- Author Jason Gerald gerald@how-what-advice.com.
- Public 2024-01-19 22:11.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 12:04.
As long as you know the measure of the other two angles, finding the third angle of a triangle is easy. You just need to subtract the sum of the two angles by 180 degrees. However, there are also other ways that you can use to find the third angle of a triangle if the shape of the problem is a little different than usual. If you want to know how to find the third angle of a triangle, follow the guide below.
Step
Method 1 of 3: Using the Measures of the Other Two Angles
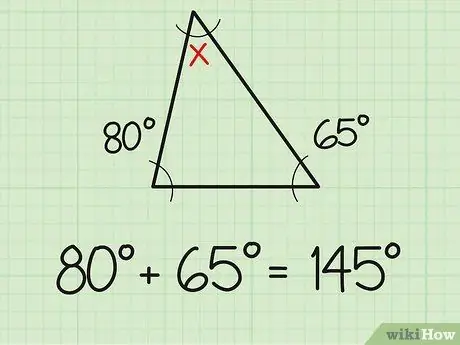
Step 1. Add up the two known angles
One fact you should know is that the sum of the three angles of a triangle is always 180 degrees. So, if you already know the measure of two angles of a triangle, finding the third angle will be as simple as doing simple addition and subtraction problems. First, add up the two angle measures you already know. For example, two known angles measure 80 and 65 degrees. Add the two together (80+65), and you get 145 degrees.

Step 2. Divide that number by 180
The sum of the three angles of a triangle is always 180 degrees. Therefore, the third angle must yield 180 when added to the sum of the two known measures of the angle. In the example above, this means 180-154=35.
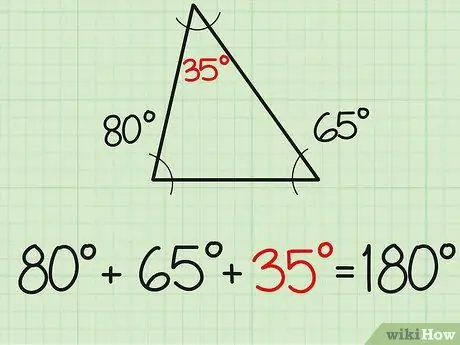
Step 3. Write your answer
Now you have the answer to the third angle (in the example 35 degrees). If you are still in doubt, see for yourself. Add the three angles together, and you should get a result of 180. If you don't, your calculation is wrong. For this example, 80+65+35=180. If it is correct, it means you have solved the problem.
Method 2 of 3: Using Variables
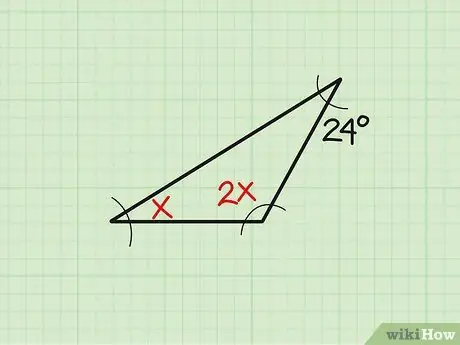
Step 1. Write down the problem
Sometimes, the size of the existing angle is shown in a variable form. Let's take this example: “Find the angle “x” of a triangle if the three angles measure “x”, “2x”, and 24, respectively.” First, write down the problem.
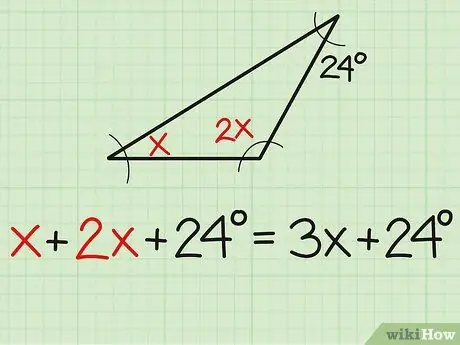
Step 2. Add up all the angle measures
The principle you must remember remains the same. So, first add up the three angles in the problem, namely "x+2x+24 = 3x+24".
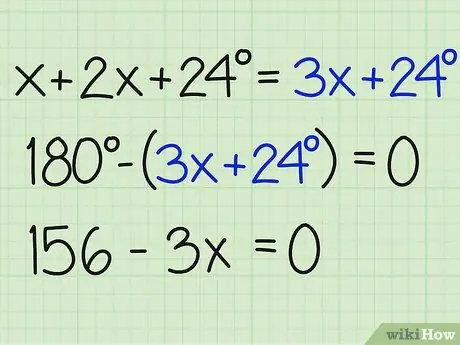
Step 3. Divide the sum of the angles by 180
Now, difference that number by 180 degrees to find x and find out the answer to the problem. Make sure you end the equation equal to zero. Here's how it's written:
- 180-(3x+24) = 0
- 180-3x-24 = 0
- 156-3x = 0
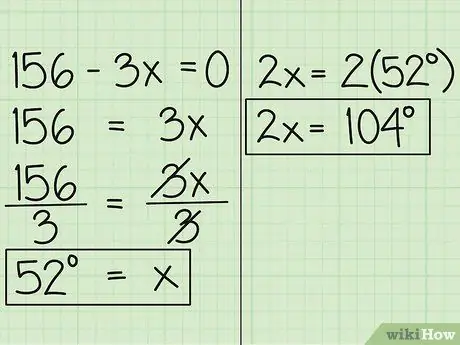
Step 4. Find the value of x
Now, move the variable to the other side of the equation, and you'll get 156 = 3x. Then, divide the equation by 3, so you get x = 52. This means that the measure of the angle expressed in x is 52 degrees. The other angle, expressed in 2x is 52 degrees times 2, which is 104 degrees.
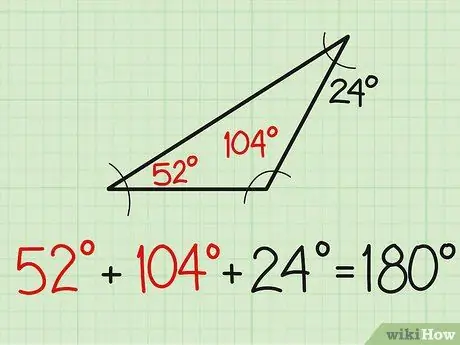
Step 5. Check your results
If you want to make sure your answer is correct, simply add up the three angle measures you've already found the answer to. If the result is 180, it means that your answer is correct. For this example, 52+104+24 = 180.
Method 3 of 3: Using Other Methods
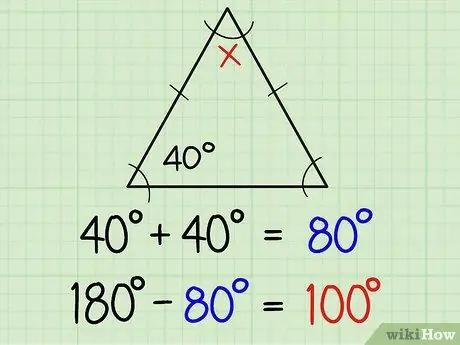
Step 1. Find the angles of an isosceles triangle
An isosceles triangle has two equal sides and two equal angles. Two equal sides are usually marked with a small line in the middle of the side line, which means that the two opposite angles on the line are the same measure. If you already know the size of one angle, you automatically know the other angle. Here's further explanation:
If one of the equal angles is 40 degrees, then the other is 40 degrees. That way you can find all three angles with the difference between the sum of 40+40 (i.e. 80) and 180, or in other words 180-80 = 100
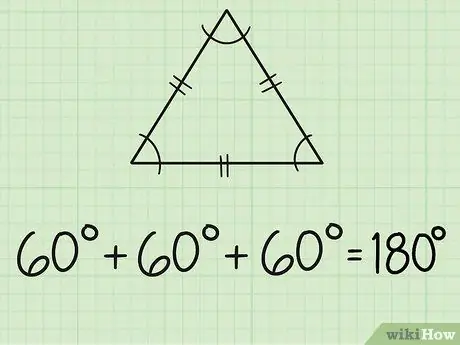
Step 2. Find the angles of an equilateral triangle
An equilateral triangle has three equal sides and three equal angles. Each side is usually marked with two short lines in the middle. Since all three angles are equal, it means that all the angles measure 60 degrees, because 180/3 = 60.
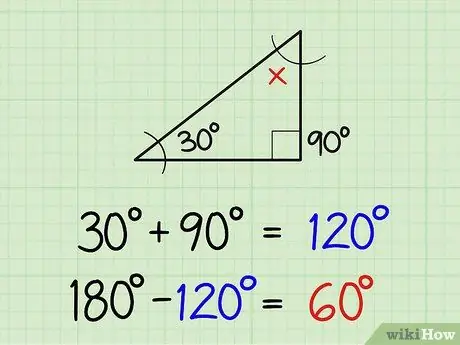
Step 3. Find the third angle in a right triangle
Suppose you get a right triangle, with one of the acute angles measuring 30 degrees. Since the triangle is a right angle, it means that one of the angles, namely the right angle, must measure 90 degrees. Then use the triangle principle, the difference between the sum of the two angles (90+30 = 120) by 180, then you will get 180-120 = 60 degrees.






