- Author Jason Gerald gerald@how-what-advice.com.
- Public 2024-01-19 22:11.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 12:04.
GIMP is a software package that provides many of the functions of Adobe Photoshop, but has a very big price difference: it's free!
Step
Method 1 of 5: Installing GIMP

Step 1. Download the latest version of GIMP (GNU Image Manipulation Program)
You can find it from the developer's website here. Click the Download GIMP X. X. X link under the GIMP for Windows heading. The setup file will start downloading in a few seconds.
Step 2. Run the installer
Windows will ask if you want to run the file. Check to make sure you actually downloaded GIMP from the developer. Select the language to continue the installation.
- The GIMP installer will open. To install GIMP to the default folder, click the Install button. To change the installation settings and choose which add-ons to install, select Customize.
- GIMP will automatically associate the GIMP image file. To be able to open other file types, select the Customize option. You will be given the option to set file associations.
Method 2 of 5: Starting GIMP
Step 1. Run the installed program
When GIMP opens, several data files will load. This process may take several minutes. When it finishes loading, several windows will appear on the screen. On the left side is the Toolbox. On the right side is the Layers menu. The middle window is where the image will be opened.
Step 2. Create a new image
To start a blank image, click the File menu in the middle window and select New. The Create a New Image window will open, asking for the size of the image to be created. You can set the image size manually or choose from predefined templates using the drop-down menu.
Click OK and a new image will open. The cursor will change to the Pen tool and you can start drawing. Use the Layers and brush menus to adjust the brush type
Step 3. Open the saved image
Click File, then Open. Browse for the image you want to edit. After selecting the desired file, the image will open in a new window.
Method 3 of 5: Cropping Image
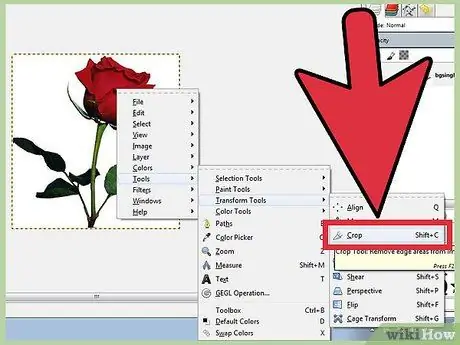
Step 1. Open the image to be cropped
Right click on the image and select Tools, then Transform Tools, then Crop & Resize. The cursor will change to a Crop cursor that looks like a knife. You can also select a crop tool from the Toolbox.

Step 2. Drag the box to the area of the image you want to save
Interestingly it doesn't have to be accurate, as you will be able to manually adjust the box. Click the squares in the corners or on the sides to adjust the points of the box.
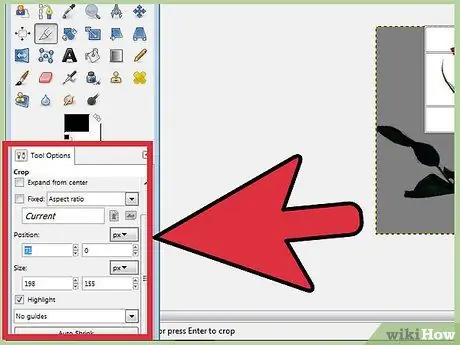
Step 3. Adjust the grid pixel by pixel
To make fine adjustments, use the Tool Options at the bottom of the Toolbox. You can change the position of the box in the image by adjusting the numbers in the Position field. You can fine-tune the size of the box by changing the values in the Size field.

Step 4. Crop the image
After making adjustments, crop the image by middle-clicking the created square. Everything around the image will be removed, leaving the inside of the box.
If you are not satisfied, you can undo the action by pressing Ctrl+Z
Method 4 of 5: Inverting and Rotating Images
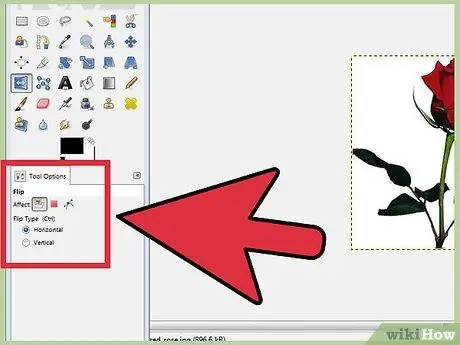
Step 1. Flip the image
Right-click on the image and select Image, then Transform, then Flip Horizontally or Flip Vertically. Alternatively, you can click the Flip icon in the Toolbox. Under Tool Options, you can choose whether to flip horizontally or vertically.
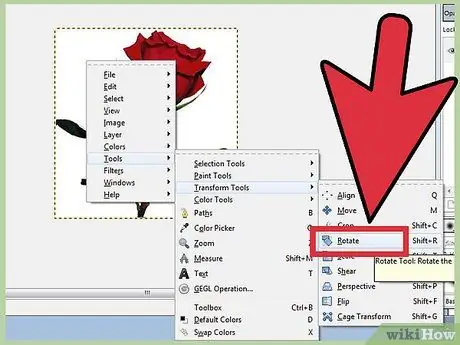
Step 2. Rotate the image by 90°
To rotate the base image, right-click the image and select the image, then Transform, then choose whether you want to rotate it 90° clockwise, counterclockwise, or 180°.
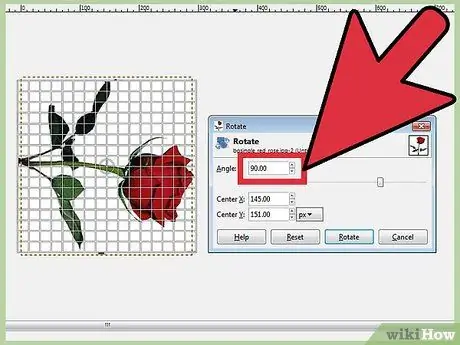
Step 3. Rotate the image by a certain angle
If you want to rotate the image by a certain angle, right-click the image, then select Tools, Transform Tools, then Rotate. This will open the Rotate tool where you can adjust the rotation angle either with the slider or by entering a number. You can also move the center of rotation by entering coordinates or dragging a circle in the image.
Method 5 of 5: Mastering the Other Basics
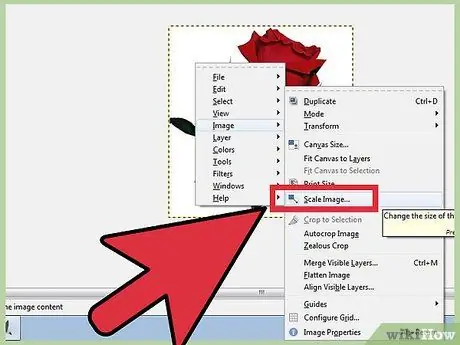
Step 1. Resize the image
Right-click the image. Select Image from the menu, then click Scale Image. The Scale Image window will open and you can adjust the size of the image. Enter a new value for the length or width and the image will adjust accordingly.
- GIMP will automatically keep the aspect ratio the same by locking the length and width values. This means that if you change only one value, the other values will change automatically to keep the image from stretching or compressing. You can disable this by clicking the chain icon between the two boxes.
- Once satisfied with these settings, click Scale to resize the image.

Step 2. Draw a straight line
Choose a drawing tool such as Pencil or Airbrush. Click on the image to create a starting point for the line. Hold down the Shift key and move the mouse to the position of the end point of the line. You will see a line appear connecting the start point and end point. Click to draw a line. Continue holding Shift to add new lines, each starting from the position of the previous ending line.
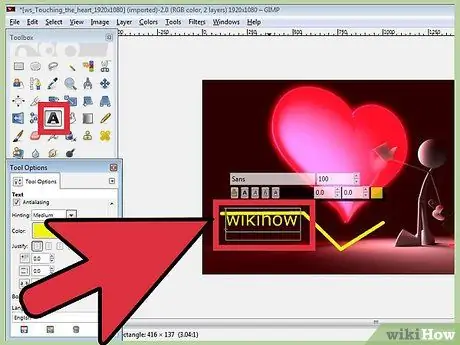
Step 3. Add text to the image
Press T on the keyboard and click where the text is to be added. This will open the Text Toolbox. You can start typing and your text will appear on the image. Use the toolbox to set fonts and text effects.
Tips
- The www.gimp.org site only distributes GIMP source code (building blocks). However you can download the executable version by following the download instructions.
- There are many user support sites on the web that will help those who are not familiar with the building blocks of free Unix-based graphics software. It should be noted that the www.wiki.gimp.org site has been deactivated. It is suspected that the site has moved, but has not been found.
- At the bottom of the gimp.org page is a "contact us" link which leads to several support links, discussions, forums, and resources for most of the latest GIMP versions.
- GIMP stands for GNU Image Manipulation Program. GIMP originally stood for General Image Manipulation Program and can be downloaded for free from www.gimp.org or one of its mirror sites. Just like any other download software, read it carefully to make sure your operating system is compatible. GNU is a Unix-like computer operating system developed by the GNU project, and aims to be a "unix-compatible complete software system" consisting entirely of free software.






