- Author Jason Gerald gerald@how-what-advice.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 10:50.
- Last modified 2025-06-01 06:05.
Sometimes, you need to check the network connectivity used while using your Windows computer. There are some simple methods you can do. For Windows 10 users, you can access the Network and Sharing Center (network and distribution center). For other versions of Windows, use “netstat,” aka network statistics, which is a command-line tool to find problems or detect traffic on the network. Best of all, this command can be implemented with just a few simple steps.
Step
Method 1 of 4: Accessing the Network and Sharing Menu in Windows 7 to 10
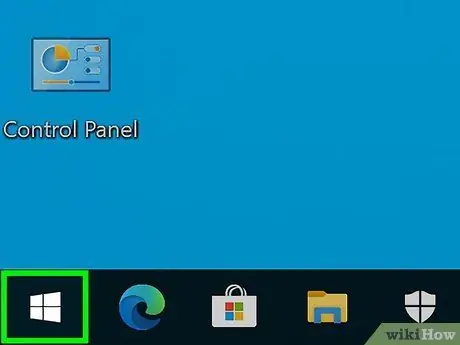
Step 1. Click Start
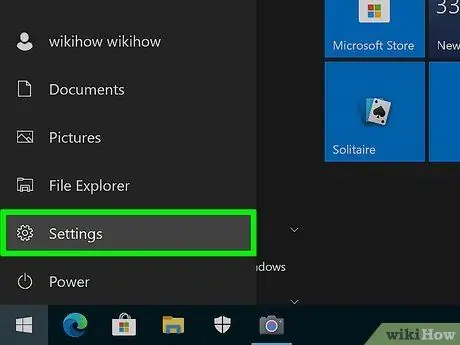
Step 2. Choose Settings
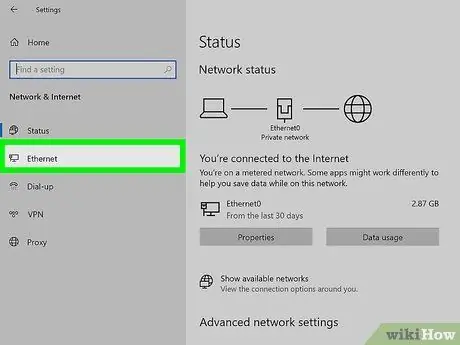
Step 3. Select Ethernet
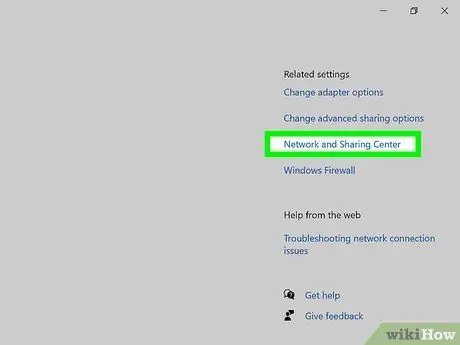
Step 4. Select Network and Sharing Center
Network and Sharing Center is a feature in Windows 10 where you can find the status of your network, the type of communication you have, connections to other people's computers (if any), and your current connection to the internet.
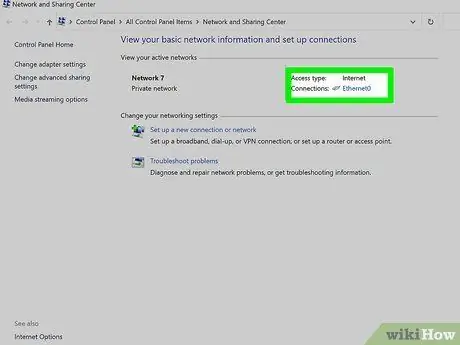
Step 5. Click the icon next to “Connections
"The icon that appears depends on the type of connection. For example, “Ethernet " will be paired with an ethernet cable “plug” icon and a wireless connection will be paired with a five-bar icon.
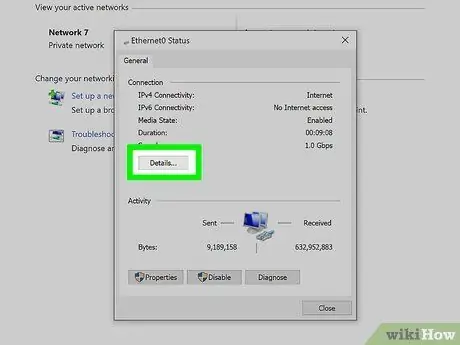
Step 6. Click Details
You will open a window showing your network connection details.
Method 2 of 4: Using the Network Connections Folder in Windows 7
Step 1. Open the Start menu
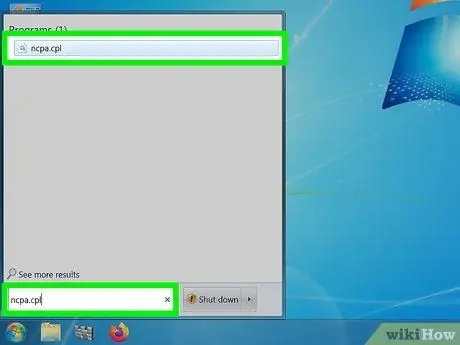
Step 2. Search for "ncpa.cpl" without quotes in the search box
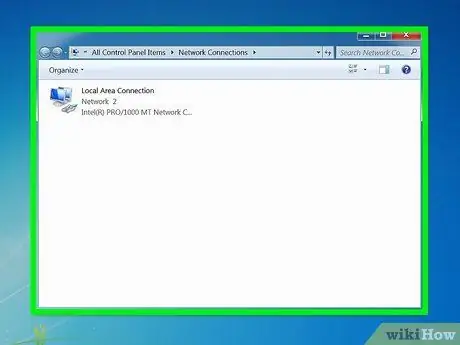
Step 3. Wait until the Network Connections folder appears
This folder will display all available connections on your network.
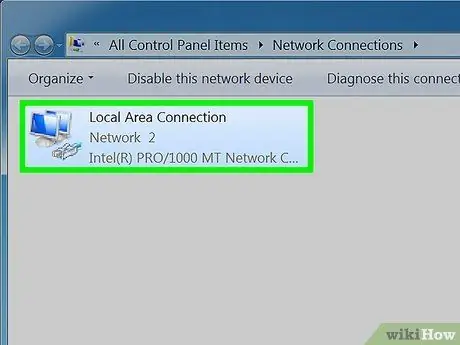
Step 4. Right click on the desired connection
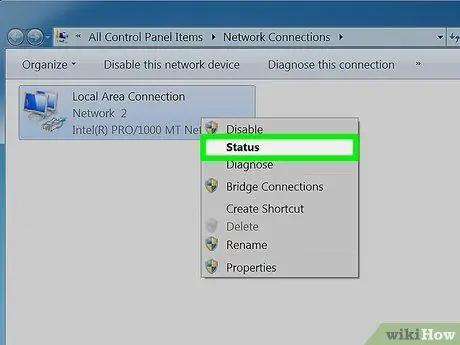
Step 5. Click Status in the drop down menu
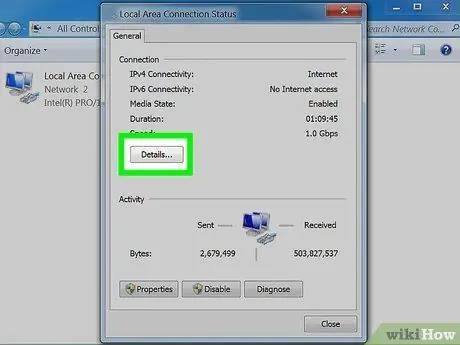
Step 6. Wait until the Network Connection Status page appears
On this page, you can see the network status. Click Details to see more information.
Method 3 of 4: Using the Netstat Command on Vista or Later
Step 1. Click the Start menu
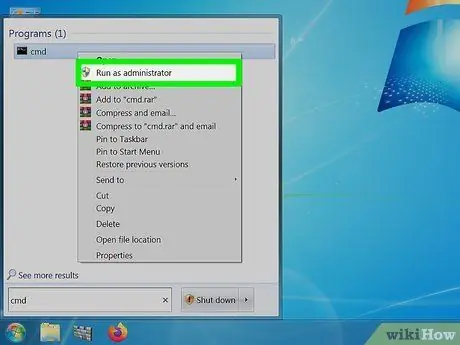
Step 2. Search for “cmd
Enter "cmd" without the quotes in the search box on Vista or later versions of Windows to open a command prompt.
Step 3. Wait until a black window or terminal appears
This is where the netstat command will be entered. There are several options to choose from, and some of the most popular are listed below.
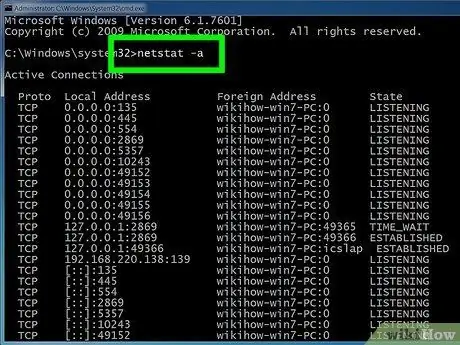
Step 4. Enter netstat -a to display current connections
This command will list the current TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) ports and connections, with the physical computer name for the local address and the hostname for the remote address. You will also get port status information (waiting, established, etc.)
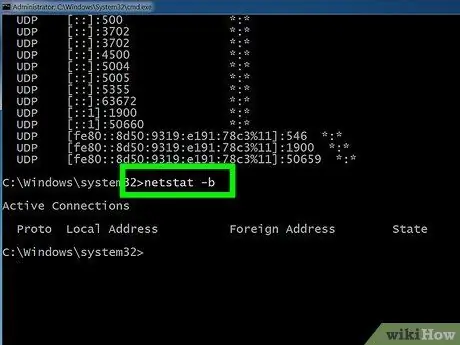
Step 5. Enter netstat -b to show what program is using the connection
This command will show the same list as netstast -a, but with the name of the program using the connection/port.
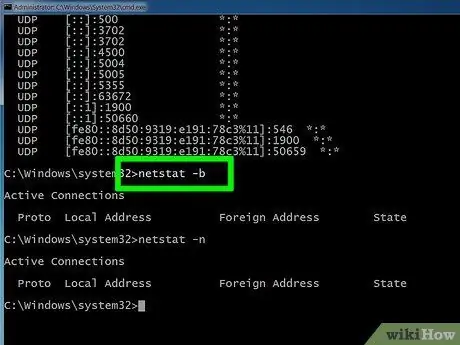
Step 6. Enter netstat -n to display the IP address
This command will show the same list of TCP connections and ports, but with numbers or IP addresses instead of the actual name of the computer or host.
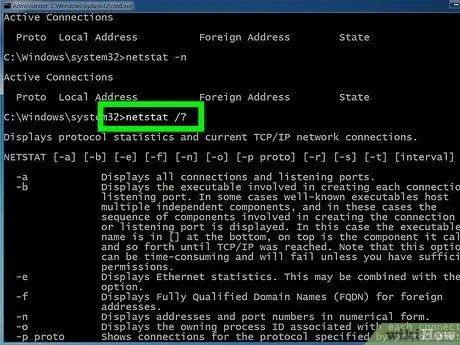
Step 7. Enter netstat /? to display the various commands you can use
This command will give you statistics for all variations of the netstat protocol.
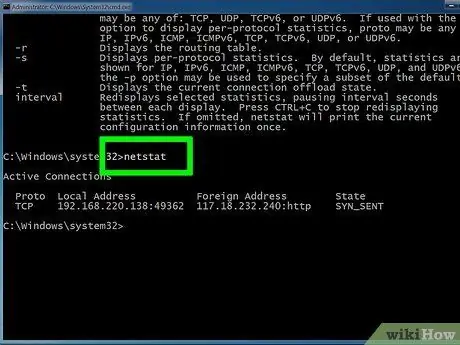
Step 8. Check your active network connection
After the netstat command is entered, a list of TCP/UCP connections with IP addresses will be displayed.
Method 4 of 4: Using the Netstat Command on XP

Step 1. Press Start
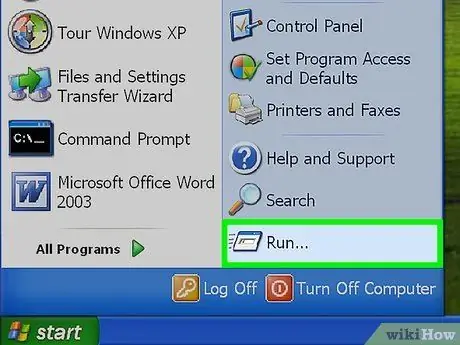
Step 2. Click " Run
A text box will open.
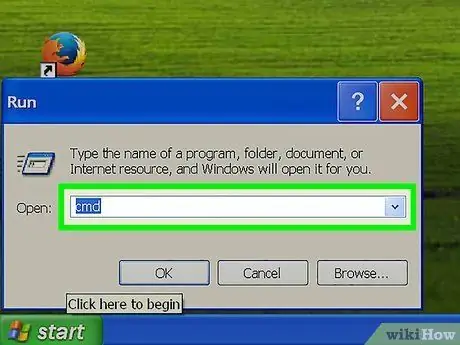
Step 3. Type "cmd" without the quotes
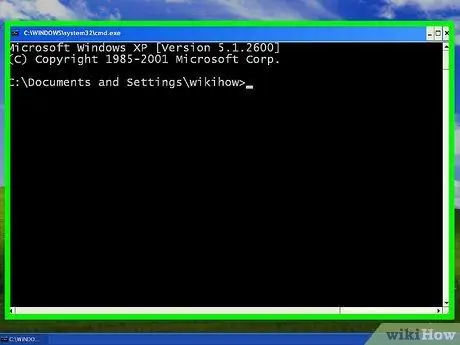
Step 4. Wait until the black window or terminal appears
This is where the netstat command will be entered. There are several options to choose from and some of the most popular are listed below.
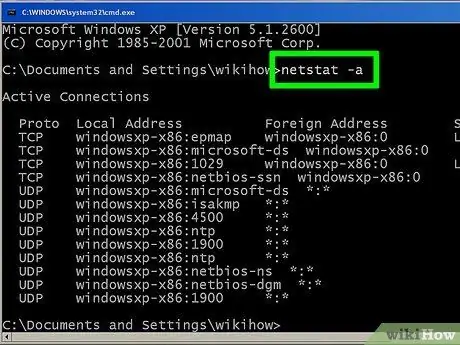
Step 5. Enter netstat -a to display current connections
This command will list the current TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) ports and connections, with the physical computer name for the local address and the hostname for the remote address. You will also get port status information (waiting, established, etc.)
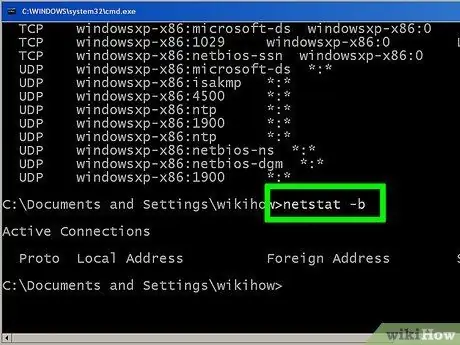
Step 6. Enter netstat -b to display what programs are using the connection
This command will show the same list as netstast -a, but with the name of the program using the connection/port.
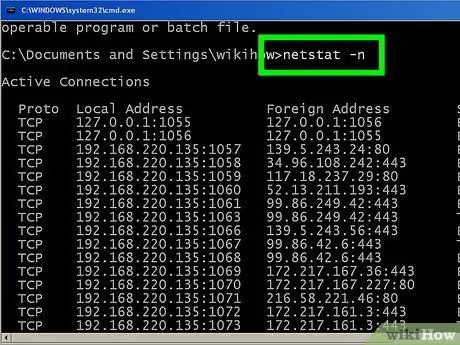
Step 7. Enter netstat -n to display the IP address
This command will show the same list of TCP connections and ports, but with numbers or IP addresses instead of computer or host names.
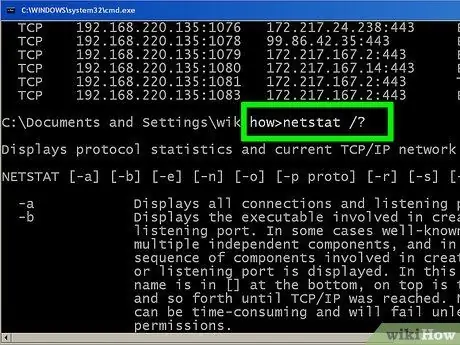
Step 8. Enter netstat /? to display the various commands you can use
This command will give you statistics for all variations of the netstat protocol.
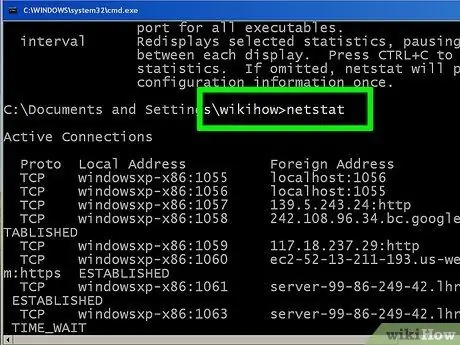
Step 9. Check your active network connection
After the netstat command is entered, a list of TCP/UCP connections with IP addresses will be displayed.
Tips
- Alternatively, try downloading and using the TCPView program from SysInternals
- Experiment. There are many UNIX commands available (eg " netstat " discussed above). Search the internet.
- Note that the netstat command is out of date on Linux. Instead, use "ip -s," "ss," or " ip route " instead of the netstat command






