- Author Jason Gerald gerald@how-what-advice.com.
- Public 2024-01-19 22:11.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 12:04.
This wikiHow teaches you how to reset the BIOS (short for Basic Input/Output Settings) to its default settings on a Windows computer. You can do a reset on most computers from the BIOS page. However, if you cannot access the BIOS, you will need to reset it by opening the computer cover and removing the CMOS battery from the motherboard. If you are using a desktop computer, you can also reset the jumper switches on the motherboard.
Sometimes, opening the computer cover will void the product warranty. Also, you run the risk of causing permanent damage to your computer when you open it. If you can't access the BIOS page, the best thing you can do is take the computer to a technology department or department rather than resetting it yourself.
Step
Method 1 of 3: Performing a Reset Via BIOS Page
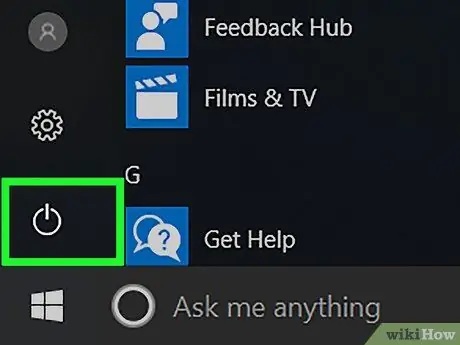
Step 1. Restart the computer
Open the "Start" menu
click the power icon
and click Restart ”.
- If your computer is locked, click the lock page, and then click the power icon in the lower-right corner of the screen. After that, select " Restart ”.
- If the computer is off, simply press the/or power switch ("On") of the device.

Step 2. Wait for the computer's startup page to appear
Once it appears, you can see a window limited to pressing the reset button.
If the message " Press [key] to enter setup " or something like that appears at the bottom of the screen and then disappears, you need to start up the computer and try pressing the correct key again
Tip:
You should start pressing the reset key combination as soon as the computer starts up.
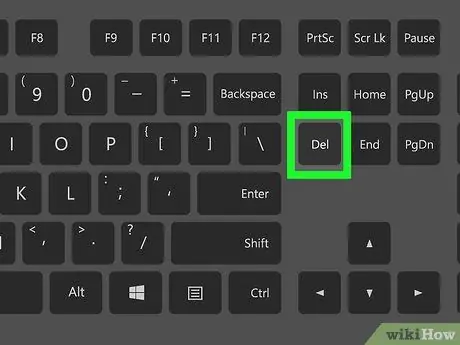
Step 3. Press Del key or F2 repeatedly to enter the settings page.
The buttons that need to be pressed may be different. In this situation, use the assigned key to access the BIOS.
- If the Del or F2 keys don't work, try pressing F8 F10 Esc or Tab.
- Generally, you can press the "F" key (eg “F2”) to access the BIOS. This key appears at the top of the keyboard. You may need to find and hold the Fn key while pressing the proper "F" key.
- You can refer to your computer's user manual or online support pages for the computer's BIOS key.
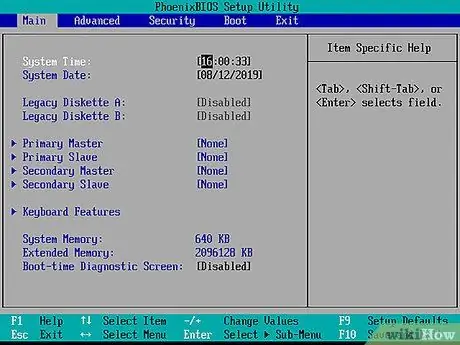
Step 4. Wait for the BIOS to load
After pressing the reset button, the BIOS will load. This process only takes a few moments. Once it's finished loading, you'll be taken to the BIOS setup menu.
If you cannot access the BIOS because the BIOS page is password locked or corrupted, use the other methods shown in this article
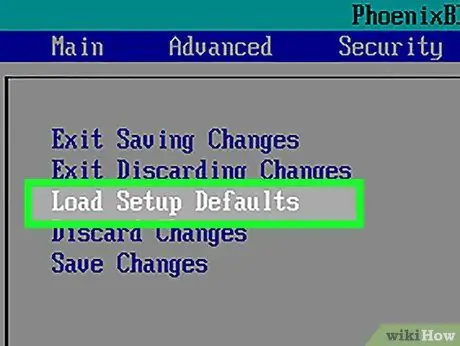
Step 5. Look for the "Setup Defaults" option
The placement and label of these options is different for each BIOS, but they are generally labeled as "Reset to Default", "Factory Defaults", "Setup Defaults", or something similar. This option may be on one of the tabs, or displayed near the navigation buttons.
If your BIOS doesn't have this option, use one of the other methods in this segment
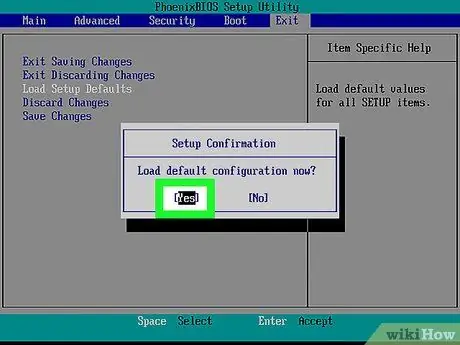
Step 6. Select "Load Setup Defaults" option and press Enter key
Use the arrow keys to select an option. After pressing the Enter key, the BIOS usually resets immediately.
Again, the label of the selected option may be different for each BIOS
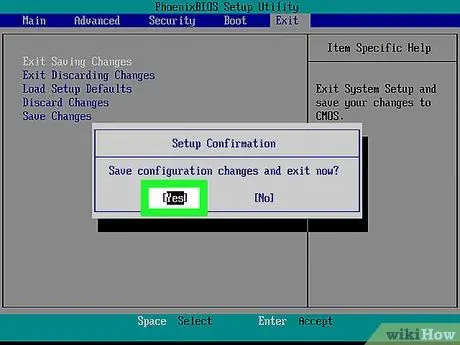
Step 7. Save changes and confirm selection if necessary
Often, this step includes exiting the BIOS page. The computer will restart automatically. If you need to change the BIOS settings after a reset, you will need to restart the computer and access the BIOS page to make the changes.
Method 2 of 3: Removing the CMOS Battery

Step 1. Turn off the computer
Use the “Start” menu to turn off the computer, or press and hold the computer's power button until the device turns off.
If you're using a desktop computer, you can usually turn off the CPU entirely by pressing the switch on the back of the CPU case
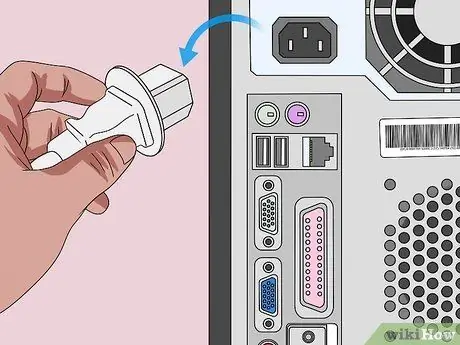
Step 2. Unplug the computer from the power source
Unplug the power cord for the desktop computer and the charging cable for the laptop.
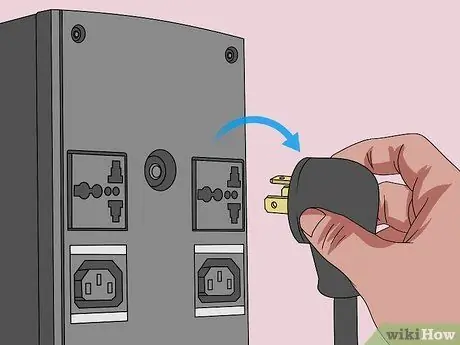
Step 3. Disconnect the computer battery if necessary
If you are using a laptop (or desktop computer with a spare battery), remove the battery from the device before proceeding.

Step 4. Remove static electricity before proceeding
Touch an unpainted metal surface to dissipate static electricity before you open the CPU. Touching the motherboard or internal computer components without proper grounding can cause permanent damage to the computer.
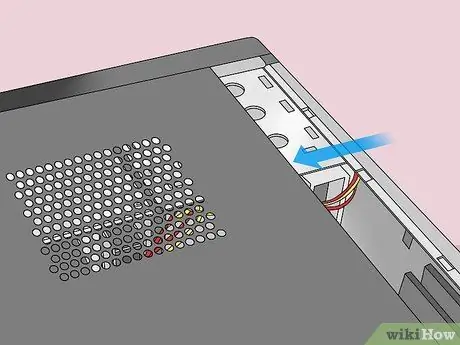
Step 5. Open the CPU outer cover
You need to access the computer's motherboard. Be careful when disassembling or touching the components inside the computer as electrostatic discharges can easily damage sensitive components.
On most laptops, you can access the CMOS battery via the removable panel on the bottom of the device. If there is no panel, you may need to disassemble the laptop to access the battery
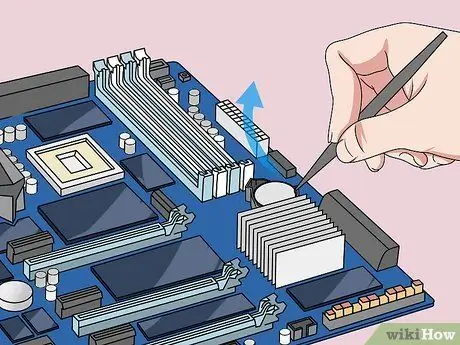
Step 6. Remove the CMOS battery
These batteries are generally located near the PCI slots, but their placement may vary depending on the manufacturer or motherboard manufacturer. The battery may be hidden behind expansion cards and cables. Generally, this battery is a round 3V flat clock battery (CR2032).
Tip:
The CMOS battery is not always removable. If the battery cannot be removed, do not remove it by force. Alternatively, try resetting the motherboard jumpers.

Step 7. Press the power button
Press and hold the computer's power button for about 10-15 seconds to release any remaining power in the capacitor. By removing the power, the CMOS memory will be cleared so that the BIOS settings can be returned to their default settings.
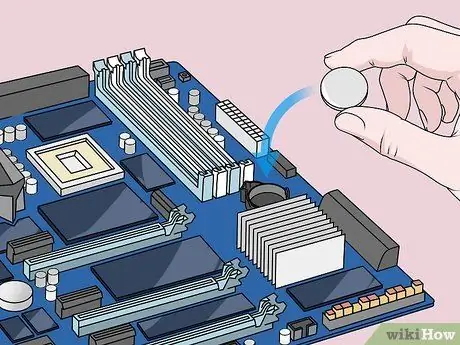
Step 8. Replace the CMOS battery
Carefully put the CMOS battery back in place. Make sure the battery is installed in the right direction. The smaller side should face down.

Step 9. Reinstall the computer
Install it carefully and remember to ground it periodically.
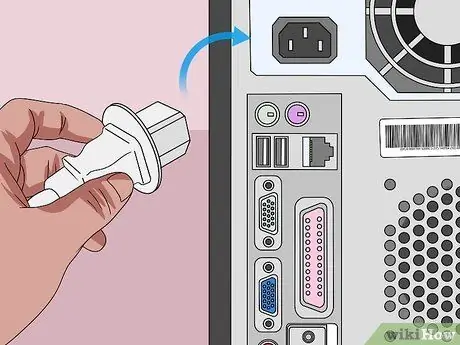
Step 10. Connect the computer to a power source
If you unplugged the computer cable from the plug and/or removed the battery, reconnect the cable and/or reinstall the battery.

Step 11. Restart the computer
You may need to access the BIOS and reconfigure options, including primary boot options or date and time settings, depending on the computer you are using.
Method 3 of 3: Reset Jumper

Step 1. Turn off the computer
Use the “Start” menu to turn off the computer, or press and hold the computer's power button until the device turns off.
If you're using a desktop computer, you can usually turn off the CPU entirely by pressing the switch on the back of the CPU case

Step 2. Unplug the computer from the power source
Unplug the power cord for the desktop computer and the charging cable for the laptop.
Step 3. Disconnect the computer battery if necessary
If you are using a laptop (or desktop computer with a spare battery), remove the battery from the device before proceeding.
Step 4. Eliminate static electricity before proceeding
Touch an unpainted metal surface to dissipate static electricity before you open the CPU. Touching the motherboard or internal computer components without proper grounding can cause permanent damage to the computer.

Step 5. Open the CPU outer cover
You need to access the computer's motherboard. Be careful when disassembling or touching the components inside the computer as electrostatic discharges can easily damage sensitive components.
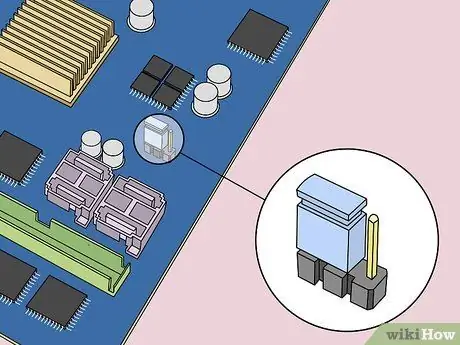
Step 6. Look for the CMOS jumper
Locate the three-pin jumper controlling the BIOS on the motherboard. Generally, the device is near the CMOS battery. Jumpers can cover two of the three pins or pins.
Notes:
Jumpers may be labeled with “CLEAR”, “CLR”, “CLEAR CMOS”, “PSSWRD”, or various other text. Try reading the motherboard user manual for the correct jumper.
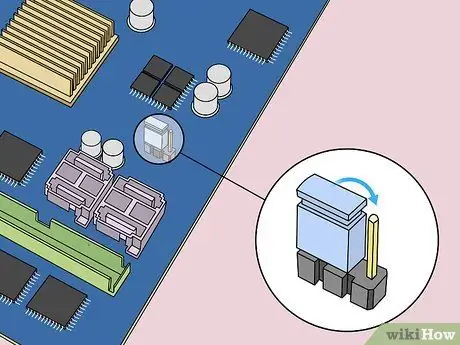
Step 7. Move the jumper to the other two pins
For example, if the jumper covers or is attached to the first and second needles, move the jumper so that it covers the second and third needles. Make sure you pull it vertically so that the needle doesn't bend.

Step 8. Press the power button
Press and hold the computer's power button for 10-15 seconds to release any remaining power stored in the capacitor. After that, the BIOS will be reset.
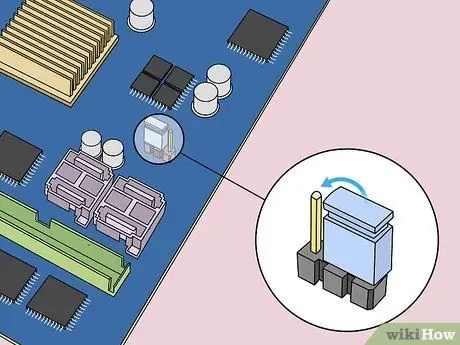
Step 9. Return the jumper to the starting position
Place the jumper back on the original needle. After that, you can access the BIOS when starting the computer.

Step 10. Reinstall the computer
Do the installation carefully and don't forget to do the grounding periodically.

Step 11. Connect the computer to a power source
If you unplugged the computer cable from the plug and/or removed the battery, reconnect the cable and/or reinstall the battery.

Step 12. Restart the computer
You may need to access the BIOS and reconfigure options, including primary boot options or date and time settings, depending on the computer you are using.






