- Author Jason Gerald gerald@how-what-advice.com.
- Public 2024-01-15 08:07.
- Last modified 2025-06-01 06:05.
Dividing by decimal numbers seems difficult at first because no one has taught you the “0, 7 times table”. The secret to doing this is to convert the division problem to a format that only uses whole numbers. After you rewrite the problem in this way, it will become a regular long division problem.
Step
Part 1 of 2: Writing Problems as Ordinary Division Problems
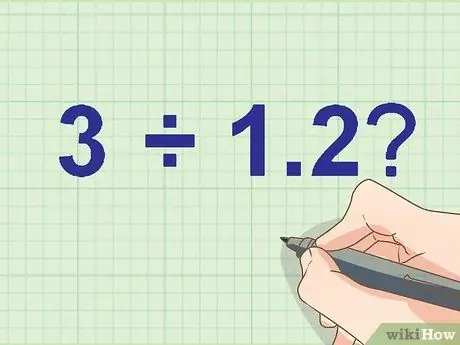
Step 1. Write down your division problem
Use a pencil if you want to improve your work.
-
Example:
How many 3 ÷ 1, 2?

Step 2. Write the whole number as a decimal
Write a decimal point after the whole number, then write a zero after the decimal point. Do this until both numbers have the same place value to the right of the decimal point. This does not change the integer value.
-
Example:
In the problem 3 1, 2, our integer is 3. Since 1, 2 has a place value to the right of the decimal point, write 3 as 3, 0 so that this number also has a place value after the decimal point. Now, our matter becomes 3, 0 ÷ 1, 2.
- Warning: don't add zeros to the left of the decimal point! The number 3 is equal to 3, 0 or 3, 00, but not equal to 30 or 300.
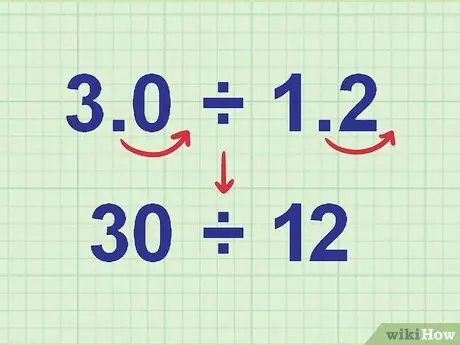
Step 3. Move the decimal point to the right until you get a whole number
In division problems, you can move the decimal points, but only if you move the decimal points on all the numbers by the same number of steps. This allows you to convert the problem to a whole number.
-
Example:
To convert 3, 0 1, 2 to a whole number, move the decimal point one step to the right. Thus, 3, 0 becomes 30 and 1, 2 becomes 12. Now, our problem becomes 30 ÷ 12.

Step 4. Write the problem using long division
Place the divisible number (usually the larger number) under the long division symbol. Write the divisor number outside this symbol. Now, you have a regular long division problem that uses whole numbers. If you want a reminder on how to do long division, read the next section.
Part 2 of 2: Solving Long Division Problems

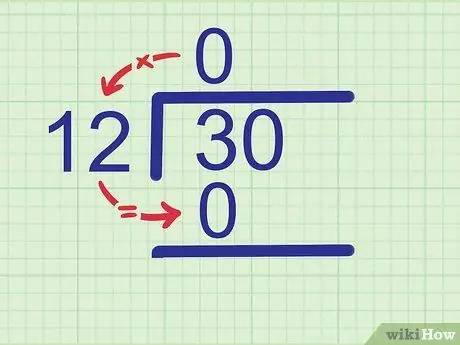
Step 1. Find the first digit of the answer
Start solving this problem the same as you normally would, by comparing the divisor and the first digit of the divided number. Calculate the result of dividing this first digit by the divisor, then write the result above that digit.
Example: We are trying to divide 30 by 12. Compare 12 with the first digit of the number divided, which is 3. Since 12 is greater than 3, 3 divided by 12 equals 0. Write down 0 above 3 in the answer line.
Step 2. Multiply the quotient by the divisor
Write the product of the product under the number that is divided. Write the result just below the first digit of the number you divided because this is the digit you just saw.
-
Example:
Since 0 x 12 = 0, write 0 under 3.
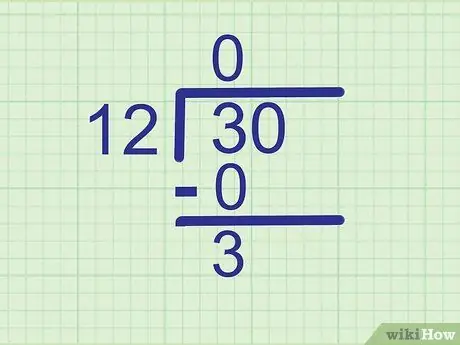
Step 3. Subtract to find the remainder
Subtract the product you just calculated from the digit directly above it. Write the answer on a new line, below it.
-
Example:
3 - 0 = 3, so write
Step 3. just below 0.
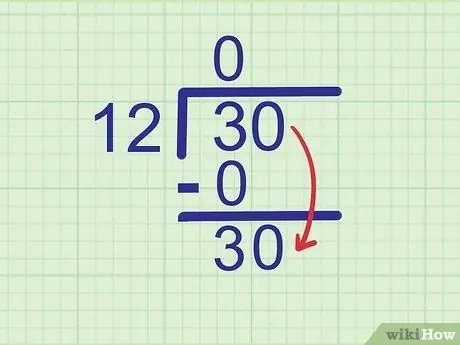
Step 4. Lower the next digit
Drop the next digit of the divided number next to the number you just wrote down.
-
Example:
The number that is divided is 30. We have seen the number 3, so the next digit that must be lowered is 0. Decrease the number 0 to the side of 3 so that it becomes
Step 30..
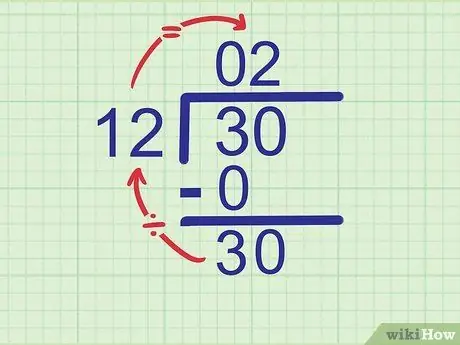
Step 5. Try dividing the new number by the divisor
Now, repeat the first step in this section to find the second digit of your answer. This time, compare the divisor to the number you just wrote down on the bottom row.
-
Example:
What is the quotient of 30 by 12? The closest answer we can get is 2 because 12 x 2 = 24. Write
Step 2. in second place on the answer line.
- If you're not sure of the answer, try several multiplications until you find the largest answer that fits. For example, if your estimate is 3, calculate 12 x 3 and you get 36. This number is too large because we are trying to calculate 30. Try lowering one number, 12 x 2 = 24. This number fits. So, 2 is the correct answer.
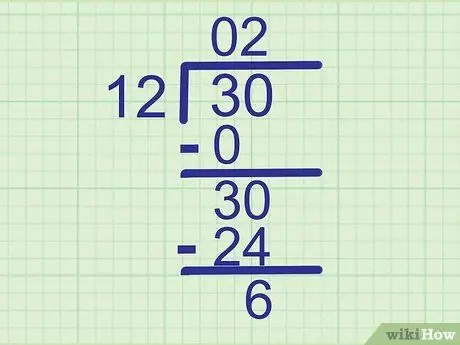
Step 6. Repeat the above steps to find the next number
This is the same long division process as used above, and for any long division problem:
- Multiply the new digit of your answer by the divisor: 2 x 12 = 24.
- Write the product on a new line, below the number that was divided: Write 24 just below 30.
- Subtract the bottom row from the row above it: 30 - 24 = 6. So, write 6 in a new row below it.
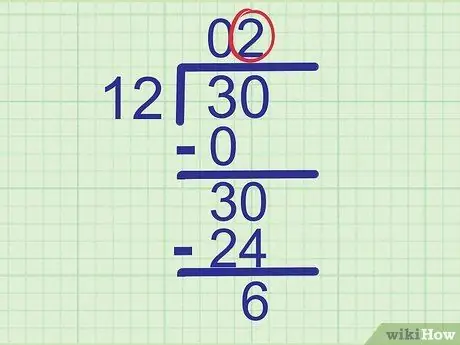
Step 7. Continue this process until you complete the last line of answers
If there are still digits left in the divided number, lower the digits down and continue solving the problem in the same way. If you have completed the last line of answers, continue to the next step.
-
Example:
We just wrote
Step 2. in the last answer line. Proceed to the next step.

Step 8. Add decimals to “extend” the divided number if needed
If the number is evenly divisible, your final subtraction result is “0”. That means, you've finished dividing and you get an answer in the form of a whole number. However, if you've completed the last line of answers and there are still digits to divisible by, you'll need to “extend” the divisible number by adding a decimal point followed by the number 0. Keep in mind that this doesn't change the value of the number.
-
Example:
We've come to the last line of answers, but the answer to our last subtraction is "6". Write “6, 0” under the long division symbol by adding “, 0” to the last digit. Also write the decimal point in the same place on the answer line, but don't write anything after that.
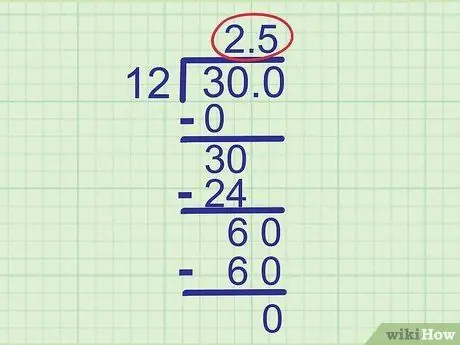
Step 9. Repeat the same steps to find the next digit
The only difference here is that you have to add a decimal point to the same place on the answer line. Once you've done that, you can search for the remaining answer digits in the exact same way.
-
Example:
Drop the new 0 down to the last line so that it becomes “60”. Since 60 divided by 12 is exactly 5, write
Step 5. as the last digit of our answer line. Don't forget that we put a decimal in our answer line. So, 2, 5 is the final answer to our question.
Tips
- You can write this as a remainder (so the answer to 3 1, 2 is “2 remaining 6”). However, because you are working with decimals, your teacher may expect you to work on the decimal part of the answer.
- If you follow the long division method correctly, you'll always have a decimal point in the correct position, or no decimal point at all if the number is divisible by divisible. Don't try to guess the decimal places. The decimal place is often different from the decimal place in your starting number.
- If the long division problem doesn't last for a long time, you can stop and round to the nearest number. For example, to solve 17 4, 2, just count to 4.047… and round your answer to “about 4.05”.
-
Remember your division terms:
- The number to be divided is the number to be divided.
- The divisor is the number used to divide.
- The quotient is the answer to the math division problem.
- Whole: Divided by Divisor = quotient.
Warning
Remember that 30 12 will give the same answer as 3 1, 2. Don't try to “correct” your answer after moving the decimal backwards
Related wikiHow Articles
- Converting Common Fractions to Decimals
- Doing Long-Determined Division
- Divide Fractions by Fractions
- Dividing Mixed Fractions






