- Author Jason Gerald gerald@how-what-advice.com.
- Public 2024-01-19 22:11.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 12:04.
Planting bags are plastic or cloth used for growing fibrous rooted plants. Planting bags are perfect for balconies or small gardens with limited space. These bags are also great because they are reusable and leave very little waste. To use it, prepare a bag for the plant you have chosen, plant it, and take good care of it so that the plant is healthy during its growing season.
Step
Part 1 of 3: Preparing the Planting Bag

Step 1. Purchase a planting bag
You can buy planting bags at a garden supply or hardware store. You can also choose the material, plastic or fabric. Cloth planting bags generally need to be watered more often than plastic ones. Choose a bag based on the size of the plant roots. Don't buy a bag that's too big, unless you really want to plant something big too.
For example, you will need a 200 liter bag if you want to plant something as large as a grapefruit tree

Step 2. Line the planting bag with clay gravel to help with drainage
If the type of ready-to-plant soil you are using is not well-drained, cover the bottom of the bag. You can add clay pebbles or pieces of pearlite. Add enough gravel or perlite to cover the entire base.
Add gravel or perlite at least 2.5 cm high into the bag

Step 3. Add soil to the planting bag
You can use ready-to-plant soil that looks like compost, compost made especially for pots, or make your own media mix. An ideal planting medium mix for bags is moss, compost mix (such as chicken manure or mushroom compost), and vermiculite (a moisture-resistant mineral). Fill the planting bag almost full, leaving about 5 cm of space at the top.

Step 4. Loosen and shape the pouch if it is not already open
Once the soil is added, shake and press to spread the soil. After that, shape the bag into short mounds. This is to ensure that the soil is evenly distributed.

Step 5. Make holes in the bag for drainage if not already there
Make a hole in the bottom of the bag with scissors. The holes should be the size of a scissor stitch and 1 cm apart each. This hole is useful for draining excess water.
If the planting bag already has drainage holes, you can skip this step
Part 2 of 3: Growing Crops

Step 1. Choose fibrous rooted plants for best results
Fibrous rooted plants are suitable to be planted here because their root growth will not be hampered by the bottom of the bag. Good choices include tomatoes, peppers, eggplant, zucchini, cucumber, pumpkin marrow, strawberries, chickpeas, lettuce, potatoes, herbs, and flowers.
However, you can also plant larger plants-such as trees-if the planting bag purchased is large too

Step 2. Place the bag in the planting area
This bag is easy to move and can be placed in various places. It can be placed on a balcony, in an outdoor garden, or in a greenhouse. Consider the quantity of sunlight and warmth your plants need when you choose a planting location.

Step 3. Make a hole in the soil to put the plant
Dig and remove the soil with your hand or a gardening shovel. Make sure to dig up enough soil so that all the roots of the plant can be buried after planting later.

Step 4. Insert the root tissue into the soil
Place the plant in the hole, where the soil is dug. Make sure all root tissue is buried in the soil. After that, fill the top with the soil that you dug out.
Part 3 of 3: Caring for Plants

Step 1. Water the plants in the bag frequently
Plants in bags generally need more water than those grown in pots. Check the planting bag daily. Water the soil when it looks dry. The plastic material will heat up the peat growing media mix quickly. So, keeping the soil moist is very important for plants to grow well.
Fabric bags usually need to be watered more often than plastic ones

Step 2. Install a self-watering system
Keeping the planting bag so well irrigated is quite difficult. So, this self-watering system will be very helpful. One option is to install a drip irrigation system (plant infusion system). Basically, you install a container that slowly and consistently drips water into the soil. Or, you can place a container under the planting bag and fill it with water.
If you put a deep container under the planting bag, prepare a second container to catch the overflowing water
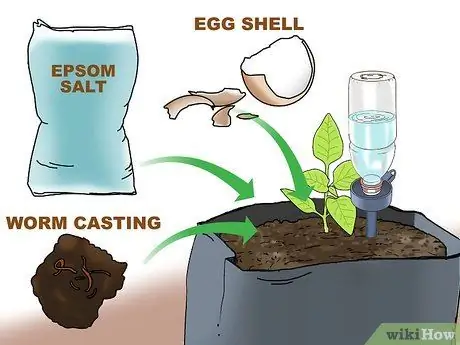
Step 3. Fertilize plants that need a lot of nutrients
Crops like this include corn, tomatoes, and the cabbage family. You can buy fertilizer or make your own natural fertilizer. Make your own fertilizer from Epsom salt and egg shells, worm compost (vermicompost), and tea compost. Spread a thin layer of fertilizer over the soil. There is still space left if you previously left 5 cm of space at the top of the planting bag. Fertilize the plant at least once a week.

Step 4. Give turquoise to tall plants if necessary
Plants that are tall or with heavy tops, may need to be grounded. You can use a bamboo stick. Insert the stick into the soil next to the plant. After that, tie the plant to the stick and tie the stick to the frame.
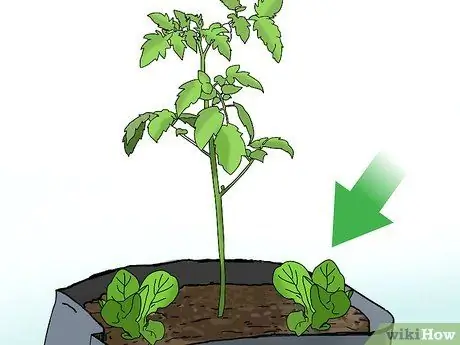
Step 5. Plant smaller plants under larger plants to take advantage of the limited space
If your growing space is quite narrow and gardening in this way is the only option for growing your own vegetables, maximize it by intercropping. For example, if you're growing tomatoes, add lettuce or radishes underneath. However, wait for the tomatoes to grow well first before planting anything else.
If you are growing more than one plant in the same bag, make sure they are all watered thoroughly

Step 6. Reuse the soil after the crop is harvested
If the soil still looks healthy, you can reuse it for the next growing season. Soil can be stored and reused for 2 to 3 seasons, as long as the soil is mixed with new compost, organic matter, or fertilizer. Even planting bags can be reused for the next season if they are washed, dried, and stored in a dry place until the planting season returns.
Tips
- For parenial plants, planting bags do not need to be stored. However, if you live in the subtropics, bring fall plants indoors if the weather is particularly cold.
- If there is an advertising label you don't like on the planting bag, cover it with a burlap sack. Or, put pebbles or place flower pots around the bag to hide the writing and color.
- Marigolds planted in pots will help keep pests away.






