- Author Jason Gerald gerald@how-what-advice.com.
- Public 2024-01-19 22:11.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 12:04.
This wikiHow teaches you how to access the Registry Editor program on a Windows computer. Regardless of whether program access has been blocked by the school computer network administrator or there is a virus on the computer that prevents the program from opening, there are several ways you can try to display and re-access the Registry Editor.
Step
Method 1 of 5: Using the Run. Program
Step 1. Open the “Start” menu
Click the Windows logo in the lower-left corner of the screen.
Step 2. Type run into the “Start” menu
After that, the computer will look for the program " Run ".
Step 3. Click Run
It's at the top of the “Start” window. After that, the Run program will be opened.
If the Run program is blocked on your computer, you won't be able to open it
Step 4. Type regedit in the Run window
This command is used to open the Registry Editor program.
Step 5. Click OK
After that, the command to open the Registry Editor will be executed. If the Registry Editor asks you to grant access permissions and it opens after you click the “ Yes ”, your problem has been successfully resolved.
- If the Registry Editor does not open, you will need to try another method in this article.
- If you get a pop-up window with the message " Registry editing has been disabled by your administrator ", you need to edit the Group Policy settings. However, you can only do this if you have the authority to control the Group Policy Editor program on the network.
Method 2 of 5: Running a Security Scan
Step 1. Disable third-party antivirus programs
Third-party antivirus programs (any program other than Windows Defender) can cause several different problems on your computer. Therefore, disable any antivirus protection that Windows Defender does not run before proceeding to the next step.
Step 2. Open the “Start” menu
Click the Windows logo in the lower-left corner of the screen.
Step 3. Type windows defender security center into the “Start” menu
After that, the computer will search for the Windows Defender program.
On some versions of Windows, this option is displayed with the label “ Windows Defender " just.
Step 4. Click Windows Defender Security Center
This option is indicated by a white shield icon on a gray background. You can see the icon at the top of the “Start” window.
Step 5. Click the shield icon
It's in the upper-left corner of the Windows Defender page.
When expanded, this option is labeled “ Viruses & threat protection ”.
Step 6. Click Advanced scan
This link is under the button “ Quick scan ” in the middle of the page.
On some versions of Windows Defender, click the “ Home ” because some versions of Defender do not have an “Advanced Scan” segment or option.
Step 7. Make sure the "Full scan" option is checked
Click the circle to the left of the "Full scan" label at the top of the page if the circle isn't already marked.
Step 8. Click Scan now
This button is in the middle of the page. Windows Defender will start scanning for malware that might be blocking/preventing Registry Editor access on your computer.
Step 9. Wait for the scan to complete
If any malicious programs or files appear during the scanning process, Windows Defender will send a warning and provide the option to remove the malicious content.
If the scan finds nothing, repeat the scan and replace the "Full scan" option with the "Windows Defender Offline scan" option
Step 10. Try opening the Registry Editor
After the scan is complete, go to the menu “ Start ”, type regedit, and press Enter. If the Registry Editor program still won't open, you may need to try another method.
You may need to restart your computer before you can access Registry Editor after scanning
Method 3 of 5: Using Command Prompt
Step 1. Open the “Start” menu
Click the Windows logo in the lower-left corner of the screen.
Step 2. Type command prompt into the “Start” menu
After that, the Command Prompt icon will be displayed in the “Start” menu.
Step 3. Right click
"Command Prompt".
It's at the top of the “Start” window. After that, a drop-down menu will be displayed.
If your computer's trackpad doesn't have a right mouse button, use two fingers to tap the trackpad
Step 4. Click Run as administrator
This option is in the drop-down menu.
If you do not use a computer administrator account, you cannot complete this method
Step 5. Click Yes when prompted
After that, the Command Prompt program will be opened in administrator mode.
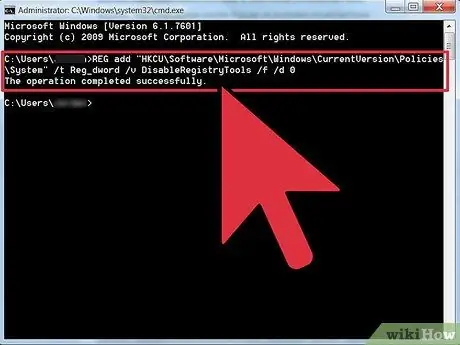
Step 6. Enter the Registry Editor program reload command
Type reg add "HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System" /t Reg_dword /v DisableRegistryTools /f /d 0 in the Command Prompt window, then press Enter.
Step 7. Close the Command Prompt window
The command that is executed will reactivate the Registry Editor program.
Step 8. Try opening the Registry Editor program
Open menu Start ”, type regedit, and press Enter. If the Registry Editor program does not open, continue to the next step.
Step 9. Restart the computer
Open menu Start ”, click the icon “ Power ”
and click " Restart " After the computer has restarted, you can try opening the Registry Editor again.
If the Registry Editor program still won't open, you can use a script to force it to open
Method 4 of 5: Using the Group Policy Editor
Step 1. Open the “Start” menu
Click the Windows logo in the lower-left corner of the screen.
Step 2. Type group policy editor into the “Start” menu
After that, the computer will look for the Group Policy Editor program.
Step 3. Click the Group Policy Editor icon
The program icon will appear at the top of the “Start” menu. Once clicked, the Group Policy Editor program will be opened.
On some versions of Windows, the option may be labeled as “ Edit group policy ”.
Step 4. Double-click User Configuration
After that, the selection will be expanded and show the folders that are below it.
- Skip this step if the option " User Configuration "has been expanded.
- If you don't see the option, double-click the option “ Local Computer Policy ” which is at the top of the program sidebar first.
Step 5. Click Administrative Templates
This folder is at the bottom of the folder list “ User Configuration ”.
Step 6. Double-click the System folder
This folder is on the right side of the Group Policy Editor window.
Step 7. Double-click Prevent access to registry editing tools
It's on the right side of the program window.
You may need to swipe the screen to find it
Step 8. Check the "Not Configured" box
It's in the upper-left corner of the pop-up window.
Step 9. Click Apply, then click OK.
These two buttons are at the bottom of the window. After that, the Registry Editor program will be reactivated on the computer.
Step 10. Try opening the Registry Editor program
Open menu Start ”, type regedit, and press Enter. If the Registry Editor program opens, you have successfully bypassed the restrictions set by the Group Policy Editor program.
Method 5 of 5: Using Virtual Basic Script (VBS or Virtual Basic Script)
Step 1. Open a new Notepad document
Open menu Start ”, type notepad, and click the program icon “ Notepad ” which is blue. After that, a new Notepad document will be opened.
Step 2. Copy the following code into a Notepad document:
Option Explicit
Dim WSHShell, n, MyBox, p, t, mustboot, errnum, vers
Dim enab, disab, jobfunc, itemtype
Set WSHShell = WScript. CreateObject("WScript. Shell")
p = "HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System\"
p = p & "DisableRegistryTools"
itemtype = "REG_DWORD"
mustboot = "Log off and back on, or restart your pc to" & vbCR & "effect the changes"
enab = "ENABLED"
disab = "DISABLED"
jobfunc = "Registry Editing Tools are now"
t = "Confirm"
Err. Clear
On Error Resume Next
n = WSHShell. RegRead(p)
On Error Goto 0
errnum = Err. Number
if errnum 0 then
WSHShell. RegWrite p, 0, itemtype
End If
If n = 0 Then
n = 1
WSHShell. RegWrite p, n, itemtype
Mybox = MsgBox(jobfunc & disab & vbCR & mustboot, 4096, t)
ElseIf n = 1 then
n = 0
WSHShell. RegWrite p, n, itemtype
Mybox = MsgBox(jobfunc & enab & vbCR & mustboot, 4096, t)
End If
Step 3. Click File
It's in the upper-left corner of the Notepad window.
Step 4. Click Save As…
It's at the top of the drop-down menu File ”.
Step 5. Select the location to save the document
Click the folder Desktop ” displayed on the left side of the “Save As” window.
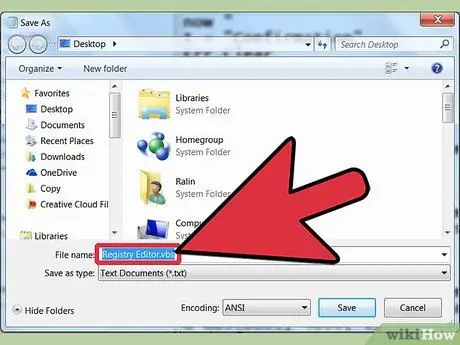
Step 6. Type
Registry Editor.vbs
as the file name.
You can enter it in the " File name: " field.
Step 7. Select the file type
Click the drop-down box next to "Save as type: ", then click " All Files " With this option, the document will be saved in the appropriate file format.
Step 8. Click the Save button
It's in the lower-right corner of the "Save As" window. After that, the file will be created.
Step 9. Close Notepad
Click the button X ” in the upper-right corner of the Notepad window to close the program.
Step 10. Double-click the VBS file
After that, the script or command will be executed.
This script or command will disable/enable the Registry Editor program settings. Don't run the script twice. Otherwise, Registry Editor will be disabled again
Step 11. Try opening the Registry Editor program
Open menu Start ”, type regedit, and press Enter. If the Registry Editor program still won't open, you may need to take your computer to the IT department or repair service provider and have an expert troubleshoot the problem.






