- Author Jason Gerald gerald@how-what-advice.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 10:50.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 12:04.
CPU overclock is the process of increasing the clock speed (clock: the level / speed of the processor in processing data) CPU. Overclocking was once only done by computer experts, but hardware manufacturers have continued to make this process easier over the years. Overclocking can significantly improve computer performance, but it can also risk damaging hardware if done incorrectly. To maximize computer performance, you should overclock the CPU. You first increase the CPU clock speed little by little, then test the stability of the computer and make sure that the CPU temperature doesn't get too high every time the clock speed increases, and finally stop when the computer becomes unstable or the CPU overheats. If the CPU gets too hot, you have to lower the clock speed to allow the CPU to run at the right temperature and then stop there. If the CPU is not overheating but the computer is becoming unstable, you can increase the amount of power given to the CPU to keep it running at that clock speed. Or, you can lower the clock speed to a stable speed last time. If you decide to continue overclocking the CPU by adding more power, make sure that the temperature doesn't rise. This is because increasing the amount of power to the CPU is the same as increasing the amount of heat it generates. Giving the CPU too much power or running it at unhealthy temperatures in the long run can be damaging. To learn how to overclock the CPU, scroll down to Step 1.
Step
Part 1 of 5: Making Preparations
Step 1. Understand the basics of overclocking
Overclocking is the process of increasing the clock speed and voltage of the CPU to increase its performance. This method is suitable for maximizing a powerful machine, or forcing an old computer to be more powerful.
- Overclocking can damage components, especially if the hardware used isn't designed for it, or you raise the voltage too high. Only overclock if you understand the risk that your hardware could be damaged.
- No two systems will overclock the same, even if they have exactly the same hardware. This is because the overclock is strongly influenced by small variations in the manufacturing process. Don't assume that the results you read on the internet will be the same if applied to your hardware.
- If your main goal is to improve video game performance, it's a good idea to overclock your graphics card as the results tend to look better.
- Laptops are not very good at overclocking due to their limited cooling capabilities. On the other hand, performance on desktop computers will improve much more in those where the temperature can be better controlled.

Step 2. Download the necessary tools
You will need some benchmarking and stress test tools to test your overclock results. These programs test the processor's performance as well as its ability to maintain performance over time.
- CPU-Z - This is a simple monitor program that will quickly display the clock speed and voltage in Windows. There's nothing to do with this easy-to-use program other than just monitoring the CPU to help make sure everything is working properly.
- Prime95 - This is a free benchmarking program widely used for stress testing. This program is designed to run for a long time.
- LinX - This is another stress test program. This one is lighter than Prime95 and is suitable for testing between changes.
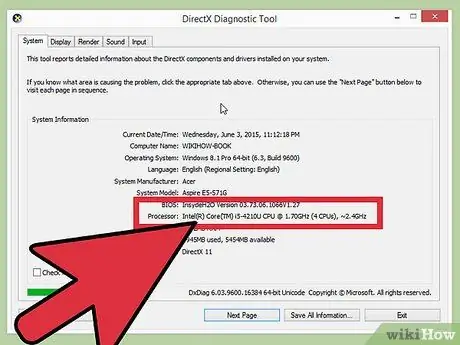
Step 3. Check the motherboard and processor
Each motherboard and processor has different capabilities when it comes to overclocking. AMD vs Intel overclocks are also slightly different, but the general process is the same. The main thing to look for is whether the existing multiplier is locked or not. If it's locked, you'll only be able to adjust the clock speed, which usually results in less.
- Many motherboards are designed for overclock action, which means they will give full access to overclock control. Consult your computer's documentation to determine the capabilities of the motherboard.
- Some processors are more likely to be overclockable than others. For example, the "K" product from Intel i7 is specifically designed to be overclocked (eg Intel i7-2700K). You can find the processor model by pressing Win+Pause and looking for it in the System section.
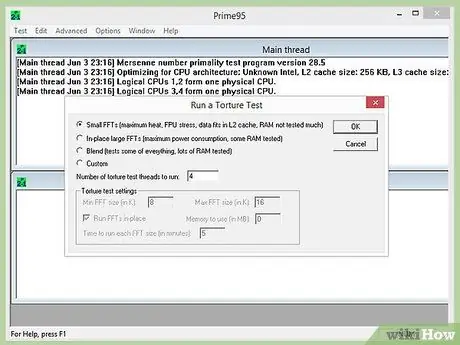
Step 4. Run an initial stress test
Before starting the overclock, run a stress test using the basic settings. This will provide a baseline against which to compare when you start overclocking, which will also indicate if there are any problems with the basic settings that need to be resolved before they get worse with the overclock.
- Be sure to check the temperature level during the stress test. If the CPU temperature is above 70 degrees Celsius, the overclock results may not be very significant when the CPU temperature becomes unsafe. You may need to apply thermal paste or install a new heatsink.
- If your system crashed during the initial stress test period, it's likely that your hardware had a problem and should be resolved before starting the overclock. Check the memory to check for errors on the computer.
Part 2 of 5: Increasing Base Clock

Step 1. Open the BIOS
You will make most changes to your computer's BIOS, which is a configuration menu that you can open before the operating system loads. You can open most BIOSes by pressing and holding the Del key while the computer is starting up. Other keys that may be used include F10, F2, and F12.
Each BIOS is different, therefore the labels and menu locations may also vary for each system. Don't be afraid to browse through the menu system to find what you need
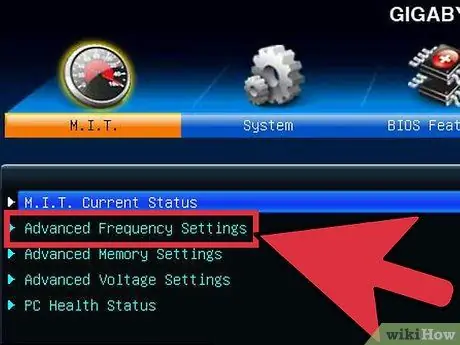
Step 2. Open "Frequency/Voltage Control"
This menu can be labeled differently, for example "Overclocking". You will spend most of your time in this menu setting the speed as well as the voltage received by the CPU.
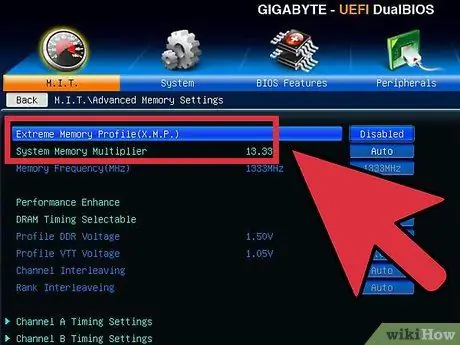
Step 3. Reduce memory bus speed
To help prevent memory from making errors, lower the memory bus before continuing. It can be referred to as "Memory Multiplier", "DDR Memory Frequency" or "Memory Ratio". Lower it to the lowest possible setting.
If you can't find the memory frequency selection, press Ctrl+Alt+F1 in the main BIOS menu
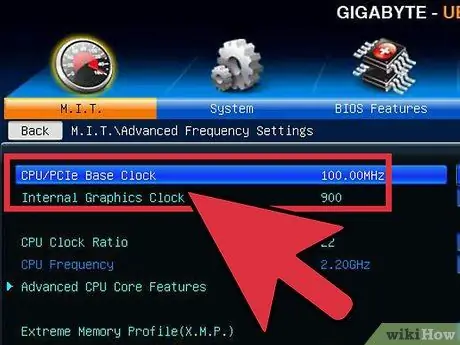
Step 4. Increase the base clock by 10%
The base clock, also known as the front side bus or bus speed, is the base speed of the processor. Usually these lower speeds are multiplied to reach the total core speed. Most processors can handle a quick 10% spike at the start of a run. For example, if the base clock is 100 MHz, and the multiplier is 16, the clock speed will be 1.6 GHz. Increasing it 10% will change the base clock to 110 MHz and the clock speed to 1.76 GHz.
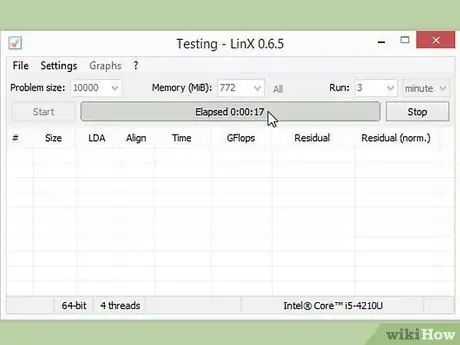
Step 5. Run a stress test
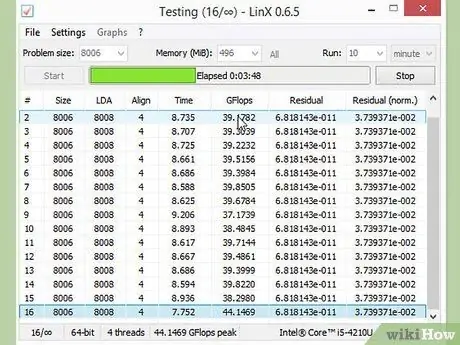
After you have made the initial 10% increase, restart the computer and enter the operating system. Run LinX and run a few cycles. If there are no problems, you are ready to move on. If the system becomes unstable, you may not be able to get significant performance from overclocking, and you will need to reset the settings to default.
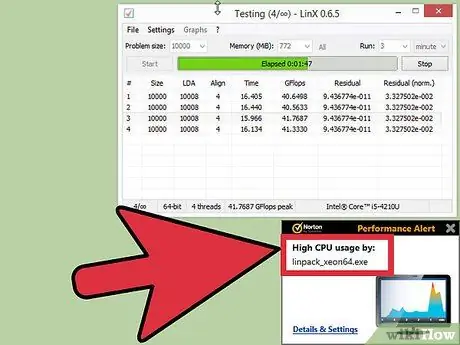
Step 6. Increase the base clock until the system becomes unstable
Instead of increasing it every 10%, reduce the increment by about 5-10 MHz per stage. This method is more effective. Run the comparison program each time you make adjustments until things become unstable. This instability is most likely caused by the processor not receiving enough power from the power supply.
If the motherboard doesn't allow you to adjust the multiplier, you can skip to Section 4. If you can adjust the multiplier, then read on to the next section to try to get more profit. Make sure you take note of your current settings, just in case you want to come back later
Part 3 of 5: Raising the Multiplier
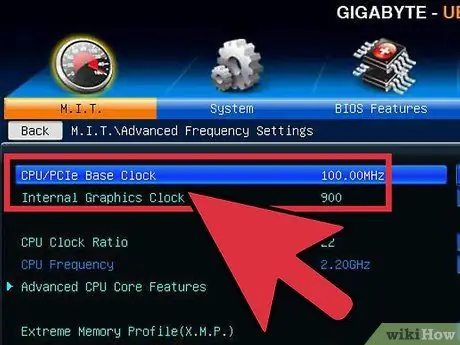
Step 1. Lower the base clock
Before you start raising the multiplier, lower your base clock a little. This will help make a more precise increment of the multiplier. With a lower base clock and a higher multiplier, a more stable system, but a higher base clock with a lower multiplier will make the performance better. For that look for the ideal balance.
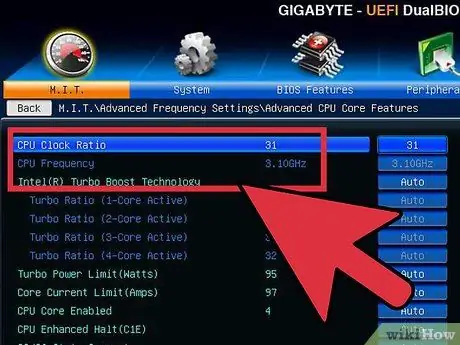
Step 2. Increase the multiplier
Once you start lowering the base clock little by little, start increasing the multiplier incrementally by 0.5. The multiplier can be called "CPU Ratio" or something similar. The initial setting might be "Auto" instead of a number.
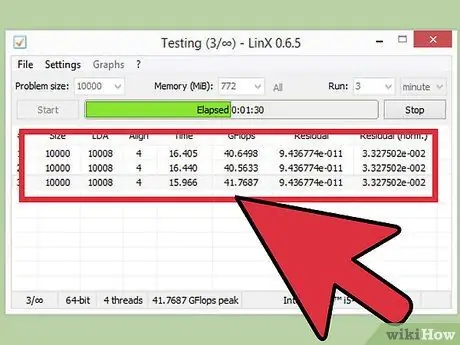
Step 3. Run a stress test
Restart the computer and run the comparison program. If the computer doesn't find any errors after running the comparator a few times, you can increase the multiplier again. Repeat this process each time you increase the multiplier by that difference again.
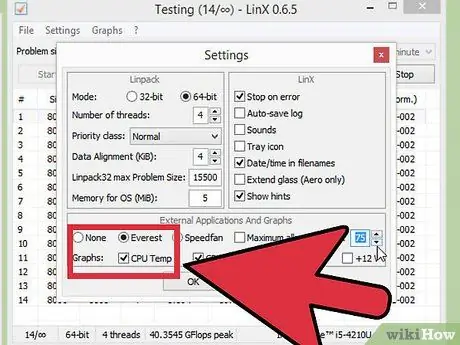
Step 4. Monitor CPU temperature
Make sure you pay attention to the CPU temperature during this process. You may reach the temperature limit before the system becomes unstable. If this is the case, the overclock limit may have been reached. At this point, you should find the best balance between increasing the base clock and increasing the multiplier.
Although each CPU has a different safe temperature range, the general rule is that the CPU should not reach 85 degrees Celsius
Step 5. Repeat until the limit is reached and the computer stops
You should now have a setting that almost caused the computer to become unstable. As long as the CPU temperature is still within safe limits, you can start adjusting the voltage level for further increases.
Part 4 of 5: Increasing the Voltage
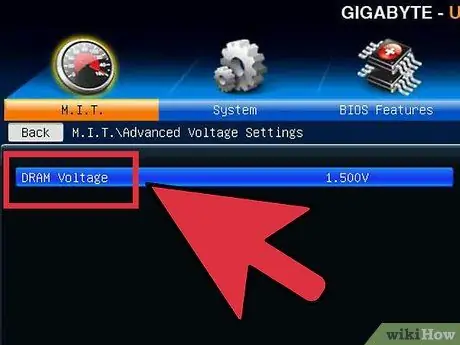
Step 1. Increase CPU core voltage
This can be referred to as "Vcore Voltage". Raising the voltage beyond a safe limit can quickly damage equipment, so this is the most sensitive and potentially damaging part of the overclocking process. Each CPU and motherboard can handle different voltage spikes, so pay extra attention to temperature.
When increasing the core voltage, increase it in increments of 0.025. More than this number, you run the risk of going too high and damaging the components
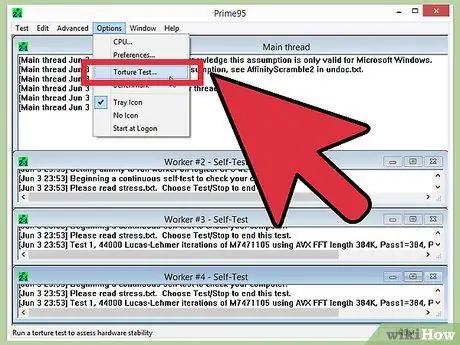
Step 2. Run a stress test
After the first hike, run a stress test. Since your system was in an unstable state in the previous section, target a stable stress test. If the system is stable, make sure the temperature is still at an acceptable level. If the system is still unstable, try lowering the multiplier or base clock speed.
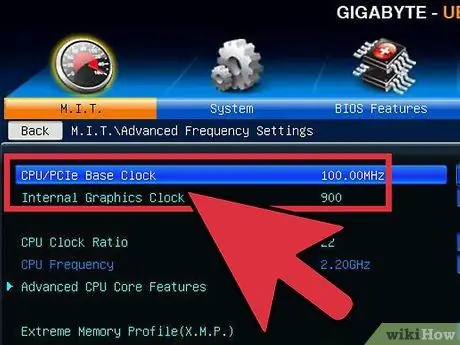
Step 3. Return to the base clock section or the multiplier section
Once you've managed to stabilize the system through voltage boosts, you can either increase the base clock or the multiplier again, depending on what you're trying to overclock. Raise it little by little, run stress test until the system becomes unstable again.
Since the voltage setting raises the temperature the most, aim to maximize the base clock and multiplier settings so as to get maximum performance from the lowest possible voltage. This all takes a lot of trial and error as you will be trying different combinations
Step 4. Repeat this cycle until the maximum voltage or maximum temperature is reached
Eventually you will reach a point of not raising any higher, or the temperature approaching an unsafe level. This is the limit of the motherboard and processor, and there is a possibility you can only get here can no longer continue to be able to advance past this point.
- In general, you should not increase the voltage more than 0.4 times above the original level, or 0.2 if you are using a basic cooling system.
- If you reach the temperature limit before reaching the voltage limit, you may be able to further improve CPU performance by improving the cooling system in your computer. You can install a more powerful heatsink/fan combo or opt for a more expensive but much more effective liquid cooling solution.
Part 5 of 5: Final Stress Test
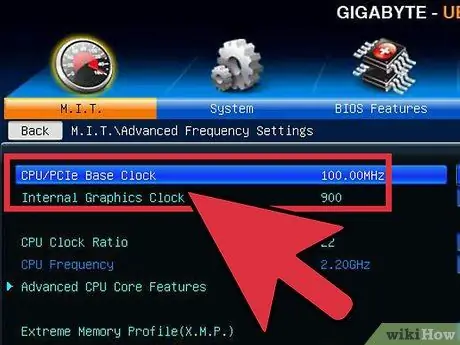
Step 1. Restore to the last safe settings
Lower the base clock or multiplier to the setting that last worked. This is the speed of your new processor, and if you're lucky your computer will be noticeably faster than before. As long as the computer is fine at startup, you are ready for final testing.
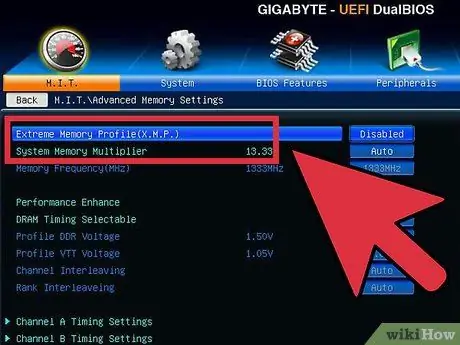
Step 2. Increase memory speed
Increase memory speed back to initial level. Take this stress test slowly. You may not be able to raise everything to its original level.
Use Memtest86 to perform a memory test when raising the frequency back up
Step 3. Run a prolonged stress test
Open Prime95 and run the test for 12 hours. This sounds long, but your goal is to ensure stability over the long term. This will result in better and more reliable performance. If during the test the system becomes unstable, or the temperature reaches an unacceptable level, go back and readjust the clock speed, multiplier, and voltage.
- When you open Prime95, select "Just Stress Testing". Click Options → Torture Test and set it to "Small FFT".
- Temperature limits are usually good because Prime95 pushes your computer higher than most programs. You can also lower the overclock a little to be safe. The idle temperature should not exceed 60 degrees Celsius.
Step 4. Do some real testing
A stress test program is great for making sure the system is stable, but you have to make sure in real situations. If you are a gamer, play the most intensive games. If you encode videos, try Bluray encoding. Make sure that everything is working as it should. Everything should be going better now!
Step 5. Read further
This guide is just an introduction to the topic of overclocking. To learn more, the key is research and experimentation. There are several communities dedicated to overclocking and various other related fields, such as cooling. Some of the most popular communities, such as Overclockers.com, Overclock.net, and Tom's Hardware, are good places to find more information.
Warning
- Overclocking by increasing the voltage will shorten the life of the hardware.
- You need a good cooling system for a serious overclock.
- Overclocking may void your computer's warranty, depending on the manufacturer. Some brands like EVGA and BFG will still honor the warranty even after the device has been overclocked.
- Most computers made by Dell (except XPS products), HP, Gateway, Acer, Apple, etc., cannot be overclocked because the option to change the FSB and CPU voltage is not available in the BIOS.
Resources and Reference
- https://www.pcstats.com/articleview.cfm?articleid=1804&page=6
- https://www.overclockers.com/3-step-guide-overclock-core-i3-i5-i7/
- https://lifehacker.com/a-beginners-introduction-to-overclocking-your-intel-pr-5580998/all
-
https://www.techradar.com/us/news/computing-components/processors/beginner-s-guide-to-overclocking-1040234/2#articleContent






