- Author Jason Gerald gerald@how-what-advice.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 10:50.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 12:04.
Taking screenshots on Linux is not as easy as on Windows or OS X, because Linux doesn't include a universal screenshot capture program. The installation of the screenshot usually depends on the distribution. Fortunately, most distributions include one program that is usually installed to take screenshots. If you don't have the program, you can still download similar programs from the internet.
Step
Method 1 of 4: Using Gnome Screen Capture
The PrtScn key does not work as a shortcut on all Linux distributions, but it can be used to capture screens in most GNOME desktop environments such as Ubuntu and Linux Mint. If this part doesn't work, try one of the methods below.
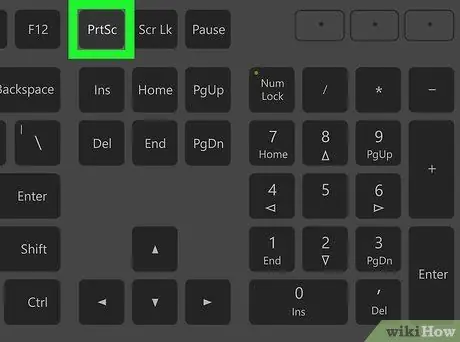
Step 1. Press
PrtScn to take a full screenshot.
The screenshot will show the entire screen view. You will be asked to choose where to save the screenshot file.
The Print Screen key is at the top of the keyboard, usually between F12 and ScrLk. The button usually says "Print Screen," "PrtScn," "PrntScrn," and the like
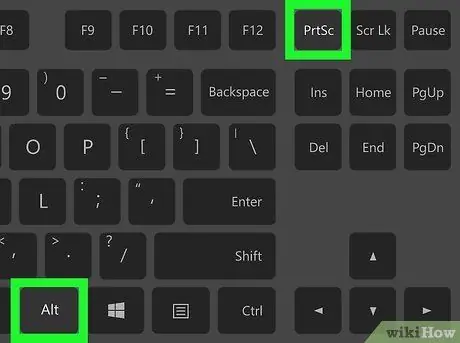
Step 2. Press
Alt+PrtScn to take a screenshot of a window.
This shortcut will create a screenshot of the active window. A file will be created in your pictures folder.
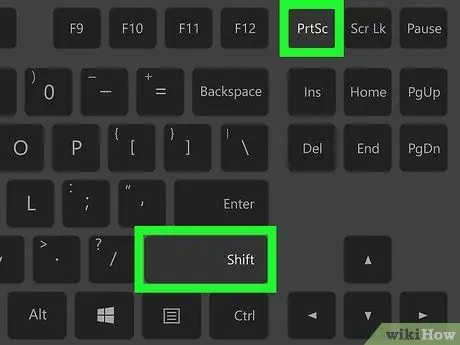
Step 3. Press
Shift+PrtScn to select the object you captured.
You can click and drag the selection box to specify what object to capture. The screenshot file will then load in your images folder.
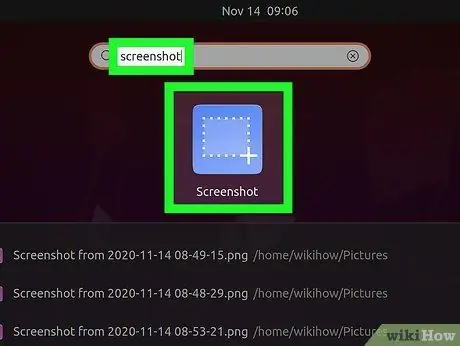
Step 4. Open the Screenshot utility
The Gnome screenshot utility allows you to perform some additional screen capture functions such as pause. You can find the Screenshot utility in the Accessories directory in your application menu.
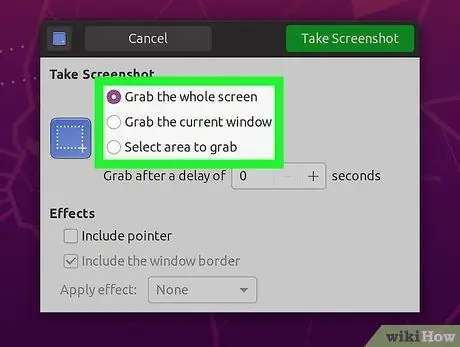
Step 5. Choose a screenshot type
You can choose from the various options mentioned above.
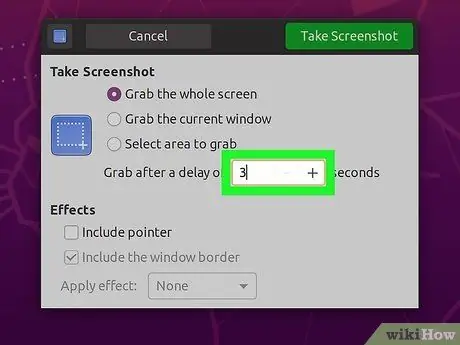
Step 6. Add a pause
If your screenshot is time dependent, you can use the Screenshot utility to add a pause before the screenshot is taken. This allows you to make sure the content you choose is correct.
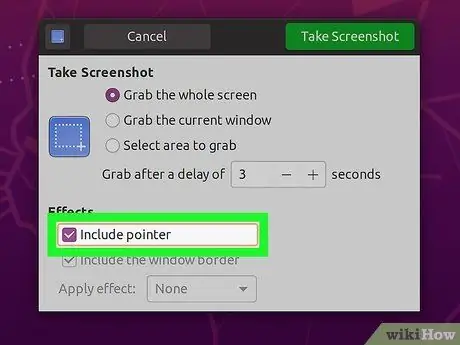
Step 7. Choose an effect
You can choose to include the mouse pointer in the screenshot. You can also add or remove lines around the screenshot.
Method 2 of 4: Using GIMP
Step 1. Install GIMP
GIMP is a free image editing program that is installed on several Linux distributions. If you haven't already installed it, you can get it for free at the Software Center. Open Software Center, search for "gimp", then install "GIMP Image Editor".
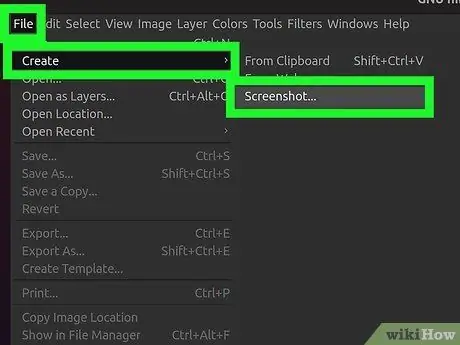
Step 2. Click the "File" menu and select "Create" → "Screenshot"
The screenshot creation tool, which is similar to the Gnome Screenshot utility, will open.
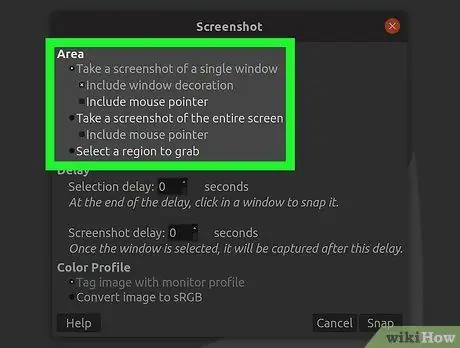
Step 3. Select the type of screenshot you want to use
You can choose three types of screenshots: single window, full screen, set selection. If you select the single window option, you will be able to click on the window you want to take a screenshot of.
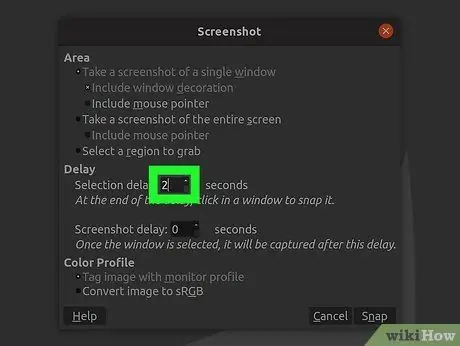
Step 4. Add a pause
You can add a pause before the screenshot is taken so you can set things up exactly the way you want. If you have selected a single window type or a set option, you will need to select your screenshot target after the lag time has elapsed.
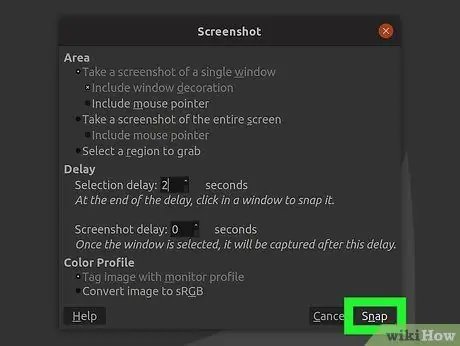
Step 5. Click "Snap" to take a screenshot
Depending on your settings, screenshots can be taken immediately. When you are done, the screenshot will appear in the GIMP editing window.
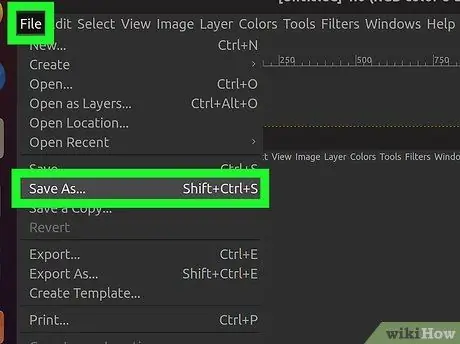
Step 6. Save the screenshot
If you don't want to edit the screenshot, you can save it on your hard disk. Click the "File" menu and select "Export". Name your screenshot and choose where you want to save it. Click the "Export" button when finished.
Method 3 of 4: Using ImageMagick
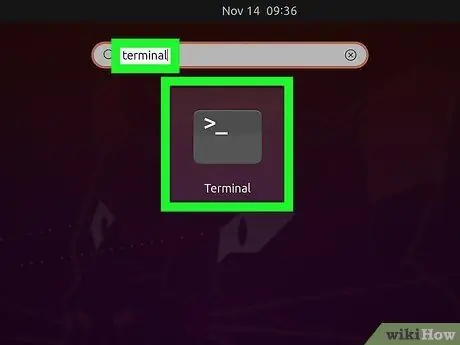
Step 1. Open Terminal
ImageMagick is a command line based utility that can take screenshots for you. Most Linux distributions have ImageMagick installed. However, if you don't have it you can download it for free.
To quickly open Terminal on Ubuntu and other distributions, press Ctrl+Alt+T
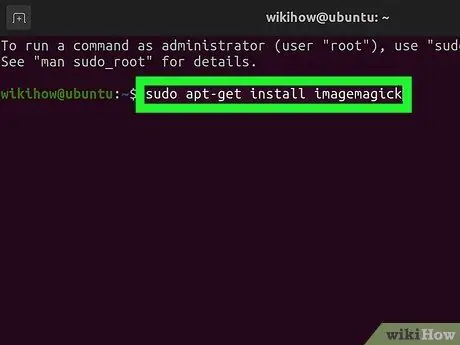
Step 2. Install ImageMagick
Type in sudo apt-get install imagemagick and press Enter. You will be asked for an administrator password. If ImageMagick is not already installed, the download and installation process will begin. If it is installed you will be notified.
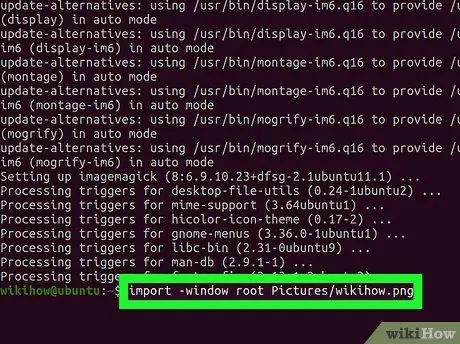
Step 3. Take a full screenshot
Type import -window root Pictures/fileName-p.webp
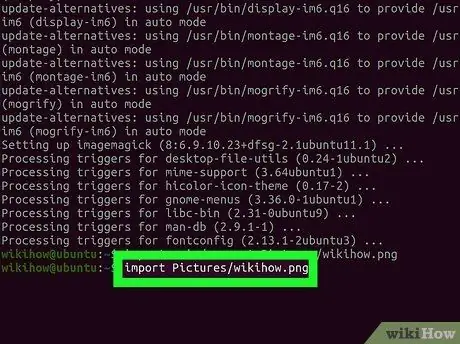
Step 4. Take a screenshot of a specific window
Type import Pictures/fileName-p.webp
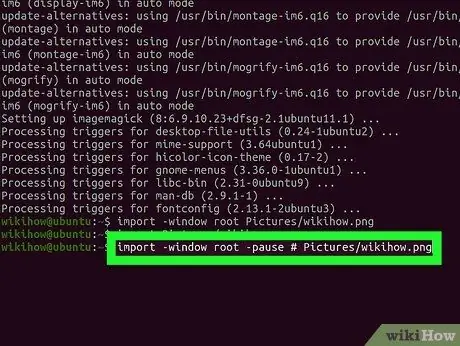
Step 5. Add a pause
Type import -window root -pause # Pictures/fileName-p.webp
Method 4 of 4: Using Shutter
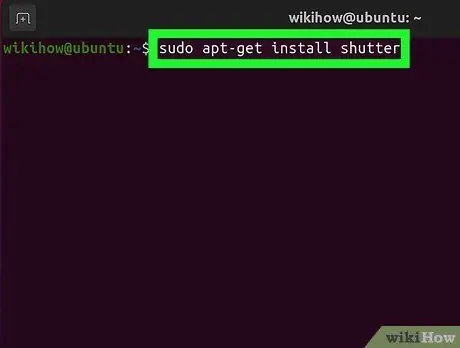
Step 1. Install Shutter
Shutter is a popular screen capture program that has excellent uploading and editing capabilities. If you often take and share screenshots, this program is worth a try.
- You can find Shutter through most distribution package managers. You just need to search for "Shutter" then install the program.
- To install Shutter from Terminal, type sudo add-apt-repository ppa:shutter/ppa and press Enter. Update your repository by typing sudo apt-get update, and install Shutter by typing sudo apt-get install shutter.
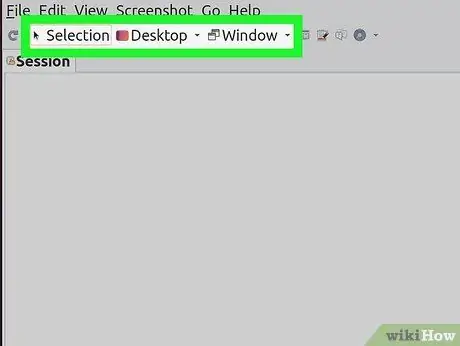
Step 2. Select the type of screenshot you want
At the top of the Shutter window, you'll see three options for you to choose from: "Selection", "Desktop" and "Window". Click the button to select the type of screenshot you want.
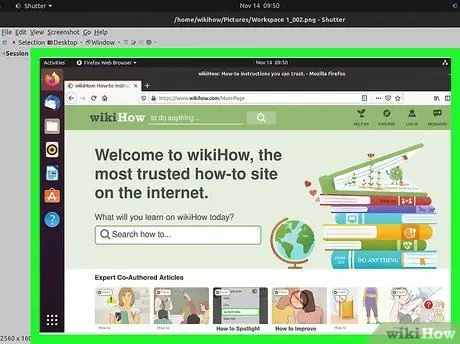
Step 3. Take a screenshot
If you select "Desktop", a screenshot will be taken automatically. If you select "Selection", the screen will dim and you can click and drag to create a selection box. Everything in the box will be pictured. If you select "Window", you can click on the window you want to take a screenshot of.
The screenshot will be saved automatically in your pictures folder
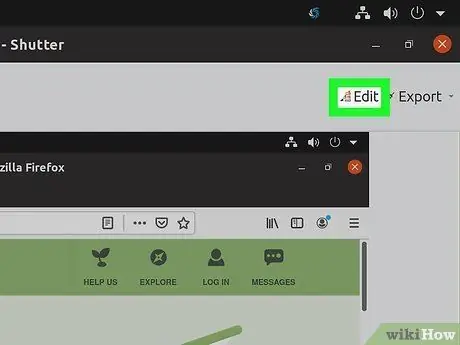
Step 4. Edit the screenshot
After taking a screenshot, a preview will appear in the Shutter window. Click the "Edit" button to open the Shutter editor. You can use an editing program to highlight things that are important or take notes. Click "Save" when finished.
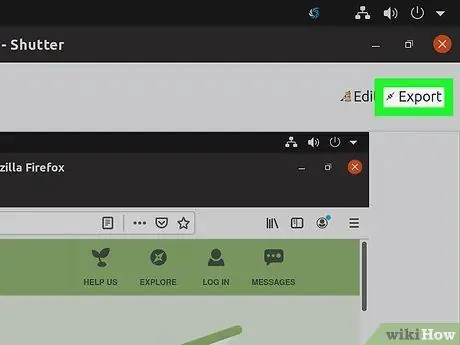
Step 5. Export (export) the screenshot
You can send the screenshot on an image uploading service or add an FTP server to upload it. Click the "Export" button to open the Export menu.
- On the "Public hosting" tab, you can choose to upload the screenshot to your Dropbox account or an online image hosting website. You will be asked for account permissions when you select one.
- On the "FTP" tab, you can enter connection information for your FTP server which is useful when you post screenshots on your blog or website.
- On the "Places" tab, you can move the screenshot to another location on your computer or network.






