hypertension. However, other conditions can also affect these results, such as an eye or head injury, or the presence of blood behind the cornea.
- Air puffs. In this exam, the patient will be asked to look straight at an instrument while a light shines on your eye. This tool will blow air directly into the eye. A special machine will read eye pressure by taking into account changes in light reflection when exposed to air that is blown into the eye.
Step 2. Understand the causes of high eye pressure
Ocular hypertension is associated with aging and a variety of other factors. Several factors that can cause ocular hypertension include:
- Excessive fluid production. Aqueous humor is a clear fluid that is produced in the eye. This fluid drains from the eye through the trabecular meshwork. If aqueous humor is produced in excess, eye pressure will increase.
- Blockage of the flow of eye fluid. Disturbance in the outflow of aqueous humor can increase eye pressure.
- Certain drugs. Certain drugs (such as steroids) can cause ocular hypertension, especially in people who already have risk factors for:
- Eye injury. Any irritation or injury to the eye can disrupt the balance of aqueous humor production and its outflow from the eye, resulting in increased eye pressure.
- Other eye conditions. Ocular hypertension is usually associated with other eye diseases such as pseudo exfoliation syndrome, corneal arcus, and dispersion syndrome.

Step 3. Identify risk factors for ocular hypertension
Everyone can experience increased eye pressure, but research shows that the following groups have a higher risk of developing it:
- African-American descent.
- People over 40 years old.
- People with a family history of ocular hypertension and glaucoma.
- People with a thinner central corneal thickness.






