- Author Jason Gerald gerald@how-what-advice.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 10:50.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 12:04.
A rectangle is a quadrilateral where two sides are the same length, the other two sides are the same width, and contain four right angles. To find the area of a rectangle we simply multiply the length by the width. To know how to find the area of a rectangle, follow these easy steps.
Step
Method 1 of 3: Understanding Rectangle Basics
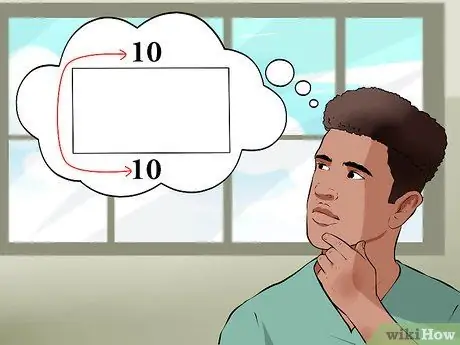
Step 1. Understand a rectangle
A rectangle is a quadrilateral, which means it has four sides. The opposite sides are the same in length and width. If one side of the rectangle is 10 for example, then the length of the opposite side is also 10.
Every square is a rectangle, but not all rectangles are squares. So treat a square like a rectangle in terms of finding the area
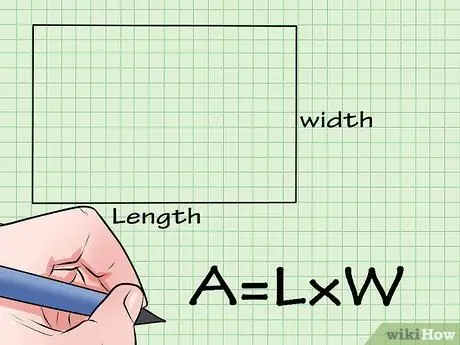
Step 2. Know the formula for finding the area of a rectangle
The formula for finding the area of a rectangle is A = L * W. This means that the area of the rectangle is equal to the length times the width.
Method 2 of 3: Finding the Area of a Rectangle
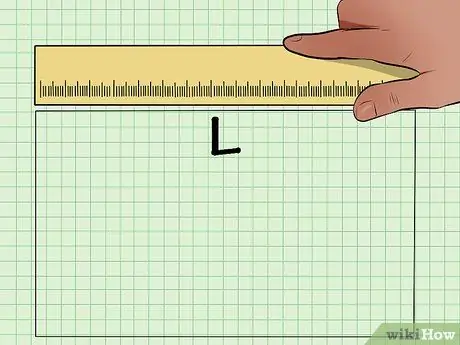
Step 1. Find the length of the rectangle
Most questions will give you length, but if you don't know the length, just use a ruler.
Note that a double hash on the long side of a rectangle means that both sides are the same length
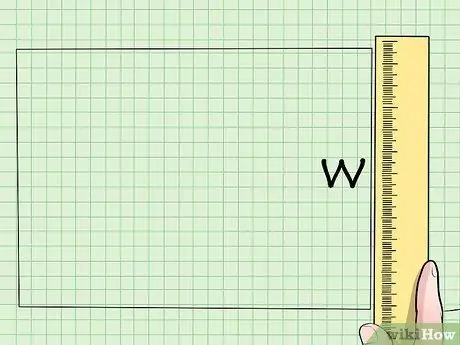
Step 2. Find the width of the rectangle
Use the same method to find it.
Note that a single hash on the wide side of a rectangle means that both sides are the same width
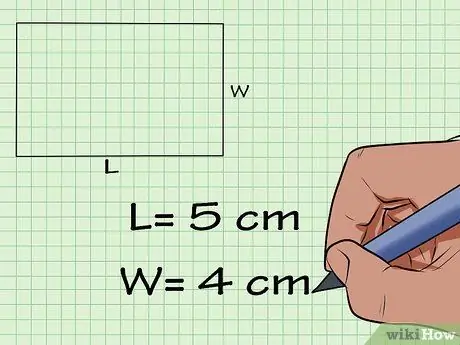
Step 3. Write the length and width side by side
In this example, the length is 5 cm and the width is 4 cm.

Step 4. Multiply the length times the width
The length is 5 cm and the width is 4 cm, plug it into the Formula A = L * W to find the area.
- A = 4cm * 5cm
- A = 20 cm^2
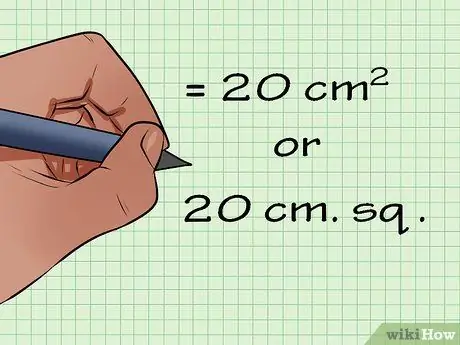
Step 5. Express the answer in square units
The final answer is 20 cm^2, which reads "twenty centimeters squared."
The final answer can be written in two ways: 20 cm.sq. or 20 cm^2
Method 3 of 3: Finding the Area if the Lengths of One Side and the Diagonal are Known
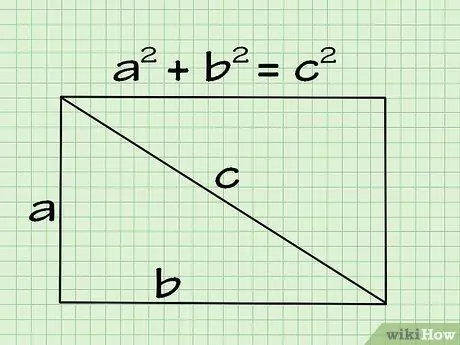
Step 1. Understand the Pythagorean Theorem
The Pythagorean theorem is a formula for finding the third side of a right triangle if the values of the two sides are known. We can use this formula to find the hypotenuse of a triangle which is the longest side, or the length or width that meets at a right angle.
- Since a rectangle is made up of four right angles, a diagonal that cuts through the shape will form a right triangle, so we can use the Pythagorean theorem.
- The formula is: a^2 + b^2 = c^2, a and b are the sides of the triangle and c is the hypotenuse or longest side.
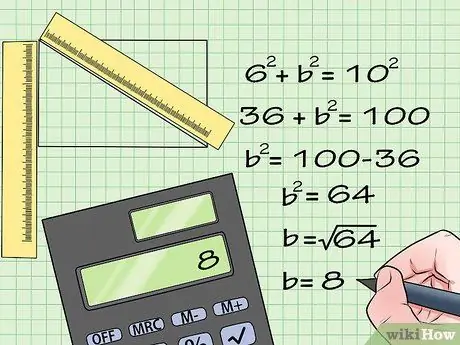
Step 2. Use the Pythagorean theorem to calculate the other sides of a triangle
Let's say a rectangle has a side of 6 cm and a diagonal of 10 cm. Enter 6 cm for one side, use b for the other side, and enter 10 cm as the hypotenuse. Now simply plug the known quantities into the Pythagorean theorem. Here's how:
-
Ex:
6^2 + b^2 = 10^2
- 36 + b^2 = 100
- b^2 = 100 - 36
- b^2 = 64
- square root (b) = square root (64)
-
b = 8
The length of the other side of the triangle, which is also the other side of the rectangle, is 8 cm
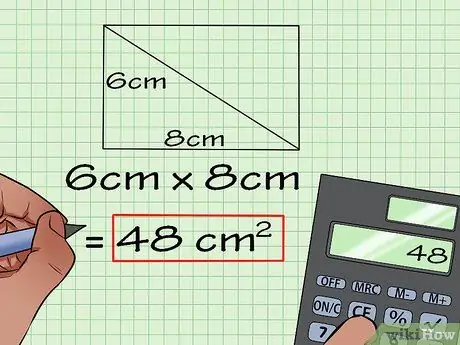
Step 3. Multiply the length times the width
After using the Pythagorean theorem to find the length and width of a rectangle, all you have to do is multiply it.
-
Ex:
6cm * 8cm = 48cm^2

Step 4. Express the answer in square units
The final answer is 48 cm^2, or 48 cm. sq.
Tips
- All squares are rectangles. However, not all rectangles are squares.
- The answer to area is always expressed in terms of a square.






