- Author Jason Gerald gerald@how-what-advice.com.
- Public 2024-01-19 22:11.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 12:04.
When you delete important files, you may think that they are gone forever. However, if you act quickly, it is possible to recover the file and return it to its original location on the hard drive. Follow this guide to recover deleted files from Windows, OS X, or Linux.
Step
Method 1 of 3: Windows
Step 1. Look for the file in the “recycle bin”
The “Recycle Bin” will hold files before deleting them permanently, allowing you to restore them to your computer if you change your mind. To recover files, open the "Recycle Bin", right-click on the file you want to recover, and select "Restore". The file will return to the original location where it was previously deleted.
Large files have the possibility of being permanently deleted without being sent to the “Recycle Bin”
Step 2. Stop accessing the drive (drive)
If your files are not found in the “Recycle Bin”, do not save or delete anything from your computer. There is a greater chance of recovering the file if you don't save the new file. This is because when a file is deleted, it is actually just set to be overwritten. If no new data overwrites the original file, it can usually be recovered.
Step 3. Download a data recovery program on your computer or another driver
Make sure you don't save the download on the drive where you deleted the file that you want to recover. If you save it on the same drive, the download will overwrite the file you want to recover. Listed below are some popular free programs:
- Recuva
- Restoration
- Glary Undelete
- Puran File Recovery
- If possible, download a portable version of the recovery program so that it can be run directly from the USB drive without having to install the program on your computer. Not all recovery programs have a portable version.
Step 4. Run the recovery program
Although different, all of these programs have the same way of use. Make sure you don't have the program installed on the drive where you deleted the files.
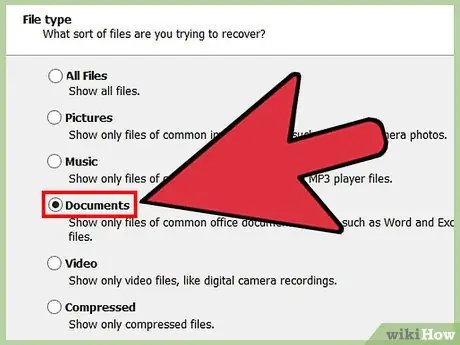
Step 5. Specify the file you are looking for
Navigate the recovery program search to the disk (disk) where the files were deleted. You can also recover files from a USB drive. Most recovery programs will ask for the type of file you are looking for. You can also search for files with a specific name or search for files by browsing the list of all recovered files.
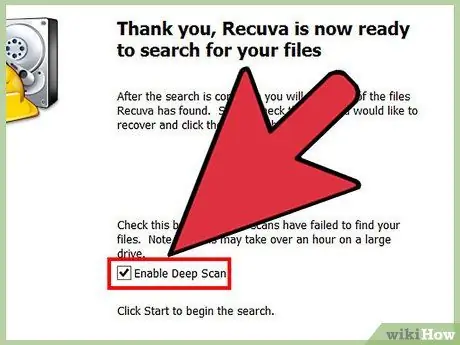
Step 6. Perform a deep scan
Some programs give you the option to perform a deep scan when searching for files. This will take a lot longer, but more files will be found.
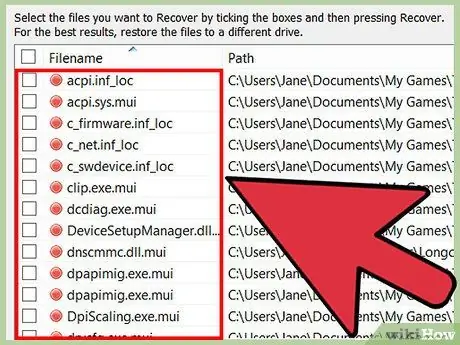
Step 7. Browse for the file you want
When the scan is complete, locate the file you want to recover. Each program has a different way of recovering files, but in general, you just need to select the file and click the “Restore” button.
- Not all files can be recovered 100%. This is because files are often stored in multiple sections on the hard drive, and one of those sections may have been overwritten.
- Some programs recover files to their original location, other programs restore files to the “Recovery” folder.
Method 2 of 3: Mac OS X
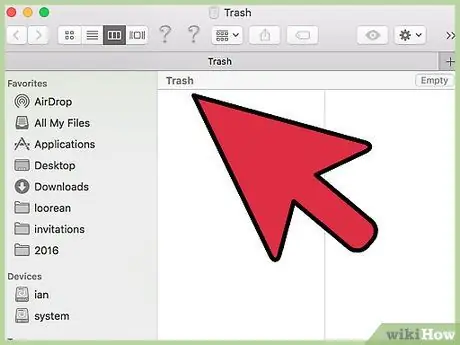
Step 1. Locate the file in “Trash”
“Trash” holds the file before deleting it permanently. If you find a file you want to recover in the “Trash”, you can restore the file to its original location or drag it to another location on your computer.
Step 2. Stop accessing the driver
If your files are not found in the “Trash”, do not save or delete anything from your computer. There is a greater chance of recovering the file if you don't save the new file. This is because when a file is deleted, it is actually just set to be overwritten. If no new data overwrites the original file, it can usually be recovered.
Step 3. Download a data recovery program
Do not download or install the program on the drive where you deleted the files. There are many programs available for Mac OS X that will allow you to search for deleted files. Listed below are some of the most popular programs:
- Data Rescue
- Salvaged files
- Boomerang
- OS X data recovery software has very few options that can be used for free.
Step 4. Start the computer with image data recovery software
Some data recovery programs take the form of a “bootable” image that ignores the OS X operating system. Starting from this image allows the data recovery software to find more data.
- Insert a “bootable” disc into the Mac.
- Restart the computer while holding down the C key.
- Hold down the C key until the Apple logo appears. Your computer will immediately open the data recovery program.
Step 5. Connect the recovery driver
For Mac recovery tools to work, you must connect a separate USB drive or internal drive. If you are using an external driver, make sure that it is at least a USB 2.0, USB 3.0, or Firewire device, USB 1.0 can slow down the recovery process.
The connected drive must have at least 2% of the target drive's storage space

Step 6. Specify the scan settings
You will be asked to select a location where you want to scan for files, make sure you select the hard drive where the files are deleted. You will also usually be given a choice between “Quick scan” or “Deep/Full scan”.
- Most of the files found during the “Quick scan” can be recovered, and the process is quite fast. It is recommended to do "Quick" first.
- “Deep scan” finds more files than “Quick scan”, but it takes a lot longer. Large hard drives and slow computers will take all day to complete a “Deep scan”.
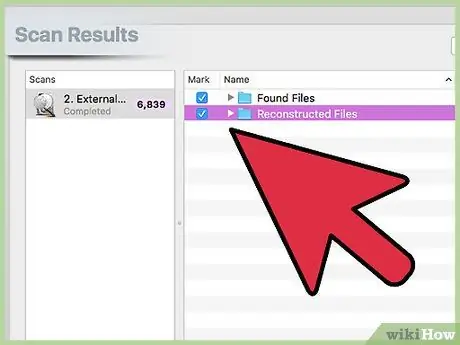
Step 7. Select the files you want to recover
When the scan is complete, there will be a list of files that can be recovered. Use the “Preview” option to make sure the file is completely intact before restoring the file.
- File names often change because the file structure is destroyed during the deletion process.
- Many files cannot be recovered because part of the file has been overwritten.
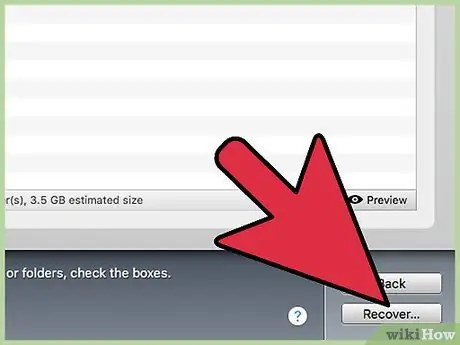
Step 8. Recover files
If you want to recover multiple files, first restore the most important ones. This will ensure that the most important files are not corrupted. The recovered files will be copied to the recovery drive you connected earlier.
Method 3 of 3: Linux
Step 1. Stop accessing the driver
There is a greater chance of recovering the file if you don't save the new file. This is because when a file is deleted, it is actually just set to be overwritten. If no new data overwrites the original file, it has a better chance of being recovered.

Step 2. Download the data recovery program to another drive
The most popular Linux recovery program for recovering specific files is PhotRec. This is an open-source program (open source) and can be downloaded for free from the developer (developer).
You must download TestDisk to use PhotoRec
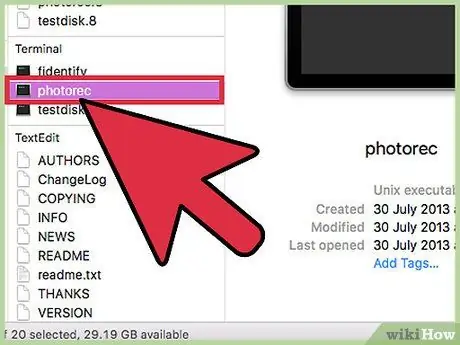
Step 3. Run PhotoRec
Run PhotoRec with “root” access (the account that has access to all commands) via the command line. Use the “sudo” command to gain “root” access while running the program.
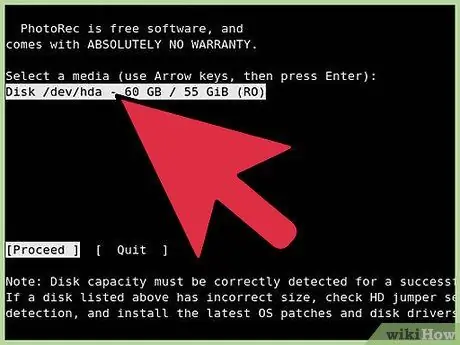
Step 4. Select the disk and partition
When PhotRec starts up, you will be prompted to select the disks and partitions you want to scan. Use the arrow keys to select the location where the file is deleted. Select “Search” and press “Enter” to continue.
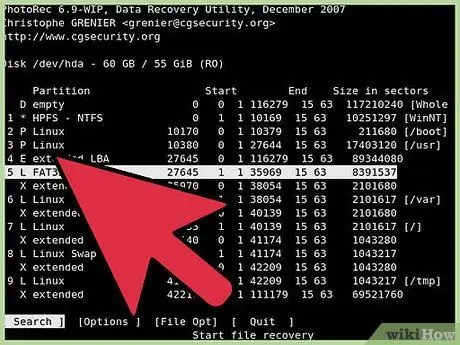
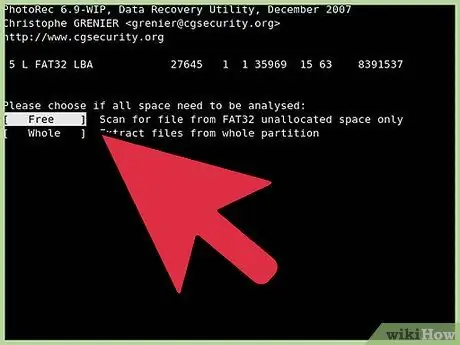
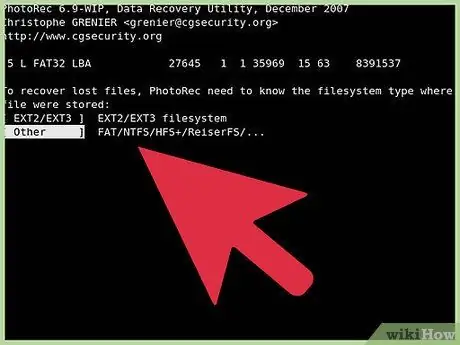
Step 5. Define the file system
PhotRec must know the format of the target driver. Choose the right format from the list. Linux-specific drivers have the EXT2/EXT3 format, while others are in the “Other” category.
Step 6. Choose a location to save the recovered files
PhotRec requires a location to save the recovered files. Make sure that the location is not the same as the target disk so that the files you want to recover are not overwritten.
Step 7. Select the files you want to recover
A list of file types will appear and you can check the files you want to recover. Highlight “Next” and press “Enter” to move to the next page about file types.
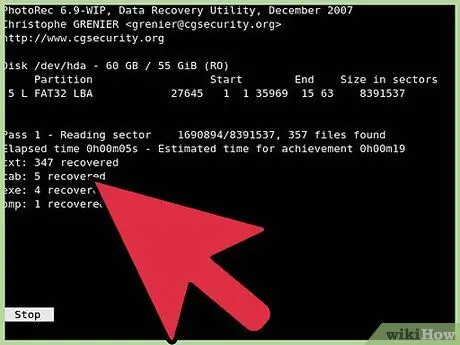
Step 8. Wait for the recovery process to complete
The recovery process may take several hours depending on the size of the drivers and the speed of your computer. When the restore process is complete, you can access the recovered files in the location you have selected.






