- Author Jason Gerald gerald@how-what-advice.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 10:50.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 12:04.
SPSS is a statistical analysis program used in various fields, from market research to government agencies. SPSS provides many functions for processing data, but you need the data before you can use the functions provided. There are several ways to enter data into SPSS, starting from entering it manually to entering data from another file.
Step
Method 1 of 2: Manually Entering Data
Step 1. Define the variables
To enter data with SPSS, you need a few variables. Variables are columns of the SPSS worksheet when you use "Data View", and each variable contains data in the same format.
- To specify a variable, double-click on the "Data View" column header, then a menu for specifying the variable will appear.
- When you enter a variable name, the name must start with a letter and capital letters are ignored.
- When you select a data type, you can choose between "String" (characters) and many other types of number formats.
- Visit the guide from the following link (in English) for more details on specifying variables.
Step 2. Create multiple choice variables
If you define a variable that has two or more possibilities, you can specify a label to hold its value. For example, if one of the variables you have determines whether or not an employee is active, the two options you might have are "Active Employee" and "Former Employee".
- Go to the Labels section of the Define Variable menu, and create a numeric value for each possible (eg "1", "2", etc.).
- For each value, provide a label that corresponds to that value (eg "Active Employee", "Former Employee").
- When you fill data into the variable, you only need to type "1" or "2" to select.
Step 3. Fill in your first case
Click on an empty cell that is directly below the leftmost column. Fill in the value corresponding to the variable type into the cell. For example, if the selected column is "name", then enter the name of the employee.
Each row represents a "case", which is known as a record in other database programs
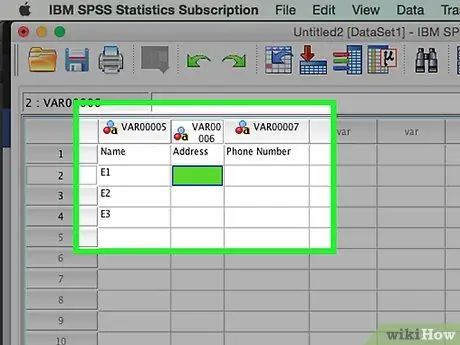
Step 4. Continue to fill in the variables
Move to the next blank cell on the right and fill in the appropriate value. Always fill in one note to completion at a time. For example, if you are entering an employee's record, fill in the name, address, phone number, and salary amount before you move on to another employee record.
Make sure that the values you enter match the format type. For example, entering a dollar value into a column that has a date format will cause an error
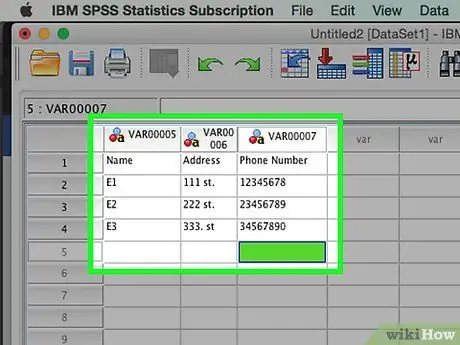
Step 5. Fill the case to completion
After each case has been completed, move to the next line and fill in the next case. Make sure that each case has data for each variable.
If you decide to add a variable, double-click on an empty column header and create a new variable
Step 6. Use your data
When you have finished filling in all the data, you can use the tools that SPSS has and start using the data you have. Some examples of things you can do for example (link in English):
- Creating a frequency table
- Perform regression analysis
- Perform a difference analysis
- Creating a Scatter Plot chart
Method 2 of 2: Entering Data from Another File
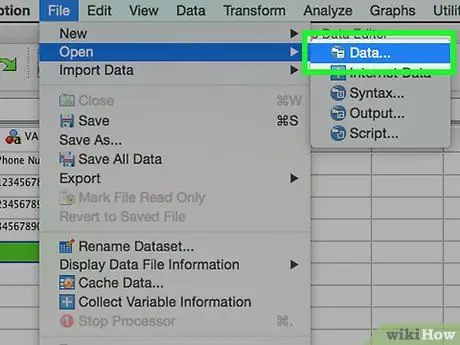
Step 1. Enter the data from the Excel file
When you enter data from an Excel file, the variable will be created based on the first row of the datasheet automatically. The row value will be the variable name. You can also choose to fill in the variables manually.
- Click File → Open → Data
- For "Files of type", select the.xls format
- Find and open the Excel file that you want to use.
- Check the "Read variable names from the first row of the data" box if you want variable names to be generated automatically.
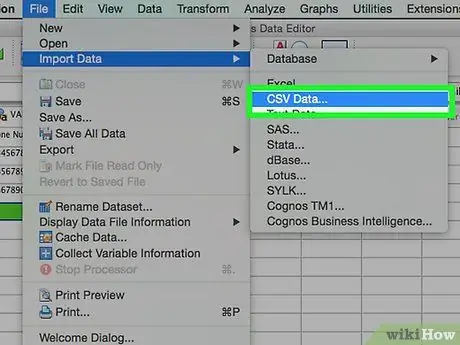
Step 2. Insert a comma-separated file
Comma-separated files usually have a plain text (.csv) format with each data item separated by a comma. You can set variables to be created automatically based on the first line in the.csv file.
- Click File → Read Text Data
- Select "All Files (*.*)" in the "Files of type" section
- Find and open the.csv file
- Follow the file entry request. Make sure that you have notified SPSS that the variable name is at the top of the file when requested, and that the first case is on the second line.






