- Author Jason Gerald gerald@how-what-advice.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 10:50.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 12:04.
There are several caches in Windows that are used to store temporary files, the goal is that the data can be retrieved quickly. When the amount builds up, this cache can cause performance issues and connectivity issues. To learn how to clear memory, DNS, thumbnails, and web browser cache, see Step 1 below.
Step
Part 1 of 4: Clearing Memory Cache
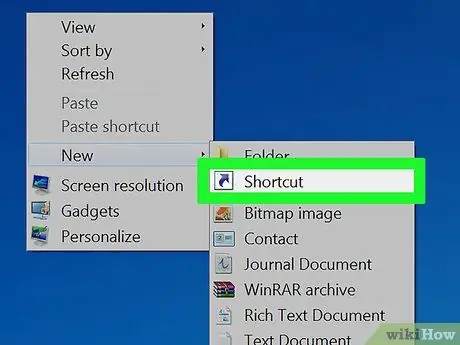
Step 1. Create a shortcut
You may already know that the longer it is turned on, the computer or laptop will slowly slow down due to idle processes. This could force you to restart your computer. You can create shortcuts on your desktop to clean up unused RAM and speed up your computer without rebooting. You can run this shortcut whenever your computer starts to slow down.
Right-click anywhere on the desktop and select New → Shortcut
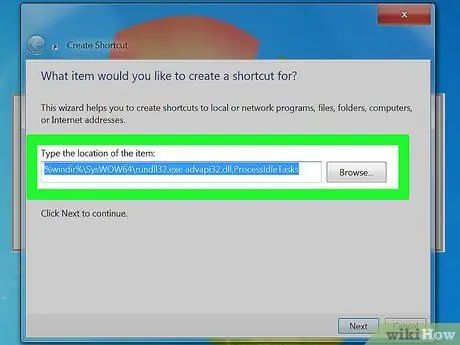
Step 2. Type in the following location
A window will appear asking you to specify the location of the newly created shortcut. You need to find out if your copy of Windows is 32 bit or 64 bit. Copy and paste one of the following locations depending on your version of Windows and then click Next:
- 32 bit: %windir%\system32\rundll32.exe advapi32.dll, ProcessIdleTasks
- For 64 bit, type: %windir%\SysWOW64\rundll32.exe advapi32.dll, ProcessIdleTasks
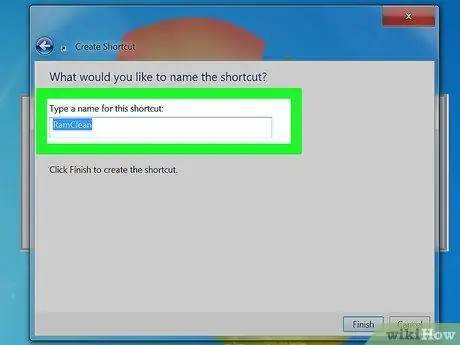
Step 3. Give the shortcut a name
Once you press the Next button, you will be asked to type a name for the shortcut, you can name it whatever you want.
Once done, hit Finish
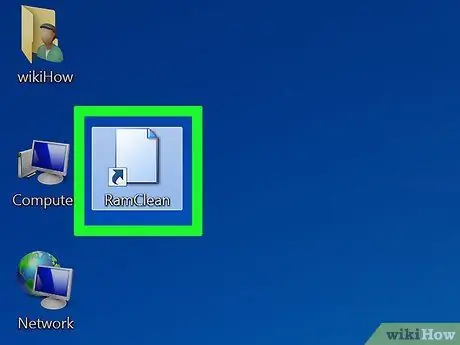
Step 4. Open the shortcut
Now, after successfully creating the shortcut, whenever the computer's performance slows down, open this shortcut to clean up the unused RAM.
This shortcut checks for running processes and ends unused processes that are taking up memory
Part 2 of 4: Clearing DNS Cache
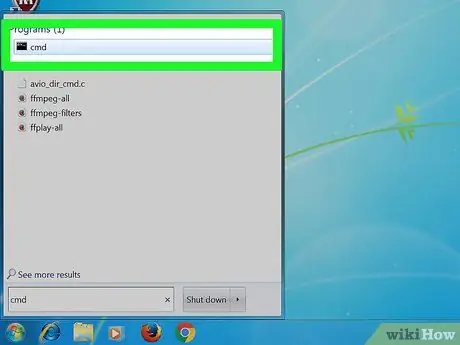
Step 1. Open Command Prompt
If you experience connectivity problems, your computer's DNS cache may be corrupt or outdated. Flushing manually is a quick way and can resolve any connectivity issues you're having.
- Click Start (the Windows icon at the bottom left of the screen) and then type "command prompt" into the search bar.
- Right-click on Command Prompt and then click "Run as Administrator". It is important to run Command Prompt as Administrator as we will be clearing the cache which can be found in the system directory.
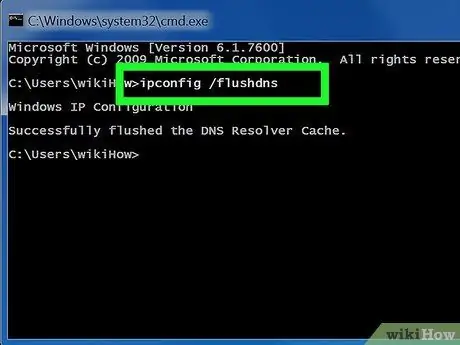
Step 2. Type in the flush DNS command
To flush or clear DNS, type ipconfig /flushdns and press Enter
You will see a message saying Successfully flushed the DNS Resolver Cache if you typed it correctly. Close Command Prompt
Step 3. Try using the internet again
If you're still having trouble opening websites, the cause of the problem may lie elsewhere.
Part 3 of 4: Clearing Thumbnail Cache with Disk Cleanup
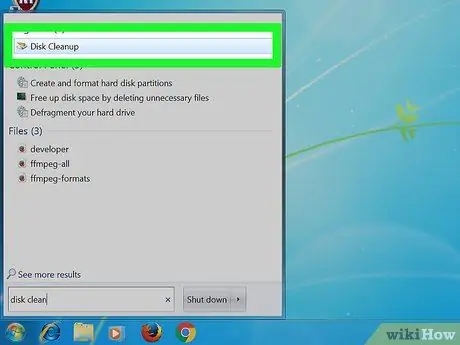
Step 1. Open Disk Cleanup
Disk Cleanup is a system tool that is installed automatically with Windows. This tool allows you to not only clean junk files and temporary data from your hard disk (drive), but also delete thumbnail cache files.
- Click Start and search for "Disk Cleanup". A small window will appear showing that Disk Cleanup is detailing unused files that can be deleted. Wait until this process is complete.
- The thumbnail cache is all the thumbnail previews that Windows uses as a preview for a directory (folder). If you have a lot of files, the thumbnail cache can take up quite a bit of storage space.
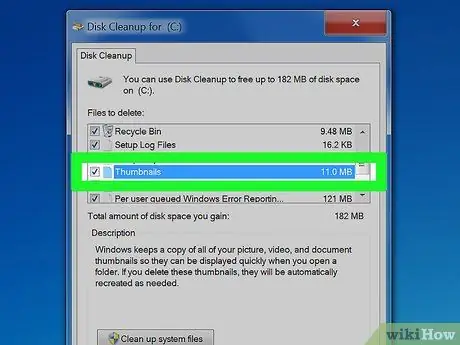
Step 2. Select "Thumbnails"
After the scan is complete, a new window will appear with a list of files that can be deleted. You'll see the name and size of the file in that category.
- Look for the "Thumbnails" option and then check the box.
- You can also include "Windows Error Report" and "Temporary Files" to free up even more storage space.
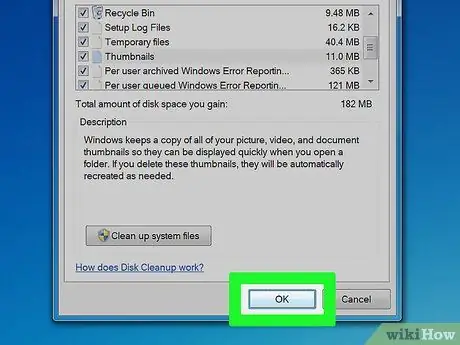
Step 3. Clear cache
After ticking the files you want to delete, including the thumbnail cache, confirm the process in the next step by clicking OK and then Delete Files.
Congratulations, you've managed to delete unwanted files, make more storage space and improve computer performance
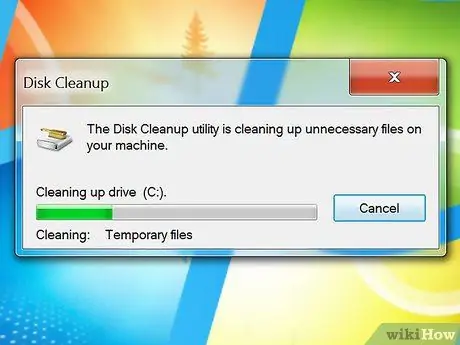
Step 4. Repeat regularly
The thumbnail cache and temporary files directory will grow rapidly, so you will need to clean them regularly. Perform this cleaning again at least once a month to maintain computer performance.
Part 4 of 4: Clearing Browser Cache
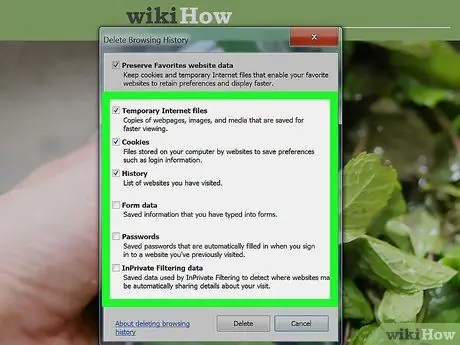
Step 1. Clear Internet Explorer cache
Click the gear icon in the top right corner, point to "Safety", and select "Delete browsing history". You can also press Ctrl+⇧ Shift+Del to open this window.
- Check the "Temporary Internet Files" box. Make sure to uncheck the boxes containing the data you want to keep.
- Click the Delete button.
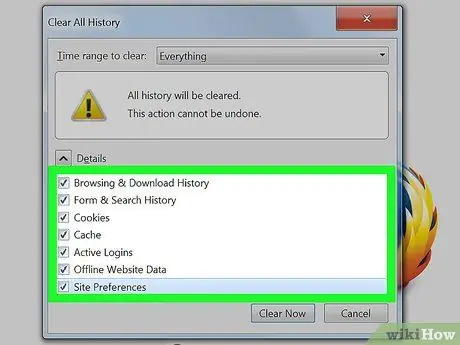
Step 2. Clear Firefox cache
Click the Firefox button in the upper-left corner of the window. Navigate to "History" and select "Clear Recent History". You can also press Ctrl+⇧ Shift+Del to open this window.
- Expand the "Details" section and tick the "Cache" box.
- Set "Time range to clear" to "Everything".
- Click the Clear Now button.
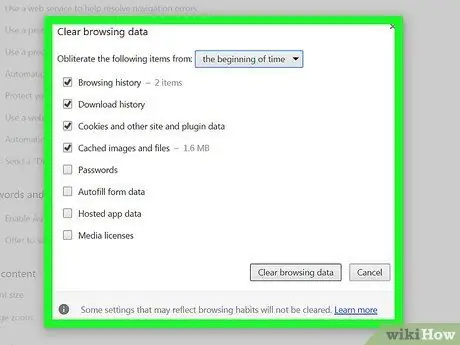
Step 3. Clear cache of Google Chrome
You can clear Chrome cache via the settings menu. To access it, click the Chrome menu button (☰) at the top right of the window and select Settings. The settings page will appear in a new tab.
- Click the "Show advanced settings" link at the top of the page.
- Look for the privacy section and click on the Clear browsing data button. You can also directly access this window by pressing Ctrl+⇧ Shift+Del
- Check the "Empty the cache" box and then click Clear browsing data.






