- Author Jason Gerald gerald@how-what-advice.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 10:50.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 12:04.
For many people, the internet is essential. You can find all kinds of information on the internet, but there are also many dangers that you can find on the internet. When you transact at the bank, shop, and interact via the internet, there is a possibility that your personal data will be exposed. To stay safe when accessing the internet, do the following strategies.
Step
Part 1 of 2: Securing Your Identity
Step 1. Create a strong password
A password is like a key to unlocking your account, so only the person with the key can access it. When setting a password, make sure the password you choose is unique, strong, and not easily guessed by anyone. Create a password that contains letters, numbers, lowercase, capital letters, and other characters.
- Passwords like "password" or "1234" are very common and easy to guess. Using the birth date of someone close to you (or your date of birth) is also not safe. The longer your password, the harder it is to guess. Try creating a password without using letters or replacing letters with numbers.
- Create a password that has references or has meaning only to you. For example, if your pet goldfish was named Si Bulet as a child, swap some letters for numbers so you'll get a good password that only you know like "s1bul3t".
- Make sure the password you create is easy to remember or write on paper. If you write it down, don't leave the paper haphazardly. Do not also keep it on your computer desk.
- Do not use the same password for multiple accounts. If you don't want to create and remember multiple passwords, use a base password (eg "s1bul3t") and add the name of the site where you created the account. For example, use "amzns1bul3t" for Amazon accounts, "gmails1bul3t" for Gmail accounts, and "twitts1bul3t" for Twitter accounts.
- It would be better if you change your password every few months.

Step 2. Pay attention when you install the program or agree to the terms and conditions
When signing up for a newsletter, installing a program, or agreeing to anything, make sure you read what's written carefully. If you don't want to receive junk messages or are listed on telemarketers, see the small box at the bottom of the page asking if you'd like to receive information and offers from companies. A good site will include a statement that the site will not sell your name and personal data to other companies (although they will still send you email).
- Many websites install adware on your computer that will monitor your every move and activity while accessing the internet. Be careful when you visit sites like this.
- Some sites ask for all your personal data before you use the products on the site. Only fill in the required fields, namely those marked with an asterisk (*). If there is an information column that does not have an asterisk, that field is optional and you can leave it blank.

Step 3. Don't give your personal data to strangers
Don't give out your full name, address or phone number to anyone you don't know or trust. This is important when you are in a chat room, negotiating work/deals, or planning to land a coffee from a friendship/dating site.
- Be careful when making friends on the internet. You can make lots of friends through social media, but there are lots of people who pretend and fake themselves on the internet.
- Be careful when you are on online dating sites. Only include your first name and don't give out specific details even if the person you know looks good. Don't give money to people you know from the internet. When you do ground coffee, be sure to meet in a crowded public place, such as a restaurant or coffee shop. Tell other people (friends or family members) that you are leaving and don't let them pick you up or take you to their place.
- Providing personal data to strangers not only threatens your account and identity on the internet, but it also threatens your safety in the real world. Many people on the internet will act friendly and nice, but you have to be careful about the possibility of people using chat rooms, social media, and other websites to obtain data about you that could threaten your life, both at work and at home.
- Always check the safety of the website where you shop. If the site is poorly designed or has a lot of pop-ups, it's most likely unsafe. Sites that do not have PayPal or credit card payments are suspect. If you shop on a site like Kaskus FJB, always be vigilant.

Step 4. Don't be lured in by phishing emails
An email like this looks like an official message from a company, such as a bank where you save or a store where you shop, that sends a link to a fake website and asks for your details.
- Always see the return address. Many phishing e-mailers don't have the same address as the company they represent. Some return addresses look the same as the company name, but are not the same.
- Be careful with spoofing emails claiming to be from eBay, PayPal, a bank, or a company you trust asking for your details. The email usually says that there is a problem with your account and/or password. The message will also include a link. If you get a message like this, don't click on the link. Go to the website by typing the URL into your browser.
- Hover over the suspicious link. Below the screen you will see the actual URL. Many scam emails show different websites under the browser window or next to the cursor when hovering over a link.
- Forward suspicious emails to companies they acknowledge. The company will confirm whether the email you receive is genuine or not.
- Email programs like Yahoo!, MSN, Hotmail, and Gmail never ask for your email password. Don't give your password to scammers.

Step 5. Beware of scams on the internet
Online scams are everywhere, in emails, tweets, Facebook posts, and many other places. Don't click on a link that doesn't contain an address you know or contains a lot of random numbers and letters.
- Never click on pop-ups or emails claiming that you won millions of rupiah. This is a scam.
- Don't be lured in by emails asking you to play the lottery from abroad. Also be wary of emails asking you to transfer large sums of money or the inheritance of someone from outside the country in question after he or she has told his sad life story.

Step 6. Limit the information you share on social media
Facebook, Twitter, Google+, Instagram, LinkedIn, and other social media sites have become a part of many people's lives. On Facebook, people will show their maiden name, their parents' names, their birthday, their child's birthday, their hometown, their home address, their home and mobile phone numbers, and a lot of other information. People with computer access will easily get their information as much as possible. Limit the content you share on the internet to protect your identity and confidentiality.
- Sharing too many details on social media sites can put you at risk in the real world. Telling your home address and where you are (at home/outside the house) could result in a burglary in your home - especially if you post photos of your new TV, computer, and jewelry. Too much personal data, such as your home address, cell phone number, and your daily activities can make you the target of stalkers.
- Many sites have security features, such as bank, insurance, loan, and school websites, which require you to answer several questions to keep your account safe. Questions like this usually read: "What's your mother's name?", "What was your father's grandparents name?", "What city do you live in?", or "When is your father's birthday?" The answer to this question can be easily found on the user's Facebook page.
- Disseminating information like this can result in identity theft.
- When choosing a security question, don't choose a question whose answers are found in easily searchable social media sites. Choose a more difficult question that only you know.

Step 7. Have multiple email accounts
It's best if you have three accounts. Having multiple email accounts helps you share different aspects of your life, share official and non-official email addresses, and stay away from spam and other identity issues.
- Have a business e-mail address for work-related correspondence. Often times, a business email will be provided by your employer.
- Have a primary personal email address. You can use this account for banking, job hunting, insurance, and other business and personal correspondence. You can share this address with close friends and family members.
- Have a junk email address. You can use this account to register various accounts on the internet, such as shops, restaurants, or other places that don't need to use your personal email address. You can also use this email to sign up for social media sites. If there is spam, your personal/business email account will not be compromised.
Part 2 of 2: Securing Your Internet Connection
Step 1. Use an antivirus, anti-spyware, and firewall program
Accessing the internet without these programs is extremely insecure and leaves your computer vulnerable to spam, hackers and viruses. Securing your computer with a security program will protect you from a wide variety of threats. Make sure these programs are regularly updated so that you are always free from the latest threats.
- Trojans, snoopers, malware, and viruses not only steal your data, but they will also weaken your computer system and make your processor run sluggishly. Antivirus and anti-snoop programs protect you from these computer diseases and keep your computer healthy. There are many programs available for you to purchase, but there are also many that you can get for free.
- A firewall is a piece of hardware or software that creates a barrier between your network and cyberspace and filters the data that is allowed in and out of your computer. You are free to use the operating system's built-in firewall program or a third-party firewall.

Step 2. Secure your wireless router
Most homes have wireless networks that connect computers, portable devices, tablet computers, and game consoles. Having a wireless network is very convenient and practical, but it can leave your device and information vulnerable.
- Change the router name from the default name. Change the router name to something unique and not easily guessed by others.
- Create a strong password for your router and not easy for others to guess. Use the instructions described above to create your router password.
- Choose WPA2 or WPA security for your router. WPA2 and WPA are much more secure than WEP.
- Disable guest login if your router has this function. If you want to let your friends access Wi-Fi, but don't want to give them the access password, create a strong and unique guest password.
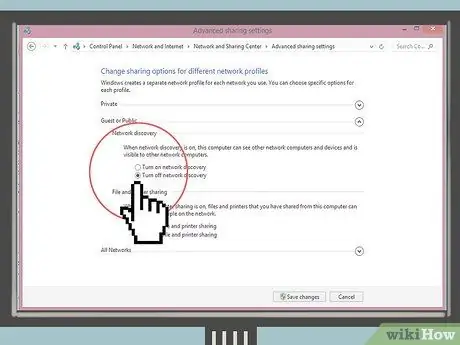
Step 3. Disable network detection and file sharing features when you use a wireless network in a public place
Otherwise, your system and files will be vulnerable to being opened by "anyone" on the same wireless network as you, not just hackers. If you are within range of a wireless network in a public place, but don't need the network, turn off the wireless features on your device.
- In Windows, you can disable it via Control Panel > Network and Internet > Network and Sharing Center.
- On Mac OS X, you can disable it via System Preferences > Sharing.
- On some devices, there is an on/off switch for wireless connection; on some other devices, you'll need to configure it manually (eg on a Mac, click the Wi-Fi icon and turn off AirPort).

Step 4. Always ensure the security of transactions
A good company will have a lot of security tools installed. You may see a gold lock at the bottom of the page indicating the site is secure. When providing your bank account info or other information, make sure your connection is secure.
- Secure URLs start with https:// instead of https://. This means that transmissions on the page are encrypted to and from the web server.
- Even if the connection is secure, pay attention to the sites you visit. Not all websites that use HTTPS or websites that accept payments can be trusted. If you don't know the website you're visiting, find out first.
Step 5. Download files from trusted sources
When downloading files or software, make sure you only download from sites that are trusted and have been approved by trusted parties. Choose a download source that lists prices and has checked downloads for threats (eg download.cnet.com).
- Be careful with extra downloads. Sometimes when you download free software, such as games, apps, or even browsers, those download links also contain browser toolbars and unwanted add-ons. When downloading and installing free programs, be sure to always select "custom installation." You can choose not to install unnecessary additional applications, such as toolbars and add-ons. Deselect and uncheck anything you don't know about before downloading the program from the website.
- When in doubt, search for the name of the download site on a search site (Google) and add "scam" in the keyword.
- Do not download illegal copyrighted material without paying.

Step 6. Don't open email attachments
Do not open attachments unless you know the exact sender of the message and the contents of the attachment are.doc,.pdf, or viewable documents, do not open the attachment. Some junk emails contain viruses or snoopers that can cause problems on your computer. Emails like this will usually be marked as "spam" or "junk" automatically, but some emails containing viruses sent by friends may disappear from system scans.
- Avoid emails that contain attachments that end in ".exe".
- If you're using an email program like Outlook or Thunderbird, you can turn off attachment previews. This setting will disable the feature so you can't preview the attachment. Go through your email program's settings and disable options like Show Attachment Previews, Display Attachments Inline, etc.
Tips
- It's very important to remember; never share your password, even with friends.
- There are several sites that require complete personal data, such as online bank sites or insurance companies. There are also some sites that have no interest in knowing your age and address. For sites like this, you can use aliases with fake birth dates and addresses so that if the site is hacked, none of your personal data is stolen.
- Never click on pop-ups. Your personal data can be stolen this way and pop-ups can install viruses and adware onto your computer unnoticed.
- Use hints that can easily help you remember passwords and answers to security questions.
- Do not use the names of parents, friends, family members, or a common password (eg 1234pink) as your password.
- Be alert at all times.
- Use complex passwords. Use numbers and letters in your password and do not share your password with anyone.
Warning
- Some of the emails may be from your friends, but they may not be what you think they are. Be aware that your friend's email account may have been hacked.
- If your computer has been hacked, chances are that all the information on that computer has been read by the hacker. Update your antivirus program and remove any viruses. If your important documents have been stolen or read without your knowledge, notify your bank or office of work (if the documents relate to these parties). Report all forms of crime to the police.
- Do not use your account if your account has been hacked/scanned and you have backed up your account. Immediately notify the bank, workplace and other parties of this incident. You may have to change your password or account number as soon as possible if the account is registered with your email address. Report this issue to your email provider.
- Always back up important emails and documents on a USB flash drive as well as in print.
- Don't follow chain e-mails asking you to do something with the promise of getting rid of something bad. This is cyber-bullying and the threat of bad things is a lie.
- Do not use the passwords exemplified in this article.
- You can never be completely safe on the internet. If you want to be safe, don't post anything on the internet.






