- Author Jason Gerald gerald@how-what-advice.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 10:50.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 12:04.
Permissions in Windows 7 define which users can access, modify, and delete files and folders. Each file and folder on your Windows computer has its own permission settings. Changing permissions allows you to lock or unlock files for users on your computer. If you recently recovered data from a used hard drive, you may need to take ownership of the files to make them accessible again.
Step
Method 1 of 2: Changing Permissions
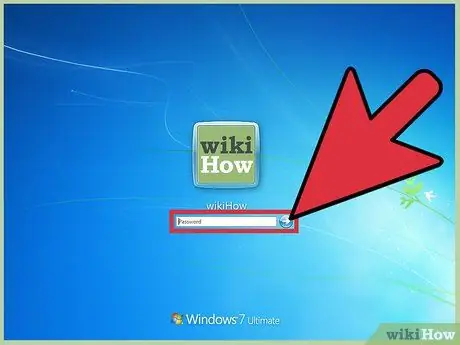
Step 1. Log in to Windows as administrator
If you are not logged in as an administrator, you can only change permissions for your own user account. To change permissions for other accounts on the computer, you must be logged in with a privileged administrator account.
If you are not logged in as an administrator, you will not be able to access most of the permission settings
Step 2. Right-click on the file or folder whose permissions you want to change
You can change permissions for all files or folders. Changing the permissions of a folder will also change the permissions for all the files and folders in it.
You cannot change the permissions for the file that is currently in use. Make sure you close any program files or folders for which you want to change permissions
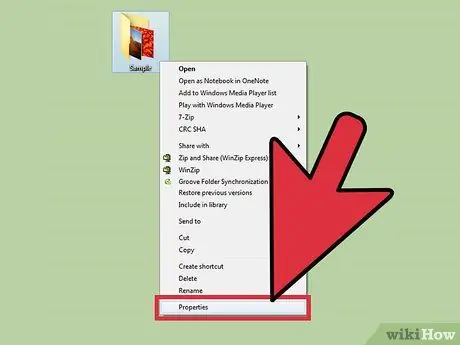
Step 3. Select "Properties. " The file or folder Properties window will open.
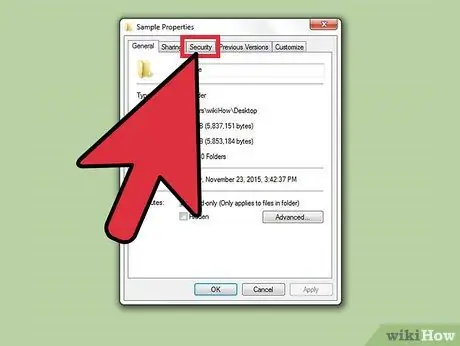
Step 4. Click the “Security” label
A list of groups and users who currently have permissions for the file or folder is displayed.
If you don't see the " Security " label, you are probably trying to change permissions for files stored on the USB drive. If your USB drive is formatted with the FAT32 file system, you cannot set permissions for the file or folder. If you want to change the permissions of a file or folder on a USB disk, the disk must use the NTFS file system
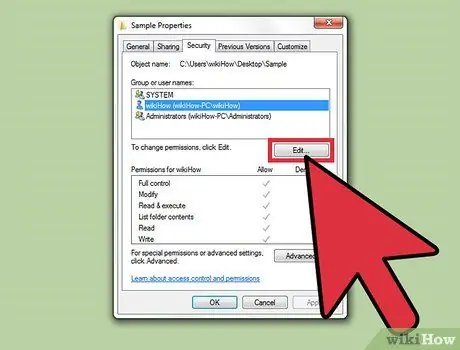
Step 5. Click the "Edit" button
This button will allow you to change the permissions for the associated file or folder for all users on the computer.
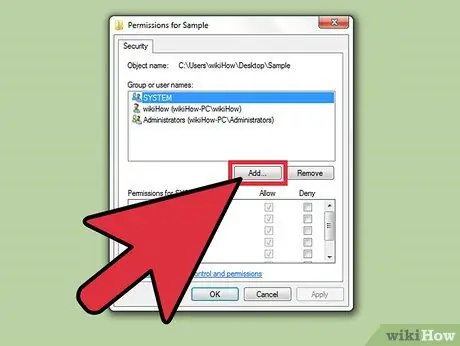
Step 6. Click the “Add” button to add a new user or group to the list
If you want to add a new user to the list of users who have permissions for the file, click the “Add” button.
- Click "Advanced" and then "Find Now" to find all users and groups on the computer.
- Select the user you want to add to the permissions list and click “OK.” These user accounts will be added to the “Group or user names” list.
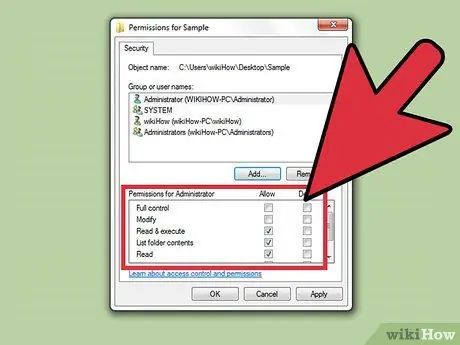
Step 7. Select the user you want to change permissions for
The available permissions will be displayed in the " Permissions for User " list.
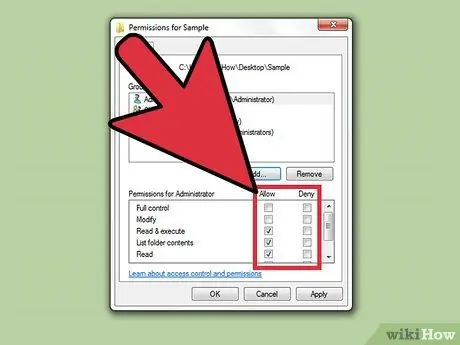
Step 8. Tick to change the permissions you want to apply to the related user or group
Each permission on the list has an “Allow” and “Deny” box. Check the permissions you want to grant or restrict from the user:
- Full control: Users can read, write, modify, or delete files.
- Modify (modification): Users can read, write, and replace files.
- Read and execute: The user can read or run the selected file.
- List folder contents: User can view files in the selected folder.
- Read (read): The user can open the file
- Write: The user can edit the file or create a new file.
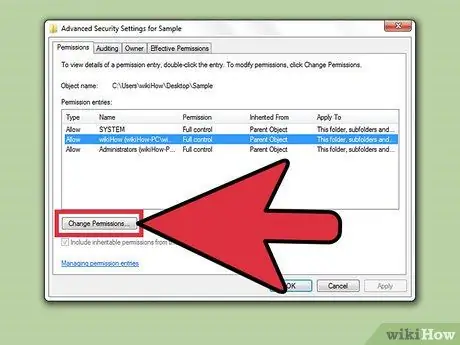
Step 9. Adjust your settings if the box is grayed out
If you can't change any of the permissions, the settings may need to be adjusted.
- Click the " Advanced " button in the Security label.
- Select your user and click "Change Permissions/Edit."
- Uncheck the "Include inheritable permissions from this object's parent" option.
- Save changes. You can now check the permissions box.
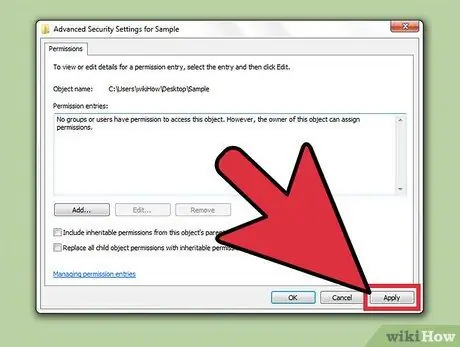
Step 10. Click "Apply" to save changes
The changes you make will be saved and applied to the user. If you change permissions for yourself, the changes will be applied automatically.
Method 2 of 2: Taking Ownership
Step 1. Log in as administrator
Only accounts with administrator privileges can change the ownership of files and folders.
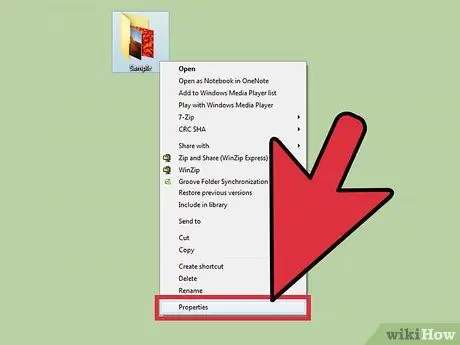
Step 2. Right-click the file or folder you want to change ownership of and select " Properties
" The Properties window will open.
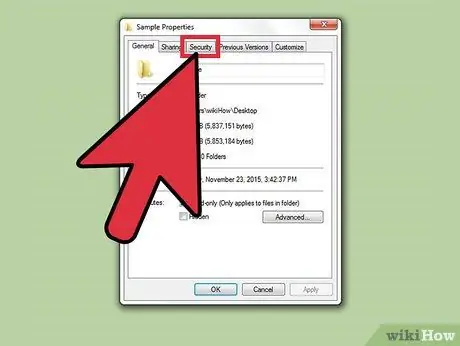
Step 3. Click the "Security" label
A list of users who have permissions on the associated file or folder is displayed.
If you don't see the Security label, you may be trying to change the ownership of a file or folder on the FAT32 USB drive. The Security option is only available on drives with NTFS format. Most USB drives are in FAT32 format
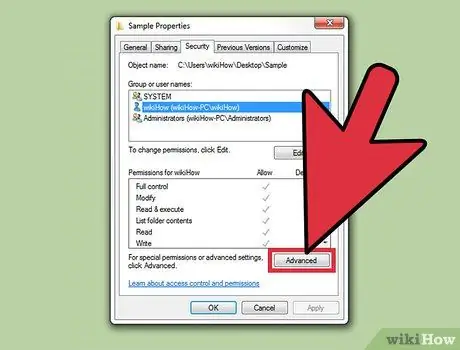
Step 4. Click the "Advanced" button
The Advanced Security Settings window will open.
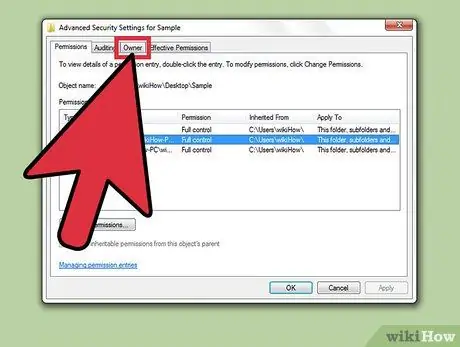
Step 5. Click the "Owner" label
The path to the selected file or folder, its current owner, and a list of potential owners will be displayed.
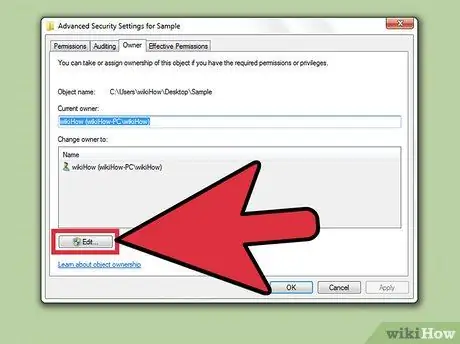
Step 6. Click "Edit" to change ownership
This button allows you to select a different owner in the list.
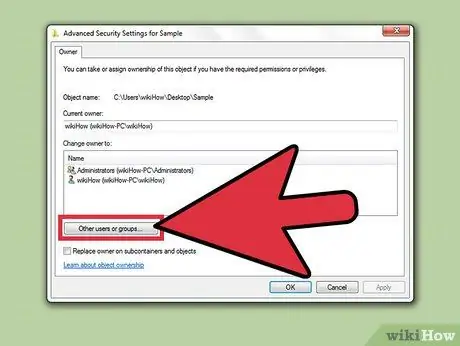
Step 7. Click " Other users or groups " if the user or group you want to assign ownership to is not listed
Click the " Other users or groups " button to find and add the user or group to the list:
- Click "Advanced" then "Find Now" to find all users and groups present on the computer.
- Select the user you want to add to the permissions list and click “OK.” User accounts will be added to the " Change owner to " list.
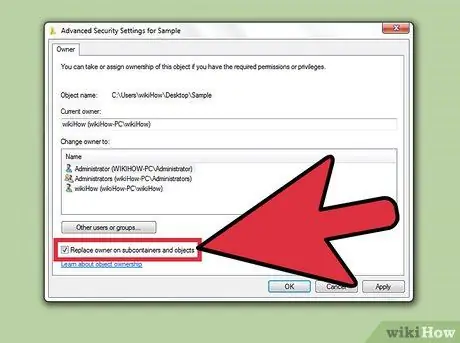
Step 8. Check the "Replace owner on subcontainers and objects" box
This option will give the new user ownership of all subfolders in the selected file or folder.
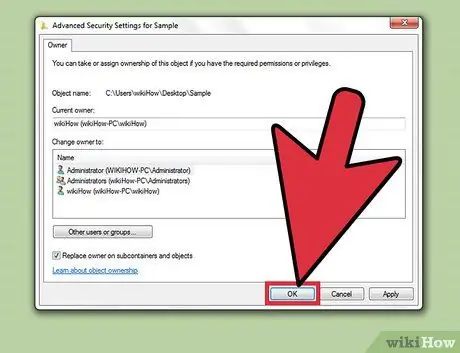
Step 9. Save changes
Click "OK" to save the change of ownership. If you reopen the Properties window and switch to the Security label, you will notice that the ownership has changed in the Advanced Security Settings window.
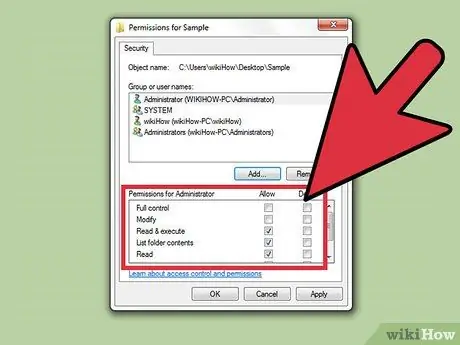
Step 10. Adjust permissions
You may still need to set the permissions for the file to “Full Control,” even after taking ownership of it. Follow the instructions in the first part of this article to do so.






