- Author Jason Gerald gerald@how-what-advice.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 10:50.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 12:04.
Zucchini or also known as Japanese cucumber is a vegetable that looks like a pumpkin or eggplant. Growing zucchini is very easy, so this plant is an ideal type of vegetable to be planted to encourage children to do gardening activities. The zucchini's fast harvest time-shortly after planting-provides a sensation for young farmers.
Step
Part 1 of 2: Preparation for Planting Zucchini

Step 1. Decide how you will start your zucchini planting
There are two ways of cultivating zucchini plants that are usually done, namely by planting seeds / seeds or buying zucchini plant seeds and then planting them in the garden. If you choose to grow zucchini seeds, you should start seeding about 4-6 weeks before your outdoor planting time depending on your environment or location. Buying pre-potted plants is always easier and saves time, but may not live up to expectations if the zucchini plants you want are from seeds.
- There are several types of zucchini, but actually these types of pumpkin are generally the same. You may find zucchini classified according to their habit or way of growing their leaves (creeping/vine-like or shrub-like), namely 'open plants' (growing erect and woody stems but rarely to much air intake) or 'solid plants' (growing upright, many stems, close together and dense tend to bush).
- Most creeping varieties of zucchini (such as grapes) are considered summer squash, while bushy varieties are called winter squash.
- Naturally, the color of zucchini varies between yellow or yellowish and dark green close to black. Some of them have very thin stripes or spots. The display is normal and nothing to worry about.

Step 2. Know when is the right time to plant
Zucchini is usually considered a summer squash, because it thrives and produces its best fruit in the summer. Some varieties are considered winter squash, but this has more to do with fruiting time than planting time. Zucchini likes a lot of sun and will not grow well in cold soil. Therefore, plant zucchini when the outside soil temperature is at least 13°C. In regions with cold winters, these conditions are reached in the first or second week of spring, after there is no snow.
If you're not sure when to plant, try contacting your local agricultural extension worker for more information on when to plant zucchini that is right for your area
Step 3. Find the perfect planting location
Zucchini will thrive in an area that gets full sun with enough room to spread out. Find a location in your garden, where the zucchini plants can get at least 6-10 hours of full sun per day and where there is not too much shade. Be sure to choose a plot of land that has good drainage; zucchini likes moist/wet soil, but not waterlogged ones.
- If the soil does not have good drainage, it will need to be cultivated to match the plant's needs, especially if you don't have a better location.
- Avoid planting zucchini on the north side of the garden, as that location tends to get very little sun.

Step 4. Prepare the soil to be planted
While not everyone has the time, it's a good idea to prepare the soil several months in advance to provide the best growing conditions for zucchini seeds. Start by mixing mulch and fertilizer, to supply the soil with the necessary nutrients. Check the acidity level (pH) of the soil and carry out processing if necessary. Zucchini plants prefer a soil environment with a pH between 6 and 7.5. To make the soil more acidic (lower pH), mix the soil with peat moss and leaves from leafy plants. needles (pine, etc.). On the other hand, to make the soil more alkaline (higher pH) mix the soil with lime.
- If you can, mix compost into the soil on a monthly basis; This method will help the soil to get more complete nutrients.
- If the soil you've chosen doesn't have good drainage, mix in some sand to help encourage drainage.

Step 5. Start growing zucchini from seeds
If you don't want to risk spreading zucchini seeds directly into the soil, you can start planting them indoors 4-6 weeks in advance, and only then plant them in the garden. Prepare a tray for seeds, a planting medium mix with a little soil, and some zucchini seeds. Place the zucchini seeds then cover with a potting mix about 0.3 cm thick, and water properly! Place it in an area that gets full sun and a temperature of at least 16°C. When the second leaf has appeared, the zucchini is ready to be planted outdoors.
Part 2 of 2: Growing Zucchini
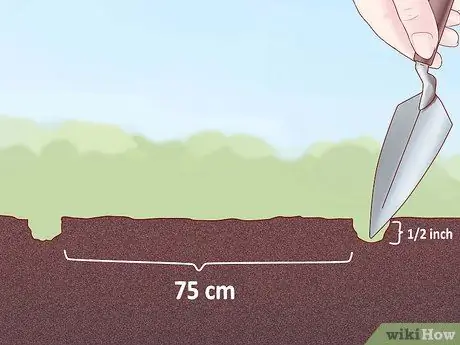
Step 1. Prepare the plot of land to be planted
Use a shovel to dig a small hole for planting your zucchini. If you are planting seeds, you will need to insert each zucchini seed into a hole at a depth of less than 1.27 cm. For zucchini seedlings, dig each hole slightly larger than the plant's root ball. Leave a distance between plants of about 75-100 cm (the same distance between rows). If necessary, you can also space the seed seedlings.

Step 2. Plant the zucchini seeds
Insert the zucchini seeds, each into one hole. Cover the hole with or inch (± 0.6 or 1.27 cm) thick soil, so the seeds can still get the sunlight and water they need to germinate. Cover the zucchini seedlings with enough soil to protect the roots without reaching the stems. Finish the planting process by watering the zucchini with plenty of water!

Step 3. Take good care of your zucchini plants
Watch your zucchini plant as it begins to grow. Although classified as a low-maintenance plant, but zucchini requires little care to remain in a productive condition. Remove any weeds or weeds from the planting site. If weeds are a persistent problem, cover the soil surface with mulch. To help promote zucchini growth, add a liquid growth fertilizer every 3-4 weeks. Cut diseased or dry stems or fruit to prevent the spread of disease to other parts of the plant as well as to promote growth.

Step 4. Increase growth
In order for zucchini plants to produce fruit, pollination is required. If you don't have bees or other insects that can help with pollination, or your zucchini plants don't seem to be producing fruit, you can self-pollinate. Take the male zucchini flowers, which are identified by long stalks, slender stems and visible stamens in the center. Carefully pull the flower by the stem and rub the stamens into the female flower. The female flower has a short stalk, the growth is round to meet the stalk and the stamens are not many.
You can do this on a few or many flowers depending on the time you have and the growth (especially fertilization) you are trying to increase

Step 5. Harvest your zucchini
When the length has reached a minimum of about 11 cm, the zucchini fruit is ready to be picked. Pick zucchini regularly to trigger more fruit. Therefore, if you want your zucchini plant to bear fruit, pick all zucchini that are ripe or ready to be picked. If you don't need too many of the squash, leave a zucchini or two depending on the plant for overall growth to slow fruit production. When harvesting, use a sharp knife to cut the zucchini from the rough stems attached to the bush.
- Enjoy zucchini flowers in salads. Zucchini flowers are delicious to eat, but if you don't pick them, a lot of zucchini will be produced.
- The zucchini plant will continue to grow. In a four-season country, zucchini will grow until the first snowfall if the plant grows well during the spring.
- You can trim the stalks of the zucchini to promote growth, if you don't want to harvest all the zucchini yet.
Tips
- Yellow and green zucchini taste the same, but yellow zucchini are easier to see (when you're about to harvest) if you grow enough of them! !
- Zucchini is a terrific ingredient, it can be added to pasta sauces, and added to soups. Zucchini can also be used as a salad mix, or grated to make "zucchini pasta".
Warning
- Zucchini pests include the following: mealybugs (whitefly), aphids (aphids), spider mites (spider mites), nematodes (a type of worm), mosses, fungi, and viruses.
- If the zucchini plant does not bear fruit properly, it may be due to insufficient pollination of female flowers. You can remove the male flowers and pollinate the female flowers by hand to make sure the process goes smoothly.






