- Author Jason Gerald gerald@how-what-advice.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 10:50.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 12:04.
This wikiHow teaches you how to speed up Mozilla Firefox on Windows and MacOS operating systems.
Step
Method 1 of 8: Updating Your Browser to the Latest Version
Step 1. Open Firefox on your PC or Mac computer
You can find this browser in the “ All Apps ” in Windows “Start” menu, or folder “ Applications ” on MacOS.
Firefox developers are always releasing updates to increase the speed of the app. Follow this method to make sure you're using the latest version of Firefox
Step 2. Click the menu
It's in the top-right corner of the screen.
Step 3. Click Help
This option is at the bottom of the menu. This button appears as a ?″ icon in some versions of Firefox.
Step 4. Click About Firefox
Firefox will check for update availability. If an update is available, you will see a button labeled Update to (version number). If the button is not visible, the computer is currently running the latest version of Firefox.

Step 5. Click the Update to button
The update will be downloaded. Once the update is ready to install, the Update button will change to the Restart to update Firefox button.
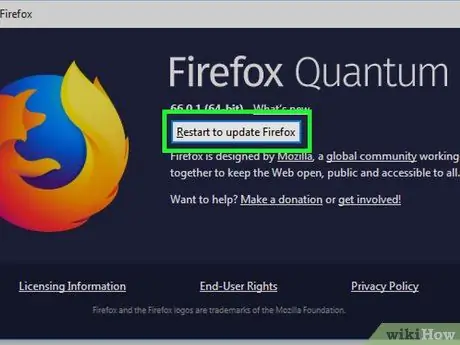
Step 6. Click Restart to update Firefox
Firefox will be closed to install the update. Once the update process is complete, Firefox will restart automatically.
You may need to grant permission for the installation to take place
Method 2 of 8: Free Up Memory
Step 1. Open Firefox on your PC or Mac computer
You can find this browser in the “ All Apps ” in Windows “Start” menu, or folder “ Applications ” on MacOS.
This method will help you when certain websites or extensions are weighing on Firefox's performance
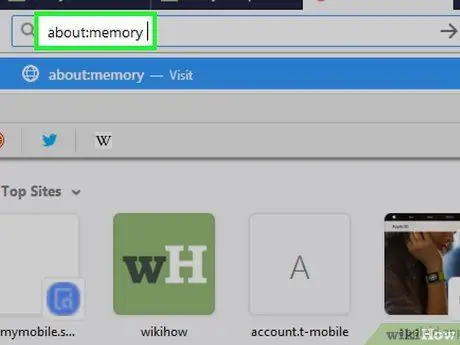
Step 2. Type about:memory into the address bar and press Enter or Returns.
The memory troubleshooting tool will be opened afterwards.
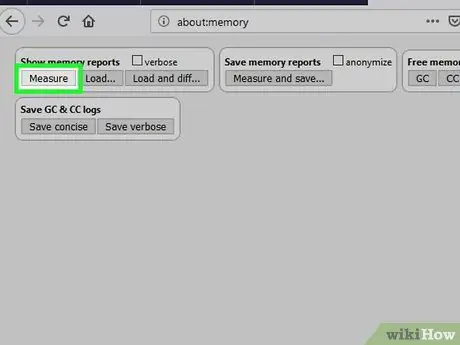
Step 3. Click Measure in the “Show memory reports” box
If you are a developer or a more advanced Firefox user, you can use this feature to determine which processes are running and how much memory each process is using. Browse the report to see each segment.
- Some add-ons are shown on the memory report by name, but other options are shown only as hex codes.
- If the support representative or developer asks you to run and save the memory report, click “ Measure and save ” in the Save memory reports box, then specify a location to save the report. After that, you can attach the report via email or upload it to the bug database if requested.
Step 4. Click Minimize memory usage
It's in the top-right corner of the page. Firefox will free up memory that is currently in use, but is no longer needed. This procedure can add to the speed or performance of the browser.
If memory usage remains high, regardless of the steps you take, your computer may not have enough RAM to support multiple tabs and/or windows being opened simultaneously. Try reducing the number of browser tabs and windows while you are browsing, and increase your computer's RAM
Method 3 of 8: Using Safe Mode
Step 1. Open Firefox on your PC or Mac computer
You can find this browser in the “ All Apps ” in Windows “Start” menu, or folder “ Applications ” on MacOS.
When you use Firefox in safe mode, you will be running a “clean” version of Firefox that does not use any add-ons (either extensions or themes). If Firefox performs faster in this mode, the performance issue may be due to an extension or theme you installed
Step 2. Click the menu button
It's in the upper-right corner of the browser window.
Step 3. Click Help
This option is at the bottom of the menu. This button appears as a ?″ icon in some versions of Firefox.
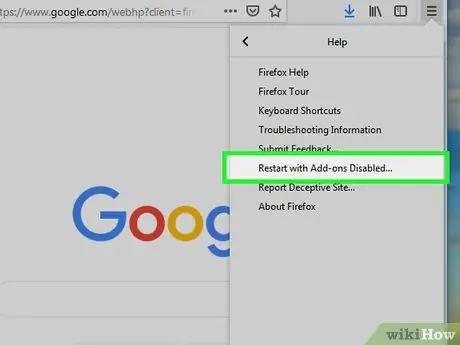
Step 4. Click Restart with Add-ons Disabled
A confirmation message will be displayed.
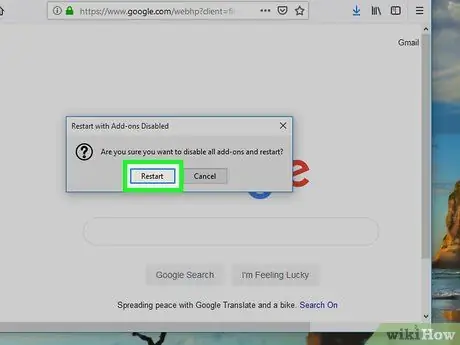
Step 5. Click Restart
A message with information regarding safe mode will be displayed.
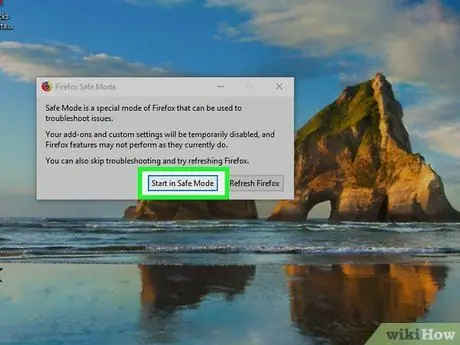
Step 6. Click Start in Safe Mode
Firefox will run without extensions and themes.
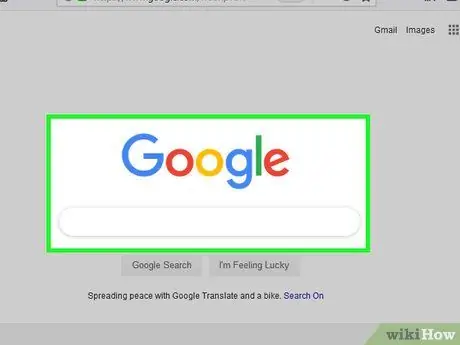
Step 7. Browse the internet
If Firefox's performance in this mode is significantly faster, the performance crash may be due to an add-on or add-on that's problematic.
- Read the add-on or add-on deactivation method to learn how to turn off a feature or add-on in Firefox. Start by turning off all add-ons. After that, activate only one add-on and perform a search using that add-on. If your browser still works quickly and smoothly, you can keep that add-on enabled and test other add-ons.
- Keep testing and enabling plug-ins until you find the one with which you have a problem.
Method 4 of 8: Disabling Add-Ons
Step 1. Open Firefox on your PC or Mac computer
You can find this browser in the “ All Apps ” in Windows “Start” menu, or folder “ Applications ” on MacOS.
- Installed extensions and themes often slow down performance when you browse the internet. If you feel that your browser performs faster in safe mode, follow these methods to determine which extension or theme is causing Firefox performance issues.
- If you are a more advanced user, you can run a memory report to find out how much RAM certain add-ons are using.
Step 2. Click the menu button
It's in the upper-right corner of the screen.
Step 3. Click Add-ons
It's in the middle of the menu.
Step 4. Click Extensions
This option is in the left pane.
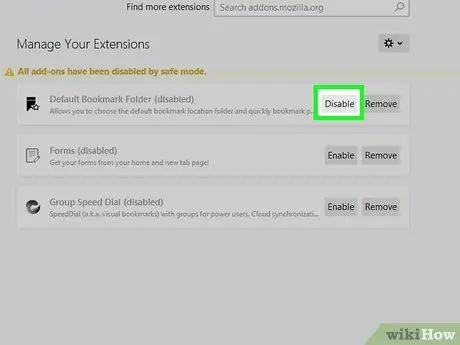
Step 5. Click Disable next to all options
Each add-on will be disabled, without being removed.
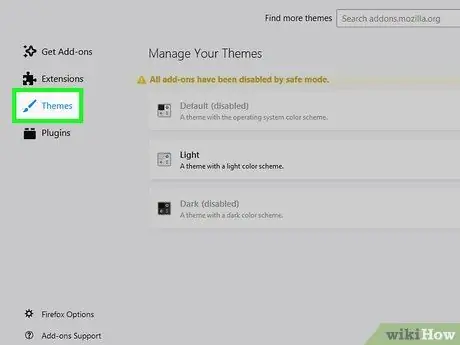
Step 6. Click Themes
This option is in the left pane.
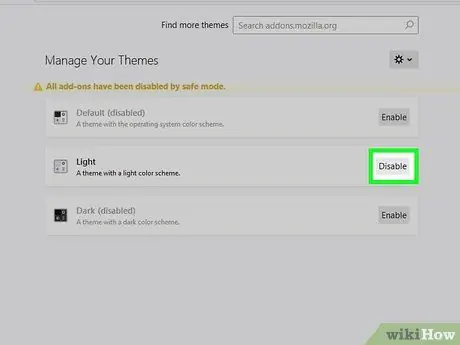
Step 7. Click Disable next to the currently active theme
You will be taken back to the default Firefox theme.
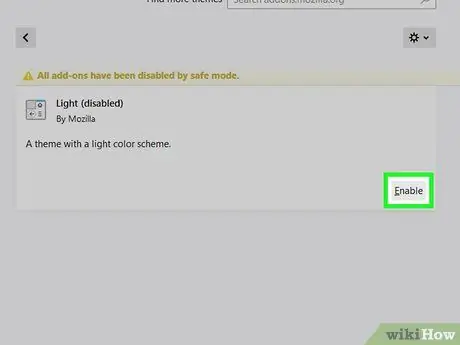
Step 8. Select one extension or theme you want to activate
To search for problematic add-ons, click “ Enable ” on one of the extensions or themes, and leave the other add-ons off.
Step 9. Browse the web
If your browser's performance is still fast when you have an add-on enabled, there's a good chance that the add-on isn't a problem.
Step 10. Enable other add-ons
Again, once the other add-ons are enabled, try browsing the web again. Repeat the steps above until you find an add-on that is slowing down your browser's performance.
If Firefox continues to perform slowly, regardless of the browser you're using, the crash may be due to a problematic driver. If the problem only appears when you access a certain website, that site may be the cause of the disturbance you are experiencing
Method 5 of 8: Clearing Cache, Cookies and Browsing History
Step 1. Open Firefox on your PC or Mac computer
You can find this browser in the “ All Apps ” in Windows “Start” menu, or folder “ Applications ” on MacOS.
- If your browser is feeling sluggish, the crash may be due to cache, corrupted cookies, or too much web browsing history. Follow this method to clear those contents.
- Clearing cookies will log you out of the websites you are currently accessing.
Step 2. Click the menu icon
It's in the upper-right corner of the browser window.
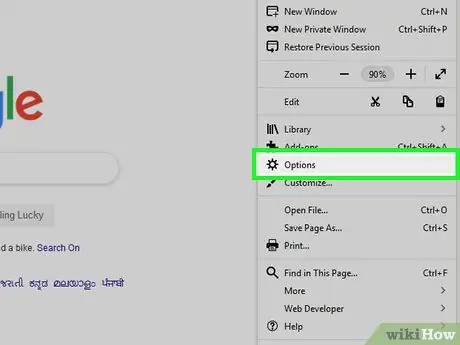
Step 3. Click Options
It's in the middle of the menu.
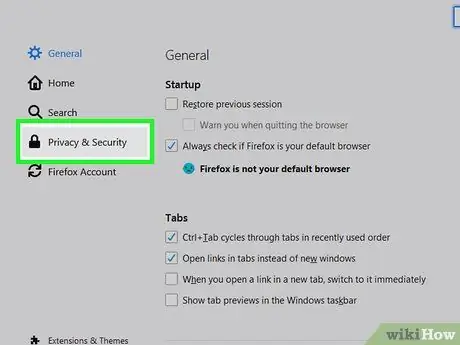
Step 4. Click Privacy & Security
This option is in the left pane.
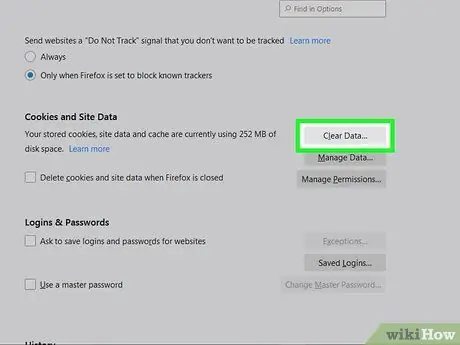
Step 5. Scroll the screen and click Clear Data
This option is under the Cookies and Site Data heading in the right pane.
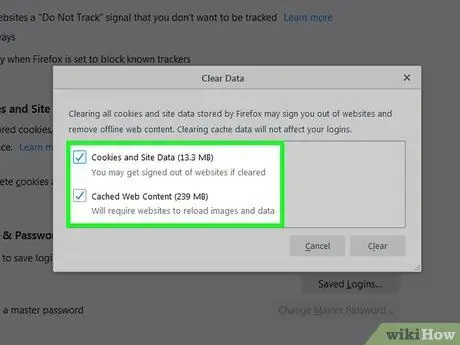
Step 6. Select the information or content you want to clear
Check the boxes next to Cookies and Site Data and Cached Web Content to select both. The amount of space each data type takes up is shown next to its name.
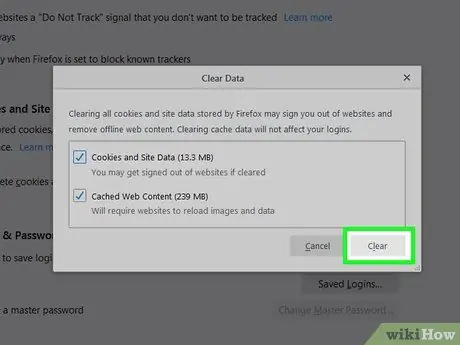
Step 7. Click Clear
A confirmation message will be displayed.
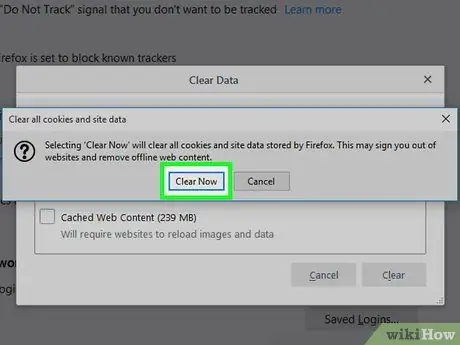
Step 8. Click Clear Now to confirm
The cache and cookies have now been cleared.
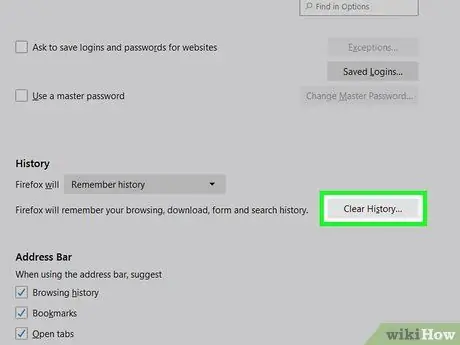
Step 9. Scroll the screen and click Clear History
This option is under the heading History.
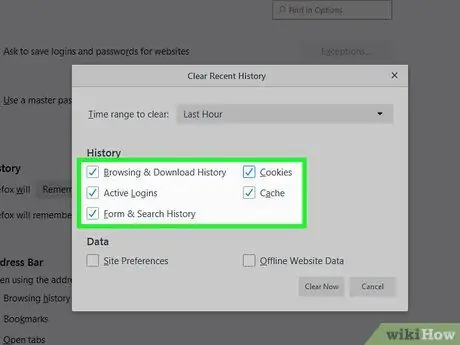
Step 10. Select the information you want to clear
Click “Everything” from the drop-down menu at the top of the screen, then check all the boxes. This will delete your entire browsing history, and not the sites you've recently visited.
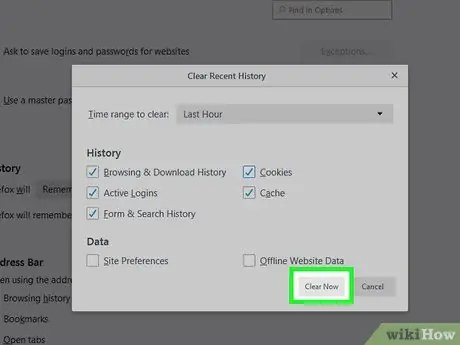
Step 11. Click Clear Now
The browsing history has now been cleared.
Method 6 of 8: Blocking Trackers and Third Party Cookies
Step 1. Open Firefox on your PC or Mac computer
You can find this browser in the “ All Apps ” in Windows “Start” menu, or folder “ Applications ” on MacOS.
Tools that also track you when you browse the web can slow down your browser or browsing performance. This method will teach you how to block these trackers so as to improve your browser speed or performance, as well as your security on the internet
Step 2. Click the menu button
It's in the upper-right corner of the screen.
Step 3. Click Options
It's in the middle of the menu.
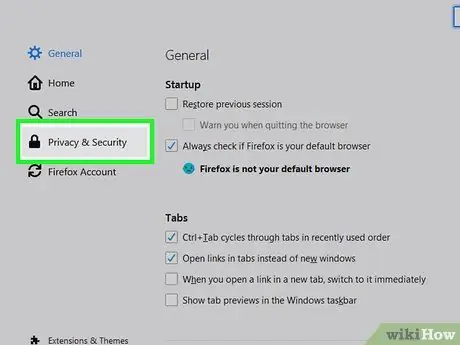
Step 4. Click Privacy & Security
This option is in the left pane. The Content Blocking segment will be displayed at the top of the right pane.
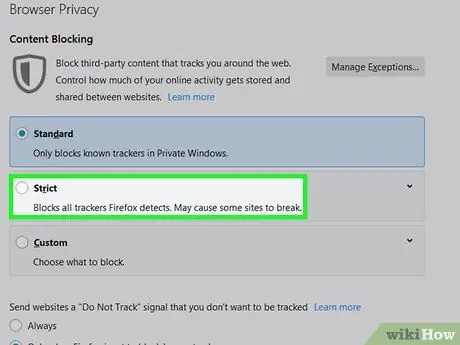
Step 5. Check the box next to All Detected Trackers
You can also choose whether you want to block all trackers on all browser windows (“Always”), or when browsing in private windows.
While you can almost always see an increase in speed, some websites and tools may not load. You can always re-access the page and enable tracking temporarily if you experience such problems
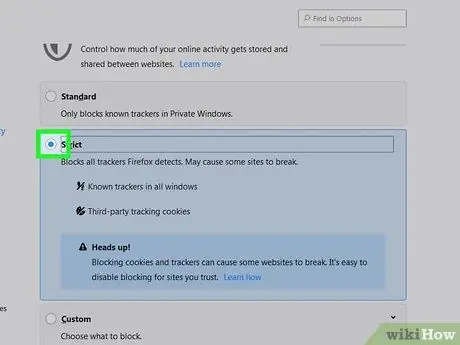
Step 6. Check the box next to Third-Party Cookies and select Trackers
With this option, third-party cookies will not “follow” you while you are browsing the web.
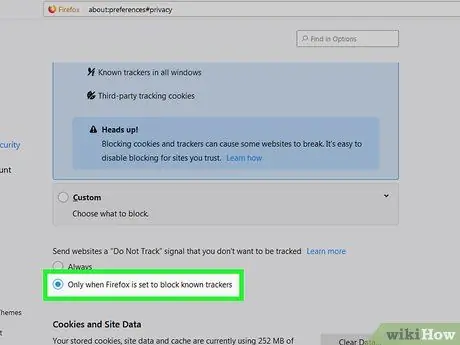
Step 7. Select the option under Send websites a ‘Do Not Track’ signal”
This option is at the bottom of the segment. The best option you can choose in this segment is “ Only when Firefox is set to block Detected Trackers ”.
This means that as long as you enable the option in step five (″ All Detected Trackers), you will not be tracked by any website. However, if you need to turn off the feature when you want to solve a problem, this feature will be turned off automatically
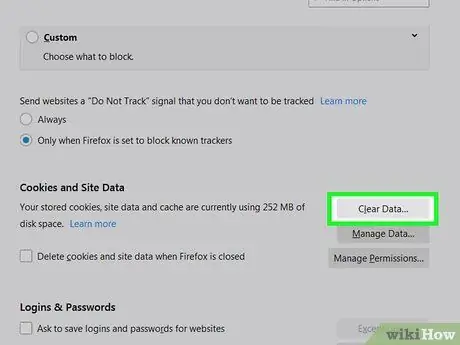
Step 8. Clear cookies and cache
After updating your settings, it's time to clear the content you've accumulated so far. Read this method to learn how.
Method 7 of 8: Disabling Hardware Acceleration
Step 1. Open Firefox on your PC or Mac computer
You can find this browser in the “ All Apps ” in Windows “Start” menu, or folder “ Applications ” on MacOS.
If your text, photos, videos, and games appear to be fragmented or corrupted, try this method
Step 2. Click the menu button
It's in the upper-right corner of the browser window.
Step 3. Click Options
It's in the middle of the menu.
Step 4. Click General
This option is in the left pane.
Step 5. Scroll to the Performance segment
This segment is at the bottom of the page.
Step 6. Uncheck the “Use recommended performance settings” box
Additional options will be displayed afterwards.
If the box is not checked, move on to the next step
Step 7. Uncheck the box next to Use hardware acceleration when available
This feature will be turned off, but you will still need to restart your browser.
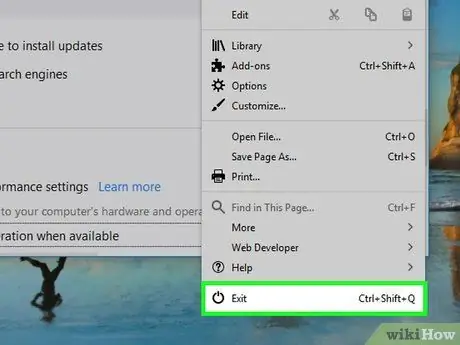
Step 8. Click the menu button and select exit.
This option is at the bottom of the menu.
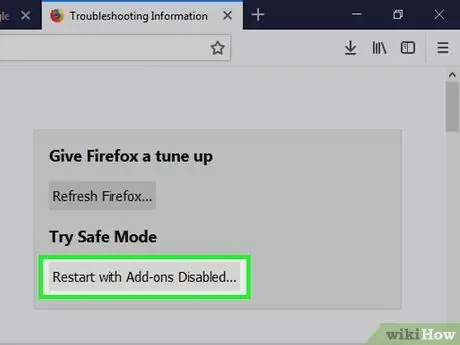
Step 9. Restart Firefox
Now, Firefox will run without hardware acceleration so it can speed up your browsing experience/performance.
Method 8 of 8: Solving JavaScript Problems
Step 1. Open Firefox on your PC or Mac computer
You can find this browser in the “ All Apps ” in Windows “Start” menu, or folder “ Applications ” on MacOS.
- If a website running JavaScript does not show a response in the browser or displays the error Warning: Unresponsive Script, this method is a good choice. You can change a Firefox setting that determines the duration of script execution before displaying a pop-up window that allows you to disable scripts.
- To give the script more time before displaying the error message, you can increase the duration to 20 seconds. Sometimes, larger and heavier scripts take more time to execute in certain “environments” or situations.
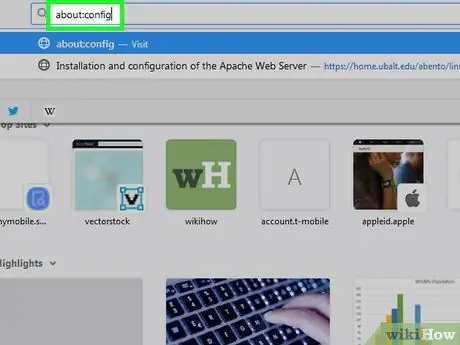
Step 2. Type about:config into the address bar and press Enter or Returns.
A warning message will be displayed informing you that the warranty may be void if you continue to the next step.
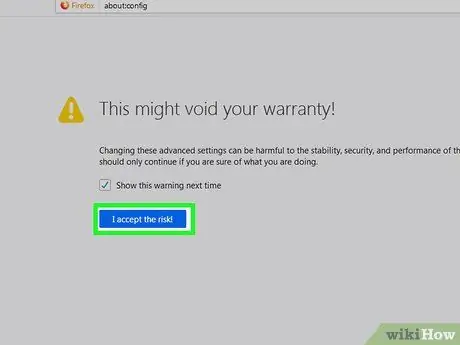
Step 3. Click I accept the risk
A list of preferences will be displayed.
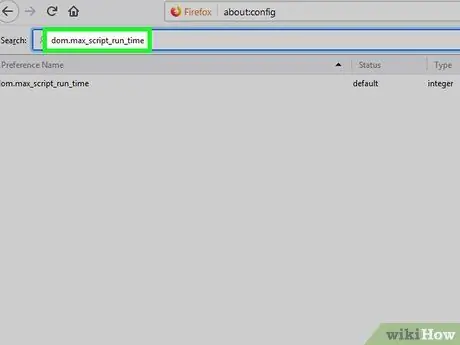
Step 4. Type dom.max_script_run_time into the Search bar
This bar is at the top of the preference list. When finished typing the entry, one search result will be displayed.
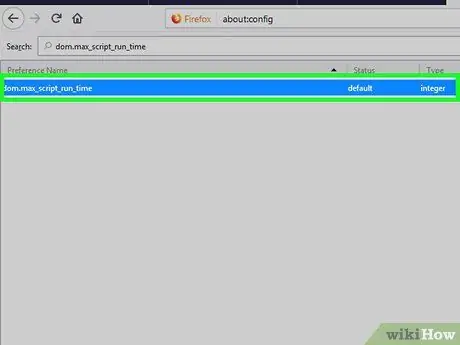
Step 5. Click dom.max_script_run_time
A pop-up window will load asking you to enter a value/number.
The default value or number displayed (typically 10 seconds, but may vary depending on Firefox version) indicates that the script has that length of time to run before displaying the error message
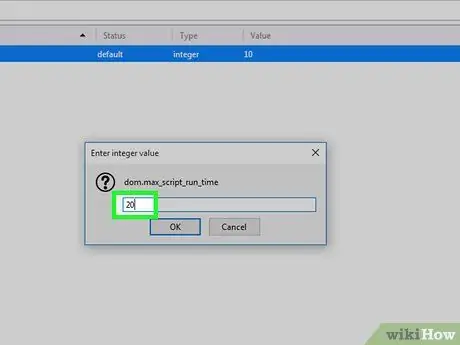
Step 6. Enter 20 as a number and click OK
After making those changes, the script will have 20 seconds to run before displaying an error message giving you the opportunity to terminate the script.






