- Author Jason Gerald gerald@how-what-advice.com.
- Public 2024-01-19 22:11.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 12:04.
Jupiter is the largest planet in our solar system. The fifth planet from the sun is one of the 'Gas Giants'. To estimate the size of Jupiter, the planet takes nearly 12 years to orbit the sun. Jupiter is famous for its Great Red Spot and a belt of clouds with contrasting dark and light. Jupiter is the brightest object in the sky after the sun, moon and Venus. For several months each year, Jupiter shines brightly for several hours before and after midnight, due to its enormous size. Many people like to look for Jupiter in the sky and this can also be done by beginners without having to have expensive equipment to enjoy observing the beauty of distant planets.
Step
Part 1 of 4: Preparing the Equipment
Step 1. Prepare a sky map
Before you start looking for Jupiter, you need to have a sky map that can show you which sky to start looking at. For the more experienced astronomer, there are many advanced sky maps showing the positions and trajectories of the planets. For those who aren't experienced at reading paper maps, there are a number of phone apps you can download to help you find Jupiter and the other planets, as well as the stars in the sky.
With this phone app, you just need to lift your phone up towards the sky and it will identify the stars and planets for you

Step 2. Prepare the binoculars
Jupiter is so large and bright in the sky that it can be seen with good binoculars. Binoculars that magnify seven times human vision will be effective and will show Jupiter as a small white disc in the sky. If you don't know the power of your binocular lens, look at the number on the binocular body. If it says 7x another number, it means that the binoculars magnify seven times and can be used to observe Jupiter.

Step 3. Prepare the telescope
To get a good view of Jupiter's features, complement your observations with a telescope. This tool will help you see Jupiter's famous belts, its four moons, maybe even the Great Red Spot. Many types of telescopes are available, but for beginners, a 60 or 70mm diameter refractor telescope is also good.
The performance of the telescope will drop if the optics are not cool enough. Store the optics in a cool place, and before you start observing, place them outside to cool down before you start
Part 2 of 4: Preparing Your Observations
Step 1. Identify good viewing conditions
You can save time and avoid wasted hours by learning to quickly identify good sighting conditions. Before setting up the telescope, look at the stars. See if the stars are twinkling brightly in the sky. If so, this indicates a turbulent atmosphere. These conditions make planetary observations more difficult, and you need a calm night sky. On a steady night with good visibility, the sky will look a bit foggy.
The Association of Lunar and Planetary Observers has a scale for viewing conditions from one to 10. If the condition value is less than 5, your observations are unlikely to go well
Step 2. Find the right time of day or night
The best time to observe the planet is at night, but Jupiter is so bright that it can sometimes be seen shortly after dusk, and just before dawn. At dusk, Jupiter will appear in the east, but as the evening progresses, Jupiter will appear to be traveling westward in the sky. At mid-north latitudes, Jupiter will set in the west just before sunrise in the east each morning.

Step 3. Choose a place and be prepared to wait
Make sure you're in a dark, quiet place so you can concentrate on observing the planet. Your backyard can be a great place to be, but remember that planet-gazing is slow and exciting, so make sure to dress warmly and be prepared for a long wait. If you plan to document your observations, take all your equipment with you so you don't have to leave the lookout.
Part 3 of 4: Observing the Planet Jupiter

Step 1. Find Jupiter with binoculars
Find a comfortable and stable position and if possible, support your binoculars on a camera tripod, or something stable and sturdy so the binoculars don't shake when you use them. With binoculars, you will see Jupiter as a white disk.
- You can also see up to four lights near Jupiter, these are the four moons called Galilee. The planet Jupiter has at least 63 moons. In 1610, Galileo named these four moons Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto. The number of moons you see depends on where they are orbiting Jupiter.
- Even if you have a telescope, use binoculars to help locate Jupiter in the sky before using the telescope for more detailed observations.

Step 2. Take a closer look using a telescope
Once you've discovered Jupiter, you can begin a more detailed observation of the planet's surface through your telescope and identify some of its key features. Jupiter is famous for its darker cloud belts and the lighter zones that look sideways across the planet's surface. Try to identify the lighter areas called the equatorial zone and the darker equatorial belts in the north and south.
When looking for a cloud belt, keep trying. It took time to learn how to find the cloud belt through a telescope. Try looking it up with someone who is used to finding it
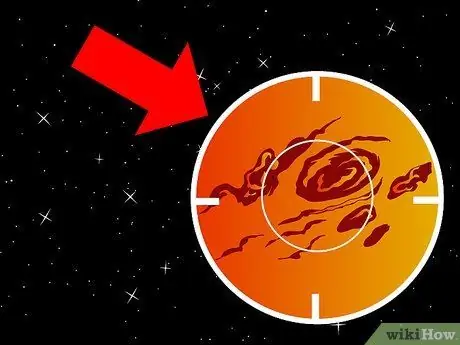
Step 3. Find the Giant Red Spot
One of Jupiter's most fascinating features is the Great Red Spot. These giant oval storms, larger than Earth, have been observed on Jupiter for more than 300 years. You can find it on the outer edge of the southern equatorial belt. These spots show how fast the planet's surface is changing. In just an hour, you will see this speck moving across the planet.
- The appearance of the Great Red Spot is uncertain, and is not always visible.
- It is less red in color, but more orange or pale pink.
Part 4 of 4: Documenting Your Observations

Step 1. Try to draw what you see
Once you have a good view of Jupiter, you can document your astronomical observations by drawing Jupiter and recording its appearance. It's basically a low-tech version of skywatching, observing, documenting and analyzing what you see in the sky. Jupiter is always changing, so try to draw it in about 20 minutes. You will follow the tradition of great astronomical drawing.

Step 2. Take a Jupiter shot
If you prefer a more technologically advanced method of recording your observations, you can try photographing Jupiter. Like a telescope, the camera you use, whether it's very sophisticated or ordinary, you will still get results. Some stargazers use charged-coupled device cameras or even small, inexpensive webcams to photograph planets with telescopes.
If you want to try using a DSLR camera, keep in mind a longer exposure time will capture a clearer image of the moon but will blur the dark and light streaks across the planet's surface

Step 3. Make a movie about Jupiter
One of the best ways to monitor the constant changes in Jupiter's surface and the position of its moons is to film them. You can do this in the same way as taking a picture.
- Use your notes to compare each observation to monitor changes in the planet's surface and find interesting things.
- The clouds are always turbulent and the appearance of a planet can change drastically in just a few days.
Tips
- NASA information about the planet Jupiter can be found at: https://solarsystem.nasa.gov/planets/profile.cfm?Object=Jupiter, and NASA information about the Galileo spacecraft can be found at: https://solarsystem.nasa.gov /galileo/.
- Always observe from a dark place, like your backyard.
- Download Google Sky Map app on your phone, it will be easier to find planets this way.






