- Author Jason Gerald gerald@how-what-advice.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 10:50.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 12:04.
Subversion (sometimes called SVN) is an open source system that remembers every change you make to files and directories. This system is useful when you want to track changes in a document over time or restore an older version of a file. Start with the first step for detailed instructions on installing Subversion on Mac OS X.
Step
Part 1 of 2: Installing the System from a Binary Package
Step 1. Visit
On that page, you'll find a number of downloadable binaries, each with varying requirements. Choose the binary that best suits your needs.
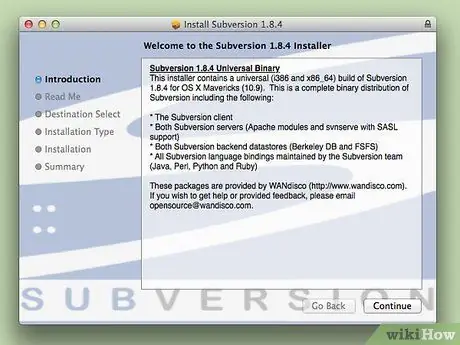
Step 2. Extract the
downloaded pkg. The Subversion installation file will be created on the desktop afterwards. Double-click the file and follow the installation steps as directed.
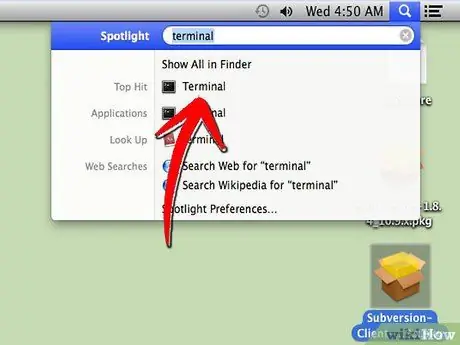
Step 3. Open Terminal which is in the “Utilities” folder
Alternatively, search for Terminal via Spotlight. Enter the following entry in the [username]$ command:
-
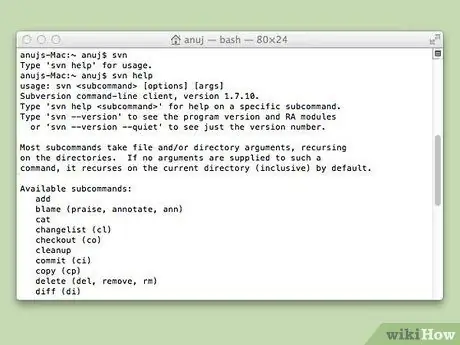
svn [enter]

Install Subversion on Mac OS X Step 3Bullet1 -
If the command returns the response " Type 'svn help' for usage ", Subversion is working fine.

Install Subversion on Mac OS X Step 3Bullet2 -
If /usr/local/bin is not available in the directory, edit the.profile file and add the following line:

Install Subversion on Mac OS X Step 3Bullet3 export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/bin
-
Open a new Terminal window and try to enter the following command: svn [enter]

Install Subversion on Mac OS X Step 3Bullet4
Part 2 of 2: Setting Up the Subversion Environment
Step 1. Set up the SVN server
You need this server to distribute Subversion projects.
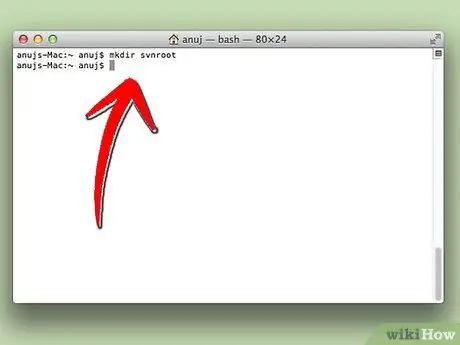
Step 2. Launch Terminal and create a directory named “svnroot” in the account directory like this:
mkdir svnroot
-
Type: svnadmin create /Users/[your username]/svnroot

Install Subversion on Mac OS X Step 5Bullet1 -
Server has been created successfully!

Install Subversion on Mac OS X Step 5Bullet2
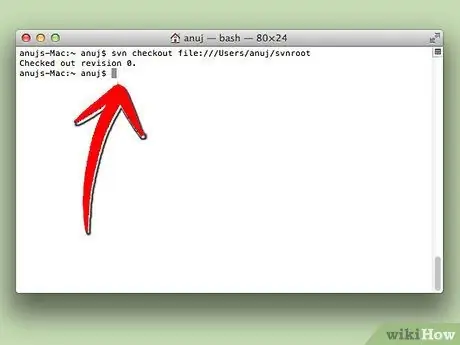
Step 3. Use SVN server with Terminal
You can check it via Terminal with the following command: svn checkout file:///Users/[your username]/svnroot
-
For remote access, enable " ssh access " (in System Preferences/Sharing) and check using the following command: svn checkout svn+ssh://my.domain.com/Users/[your username]/svnroot

Install Subversion on Mac OS X Step 6Bullet1

Step 4. Set up the Subversion manager program
For example, svnX supports all versions of Mac OS X from 10.5 to 10.8. You can get it at
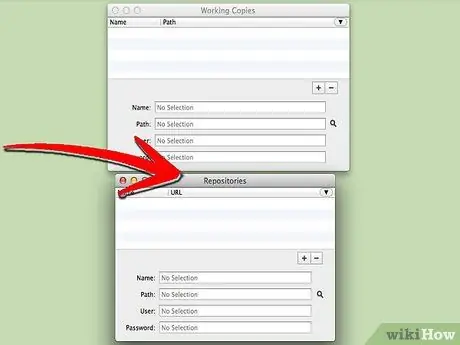
Step 5. Run SVNx after downloading, then see two windows named “Working Copies " and " Repositories".
Under “Repositories”, add the URL and login data from the SVN server.
-
Open the window. If you get an error message, check your logon.

Install Subversion on Mac OS X Step 8Bullet1 -
Switch to Terminal and type: svn import -m "your import messages" /my/local/project/path /my/remote/svn/repository. This command adds all the files from the local project to the SVN server.

Install Subversion on Mac OS X Step 8Bullet2 -
Add the SVN repository directory (from the SVN server) to the list in the “Working Copy” window of SVNx.

Install Subversion on Mac OS X Step 8Bullet3
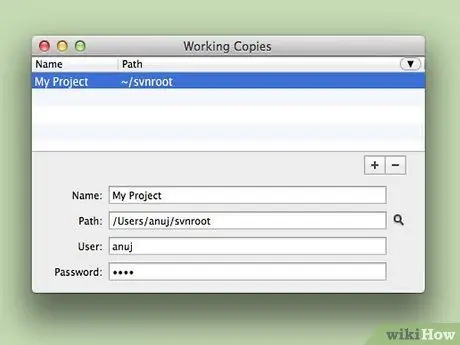
Step 6. In SVNx, open a working copy of the file/document
While working on this project, you can see the modifications in the SVNx window.
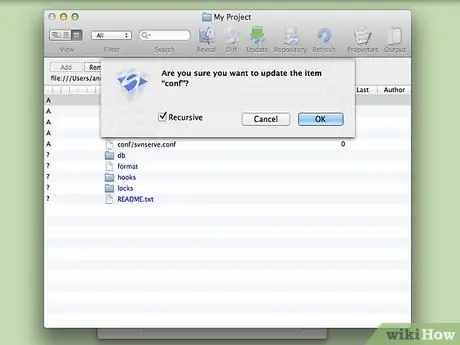
Step 7. Test the document
Make minor modifications to the copy of the file/document, then update the document in the “Working Copy” window.
SVNx displays all files with modifications. Hit the “Commit” button to add it to the SVN server repository
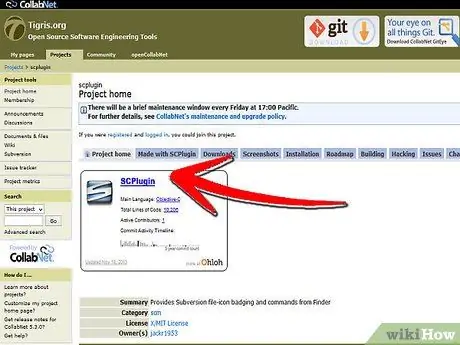
Step 8. If you want to work on documents/files in the Subversion repository directly from the Finder, it's a good idea to use SCPlugin or SVN Scripts for Finder
Tips
- Some additional documentation is available under the “doc/” subdirectory of Subversion resources. Read the file “doc/README” for more information.
- Subversion's main documentation is a free book called Version Control with Subversion or The Subversion Book. You can get it from






