- Author Jason Gerald gerald@how-what-advice.com.
- Public 2024-01-19 22:11.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 12:04.
The Chicago Manual of Style has two typical citation formats: “Author-Date” or “Author-Date” (using in-text citations), and “Bibliographic-Notes” or “Notes-Bibliography” (using footnotes or endnotes). The “Author-Date” citation format is more commonly used in the sciences and social sciences, while the “Bibliographic Notes” format is usually defined as the standard format for the arts, history, and humanities. Although both use the same format for bibliographies (“Bibliographic Notes”) or bibliographies/references (“Author-Date”), there are some minor differences. Before choosing a specific style or format, talk to your teacher, professor, editor, or publisher about the format you need to use in your writing.
Step
Method 1 of 4: Using In-Text Quotations in “Author-Date” Format

Step 1. Enter the author's last name and year of publication in parentheses
Place the citation right after the information you want to quote, before the closing punctuation mark. Insert a space between the author's name and the date, without adding a comma.
- For example: (Schmidt 1935).
- If you don't know the author's name, use the name of the organization that published the text or an abbreviated version of the title instead of the author's name. For example: (Society for Psychical Research 1935) or (“Mystery of a Talking Wombat” 1935).
-
Do not include the author's name in parentheses if you have already mentioned it in a sentence containing a quote. Instead, simply include the date (and page number if necessary). For example: “John Schmidt (1935, 217-218) claimed that a talking wombat inhabited the walls of his Illinois farmhouse for over a decade.”
Example in English: “John Schmidt (1935, 217-218) admits that a wombat that can “talk” has lived within the walls of his ranch in Illinois for more than a decade.”

Step 2. Separate 2-3 author names with commas
If the work or text you are citing is written by 2-3 authors, put all of their last names in parentheses before the date of publication. Insert a comma between each author's name, except between the last author's name and the date. Type the names in order in the source text.
- For example: (Schmidt, Bjorn, and Prince 1941).
- Example in Indonesian: (Schmidt, Bjorn, and Prince 1941).

Step 3. Write the first author's name and the phrase “et al.” or “etc.” when citing texts written by four (or more) authors
If the source text you are citing has four (or more) authors, state the last name of the first author (according to the name mentioned in the source), followed by the phrase “et al.” or “etc.” and date of issue. Don't use commas.
- For example: (Schmidt et al. 1937).
- Example in Indonesian: (Schmidt et al. 1937).

Step 4. Use the initials of the first name to distinguish several authors with the same last name
Sometimes it's confusing when you quote multiple authors with the same last name. Explain the difference between each author by inserting the initials of each author's first name before his last name in the quote.
For example: (J. Schmidt 1935), (V. Schmidt 1972)

Step 5. Differentiate multiple posts by the same author and date using letters
If you are citing more than one text written by the same author in the same year, you need to clearly distinguish between publications. To distinguish them, add a lowercase letter to each publication and place it after the date of publication in the citation entry.
- For example: (Schmidt 1935a), (Schmidt 1935b).
- Before assigning letters, arrange the sources alphabetically by title (this system also applies to the arrangement of source entries in the bibliography). Set the letters in order so that the first source is marked with the letter “a”, the second source is marked with the letter “b”, and so on.
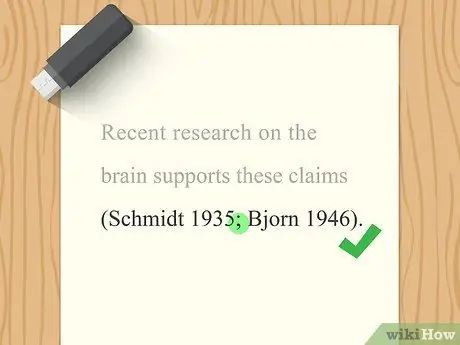
Step 6. Separate multiple quotes with semicolons
If you want to cite information obtained from several sources, you can include those sources in a single citation within the same text. List each source as usual (“Author Date”), but place a semicolon between each source.
For example: (Schmidt 1935; Bjorn 1946)

Step 7. Include page numbers when you quote specific sentences or passages
If you are citing a specific part of the text from the source text, localize the information as clearly as possible in the citation entry by including page numbers or other information (eg chapter numbers). Place page numbers or other location information after the date and separate them with a comma.
- For example: (Schmidt 1935, 217-310).
- If you're making a very general statement about the content of the source, you don't need to include the location information for that specific piece of text.
-
In addition to page numbers, you can also specify other types of location information, such as chapter numbers, document numbers, or figure numbers. For example: (Prince 1932, chap. 15) or (Bjorn et al. 1946, doc. 27).
Examples in Indonesian: (Prince 1932, chapter 15) or (Bjorn et al. 1946, doc. 27)
Method 2 of 4: Making Notes on the “Bibliographic Notes” System

Step 1. Place the number in superscript format after the information you want to quote
Unlike the “Author-Date” format or style, the “Bibliographic-Notes” (“Notes-Bibliography” or NB) system uses footnotes/endnotes instead of in-text citations (bracketed citations). The superscript number for each note entry will be the same as the note number at the bottom of the page (if you are using footnotes) or at the end of the article (if you are using endnotes). Usually, lift should be placed at the end of the relevant sentence or clause, after the closing punctuation mark.
- For example: “Schmidt's daughter, Viola, was the first person to report the phenomena.”1
Example in Indonesian: “Schmidt's daughter, Viola, was the first to report the phenomenon.”1
- With footnotes and endnotes, you can provide a more complete citation entry than the in-text citation used in the “Author-Date” system. You can also use the notes to show additional information that you didn't include in the main text. Both systems include a complete list of references at the end of the article, and this list is usually known as “Bibliography” (“Bibliography”) in the “Bibliographic-Notes” system.
- Most word processing programs have tools that help you format footnotes and endnotes. For example, if you are using MS Word, you can include notes in the text using the “References” tab.

Step 2. Begin the note with the author's first and last name
After adding numbers to the text in the section you want to quote, add an appropriate footnote at the bottom of the page. If you are using endnotes, place the notes by number at the end of the article. Note entries begin with the author's name. Do not reverse the order of the author's name (eg, last name, first name) as in a bibliography.
- For example: 1. Viola Schmidt
-
If there are 2-3 authors, list the names following the order in the publication, and separate each name with a comma. For example: 15. John Schmidt, Maureen Schmidt, and Harlan Prince
For Indonesian: 15. John Schmidt, Maureen Schmidt, and Harlan Prince
-
For source texts with four or more authors, mention only the first author's name, followed by the phrase “et al.” or “etc.”. For example: 27. Njord Bjorn et al.
For Indonesian: 27. Njord Bjorn et al

Step 3. Continue the author's name with the source title
Include the title right after the authors' names, and separate them with a comma. If you are citing a book, type the title in italics. For article or chapter titles, enclose the title in quotation marks. All titles must be typed in title or headline capitalization format.
- For example, if you quote the article: 1. John Schmidt, “Mystery of a Talking Wombat”
- For the book: 17. Njord Bjorn, My Experiences at Schmidt Farm
-
If you are quoting a chapter from an edited book, add the book title and editor's name after the chapter title. For example: 24. Bella Baylish, “An Overview of Wombat Folklore,” in The Enigma of Jules the Wombat, ed. George Finch
For Indonesian: 24. Bella Baylish, “An Overview of Wombat Folklore,” in The Enigma of Jules the Wombat, ed. George Finch

Step 4. Mention the publication information (in parentheses) after the title for the book citation
This information includes the place/city of publication, the name of the issuing company, and the date of issue. Enter all the information in brackets, right after the title in the following format: “(City: Publishing Company, Year)”.
For example: 17. Njord Bjorn, My Experiences at Schmidt Farm (London: Not a Real Publisher, 1946)

Step 5. Include the journal title, issue number, volume number, and date of publication if you are using the article as source text
If the source of the citation is published in a journal, you will need to include additional information regarding the publication. After the article title, include the journal title (in italics), followed by the volume and output number (if available). After that, add the year and type it in parentheses.
-
For example: 1. John Schmidt, “Mystery of a Talking Wombat,” Bulletin of the Illinois Society for Psychical Research 217, no. 2 (February 1935)
For Indonesian: 1. John Schmidt, “Mystery of a Talking Wombat,” Bulletin of the Illinois Society for Psychical Research 217, no. 2 (February 1935)
-
The format used is slightly different for other types of periodical publications (eg articles in newspapers or magazines). For different types, the title of the publication is followed by the month, date, and year of publication. For example: The Naperville Times, February 15, 1935.
For Indonesian, use the “date month, year” format: The Naperville Times, February 15, 1935

Step 6. End the note with a page number or other location information
If you are citing a particular sentence/paragraph, chapter or section of text, include the page number or other location details after the publication information. Add this information outside the brackets, after the book publication information or the journal publication date.
-
If you are citing a book or book chapter, state the page number or source location information after the comma. For example: 17. Njord Bjorn, My Experiences at Schmidt Farm (London: Not a Real Publisher, 1946), chap. 15.
For English: 17. Njord Bjorn, My Experiences at Schmidt Farm (London: Not a Real Publisher, 1946), chapter 15
-
If you are citing a journal article, insert a colon before the page number. For example: 1. John Schmidt, “Mystery of a Talking Wombat,” Bulletin of the Illinois Society for Psychical Research 217, no. 2 (February 1935): 275-278.
Examples in Indonesian: 1. John Schmidt, “Mystery of a Talking Wombat,” Bulletin of the Illinois Society for Psychical Research 217, no. 2 (February 1935): 275-278

Step 7. Include the URL if you are using an online source
Add the quoted text web address after the page number on the note. If you are using an electronic journal article, use the article's DOI (Digital Object Identifier) number if available. This unique identifier number also serves as a permanent URL (web address) for articles or other electronic resources. If you don't find the DOI number at the top of the article, you can look it up here:
- For example: 1. John Schmidt, “Mystery of a Talking Wombat,” Bulletin of the Illinois Society for Psychical Research 217, no. 2 (February 1935): 275-278,
Examples in Indonesian: 1. John Schmidt, “Mystery of a Talking Wombat,” Bulletin of the Illinois Society for Psychical Research 217, no. 2 (February 1935): 275-278,
- Some outdated (or not very reliable) periodicals may not have a DOI number. If you don't find the DOI number on the article or on the crossref.org site, just use the web address you accessed to read the article.

Step 8. Add a period at the end of the quote
After listing all the required information, end the quote with a period. If the citation includes a page number or URL, add a period after it. Otherwise, you can include a period right after the publication information.
- For example, if you quote a specific page in a book, the full citation entry would look like this: 12. Njord Bjorn, My Experiences at Schmidt Farm (London: Not a Real Publisher, 1946), 21-22.
- For a more general quote (without page numbers): 12. Njord Bjorn, My Experiences at Schmidt Farm (London: Not a Real Publisher, 1946).

Step 9. Create abbreviations for future reference
If you cite the same source more than once, create an abbreviated version of the source title to use after the first note. This brief reference includes the author's last name, a word or two that is clear from the title text, and the page number or other source location information you cite.
-
For example: Baylish, “Wombat Folklore,” fig. 3.
For Indonesian: Baylish, “Wombat Folklore,” chart 3
Method 3 of 4: Creating a Reference List in the “Author-Date” Style

Step 1. List the reference entries alphabetically by author's name
Sort each entry by author's last name. Type the author's last name first, and continue with the first name after the comma.
- For example: Schmidt, John.
- If there are multiple authors, only reverse the order of the first and last names of the first author. For example: Schmidt, John, and Njord Bjorn.
- If there are 10 authors (or less) for a particular source, list all the authors' names in the reference list entry. If there are more than 10 authors, state the first 7 names, then insert the phrase “et al.” or “etc.”.
- If you have multiple sources from the same author, list them in chronological order. State the author's name in the first entry, then use three dashes "em" followed by a period ("---.") at the beginning of subsequent entries in place of the author's name.
- For multiple works written by the same author, in the same year, separate each entry by inserting a lowercase letter next to the date (e.g. “1935a”, “1935b”, and so on). Arrange these entries alphabetically by title.

Step 2. Add the year of publication between the author's name and the title of the work
In the “Author-Date” style/system, the author's name is immediately followed by the date and separated by a period. After that, the date is followed by the title of the publication. This is true regardless of the type of source you cite (eg books, book chapters, or periodicals).
For example: Schmidt, John. 1935. “The Mystery of a Talking Wombat.”

Step 3. Write the publication information after the title if you are citing a book
Continue the title of the book with the place/location of publication, as well as the name of the publishing company. Separate this information from the title using a period.
- For example: Bjorn, Njord. 1946. My Experiences at Schmidt Farm. London: Not a Real Publisher.
- If the book you are using is part of a multivolume set, insert the volume number after the title and before the publishing information. Include a volume subtitle if any. For example: Bjorn, Njord. 1946. My Experiences at Schmidt Farm. Vol. 2, The Investigations. London: Not a Real Publisher.
-
You can also add information such as the name of the translator (if applicable) or the edition number after the title. For example: Bjorn, Njord. 1946. My Experiences at Schmidt Farm, 2nd ed. Translated by Richard Little. London: Not a Real Publisher.
For Indonesian: Bjorn, Njord. 1946. My Experiences at Schmidt Farm, second edition. Translated by Richard Little. London: Not a Real Publisher

Step 4. State the title of the book, the editor, and the page range after the chapter title
After you have entered the chapter title, write the book title, editor's name, and a page range containing the information you quoted in the following format: “In Book Title, edited by First Name Last Name, xxx-xxx”. For Indonesian, use the following format: “In Book Title, edited by First Name Last Name, xxx-xxx”. Write the publishing information after the page range.
-
For example: Baylish, Bella. 2018. “An Overview of Wombat Folklore.” In The Enigma of Jules the Wombat, edited by George Finch, 125-162. New York: J. Q. Abernathy and Sons.
For Indonesian: Baylish, Bella. 2018. “An Overview of Wombat Folklore.” In The Enigma of Jules the Wombat, edited by George Finch, 125-162. New York: J. Q. Abernathy and Sons

Step 5. Add the journal title, volume, and location information after the article title
If you are citing an article from a periodical, all information about the publication is added after the title of the article. Use the following format: “Journal title volume number, output number (month/season): page range”. If you have an article's URL or DOI number, include that information after the page range.
- “Page range” refers to the page numbers that contain all the articles in the journal. For example, the article you are using might appear on pages 275-278 of the journal you are citing.
-
For example: Schmidt, John. 1935. “Mystery of a Talking Wombat.” Bulletin of the Illinois Society for Psychical Research 217, no. 2 (February): 275-278.https://doi.org/10.xxxx/xxxxxx.
For Indonesian: Schmidt, John. 1935. “Mystery of a Talking Wombat.” Bulletin of the Illinois Society for Psychical Research 217, no. 2 (February): 275-278
-
If you are citing a periodical such as a newspaper or magazine, include the date of publication at the end of the citation, and after the author's name. Entries like this usually don't cover the page range. For example: Whiffle, Ferdinand. 1935. “The Wombat of Schmidt Farm.” Naperville Times, February 15, 1935.
Examples in Indonesian: Whiffle, Ferdinand. 1935. “The Wombat of Schmidt Farm.” Naperville Times, February 15, 1935
Method 4 of 4: Writing a Bibliography in a “Bibliographic Notes” Style

Step 1. Write the bibliographic entries alphabetically by author's name
Arrange the entries alphabetically by author's last name. Type in the author's last name first, then separate it from the first name using a comma.
- For example: Prince, Harlan.
-
If the source is written by more than one author, reverse the order of the first author's names, but leave the following names written in the normal format (first name last name). For example: Prince, Harlan, and Njord Bjorn.
Examples in Indonesian: Prince, Harlan and Njord Bjorn
- If the entry has 10 authors (or less), state the names of all the authors in the entry. For sources with more than 10 authors, mention the first seven authors and insert the phrase “et al.” or “etc.”.
- Arrange multiple sources from the same author alphabetically by title. List the author's name on the first entry, but insert three dashes "em" and a period ("---.") at the beginning of each subsequent entry in place of the author's name.

Step 2. Put the title after the author's name
If you use the “Bibliographic-Notes” style/system, the date is placed at the end of the citation. Continue the author's name with the source title and separate the two with a period. Reinsert a period after the title.
- For example, if you are citing articles from periodicals or book chapters: Schmidt, John. “The Mystery of a Talking Wombat.”
- If you quote the book: Bjorn, Njord. My Experiences at Schmidt Farm.

Step 3. Add publishing information after the title if you are citing a book
Include the place/location of publication, the name of the publishing company, and the year of publication after the title. Do not include this information in parentheses as in notes. Insert a period between the title and the publishing information.
- For example: Bjorn, Njord. My Experiences at Schmidt Farm. London: Not a Real Publisher, 1946.
- If the book has a volume number, include the number after the title and before the publication information. If there is a volume subtitle, type the subtitle after the volume number. For example: Bjorn, Njord. My Experiences at Schmidt Farm. Vol. 2, The Investigations. London: Not a Real Publisher, 1946.
-
Additional information about the book such as the name of the translator or edition number can be added after the title and before the publication information. For example: Bjorn, Njord. My Experiences at Schmidt Farm, 2nd ed. Translated by Richard Little. London: Not a Real Publisher, 1946.
For Indonesian: Bjorn, Njord. My Experiences at Schmidt Farm, second edition. Translated by Richard Little. London: Not a Real Publisher, 1946

Step 4. List the book title, editor, and page range after the chapter title
If you are citing a book chapter, you will also need to include the title of the book, the name of the editor, and the page range of the chapter. Place this information right after the chapter title in the following format: “In Book Title, edited by First Name Last Name, xxx-xxx”. For Indonesian, follow the following format: “In Book Title, edited by First Name Last Name, xxx-xxx”. Add publishing information after the page range.
-
For example: Baylish, Bella. “An Overview of Wombat Folklore.” In The Enigma of Jules the Wombat, edited by George Finch, 125-162. New York: J. Q. Abernathy and Sons, 2018.
For Indonesian: Baylish, Bella. “An Overview of Wombat Folklore.” In The Enigma of Jules the Wombat, edited by George Finch, 125-162. New York: J. Q. Abernathy and Sons, 2018

Step 5. Continue the article title with the journal title, volume number, and location information
When you cite an article, place the publication information right after the article title. Use the following format: “Journal title volume number, output number (month/season year): page range. Insert the URL or DOI number of the article after the page range if available.
- For example: Schmidt, John. “Mystery of a Talking Wombat.” Bulletin of the Illinois Society for Psychical Research 217, no. 2 (February 1935): 275-278.
For Indonesian: Schmidt, John. “Mystery of a Talking Wombat.” Bulletin of the Illinois Society for Psychical Research 217, no. 2 (February 1935): 275-278
-
If you are citing a periodical such as a newspaper or magazine, place the date at the end of the citation (without the brackets). For example: Whiffle, Ferdinand. "The Wombats of Schmidt Farm." Naperville Times, February 15, 1935.
For Indonesian: Whiffle, Ferdinand. "The Wombats of Schmidt Farm." Naperville Times, February 15, 1935






