- Author Jason Gerald gerald@how-what-advice.com.
- Public 2024-01-19 22:11.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 12:04.
Google Chrome stores various web history data to synchronize your internet surfing experience. You may need to clear your browser history for a number of reasons. Maybe you're visiting a site you shouldn't be accessing. You may want to “tidy up” your online life and delete old autofill data. You may also need to free up memory on the computer. Deleting browsing history can be done directly through Chrome. To get started, press the shortcut “Ctrl”+”H” to access the “History” tab first.
Step
Method 1 of 3: Clearing Entire Browser History
Step 1. Click the Chrome menu in the upper right corner of the browser window
This menu icon looks like three thick horizontal lines stacked on top-some call it a "hamburger."
Step 2. Select “History”
Alternatively, press the “Ctrl” and “H” (“Ctrl”+”H”) keys on the keyboard at the same time. You can see a chronological list of every website you visit through Chrome. The browsing history segment is automatically managed on a daily basis.
Step 3. Select "Clear browsing data"
A dialog box will be displayed: (chrome://settings/clearBrowserData). You will be asked to select the historical content you want to delete, as well as the time span for deleting the content.
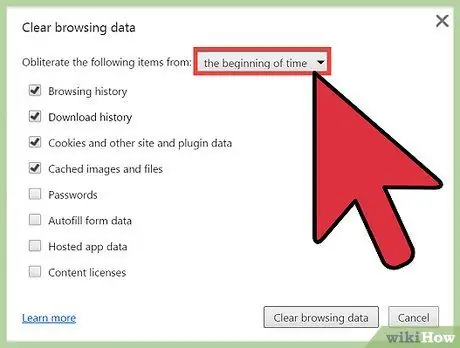
Step 4. Select the amount of history you want to delete
You will be asked to “destroy” history entries from the last hour (“the past hour”), last day (“the past day”), last week (“the past week”), last four weeks (“the last four weeks”), or since Chrome was first used (“the beginning of time”). The last option will delete all browsing history from your Chrome account.
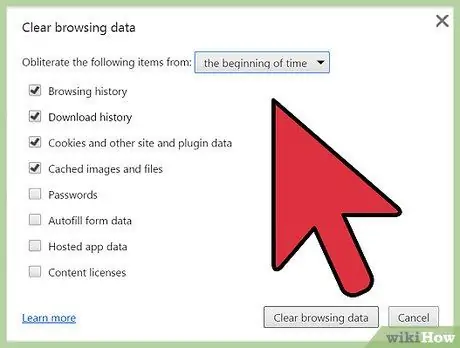
Step 5. Select the type of entry you want to delete
Check the box for each option. All browsing data from the selected category will be deleted after you select "Clear browsing data". You can delete browsing history, download history, cookies and site/add-on data ("Cookies and other site and plug-in data", cached images and files, saved passwords, auto-fill data, installed application data, and content license. Usually, deleting your browsing history, download history, and cookies is sufficient. Check the Understanding Web History section of this article for a more detailed explanation of each category.
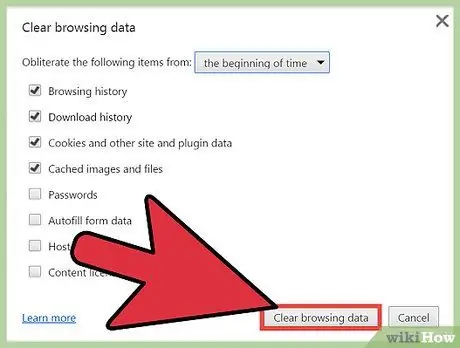
Step 6. Click the "Clear browsing data" button once ready
All selected browser data will be permanently deleted. Therefore, double check the checked boxes before you click the button.
Method 2 of 3: Understanding Web History
Step 1. Understand the specific types of web history that can be deleted
You will be required to delete your browsing history, download history, cookies and site/add-on data, cached images and files, saved passwords, auto-fill data, installed application data, and content licenses. Actually, you don't need to delete all data from each of these categories, depending on the reason for the history deletion. Usually, deleting browsing history, download history, and cookies will suffice.
Step 2. Clear browsing history
Clearing your browsing history will delete the recorded web addresses you have visited on your computer, cached text for those pages, page snippets as images displayed on new tab pages, and recorded IP addresses from the pages you visited.
Step 3. Delete download history
The list of files you downloaded via Google Chrome will be deleted, but the original files will remain. If you've downloaded sensitive files, but have hidden them on your computer, deleting your download history can further secure those files. Also, deleting download history can free up a bit of memory for other apps (depending on how much content has been downloaded).
Step 4. Delete cookies and site/add-on data ("Cookies, site, and plug-in data"):
- Cookies: This content refers to files stored on your computer from the websites you visit. These files contain user information, such as website preferences or profile information.
- Site data: This data refers to HTML5 enabled content, including application cache, web storage data, web SQL database entries, and indexed database entries.
- Add-on data: Data on the client stored by add-ons using the NPAPI ClearSiteData API.
Step 5. Delete images and files stored in the browser cache
The cache contains the text and content of web pages you've visited via Google Chrome. Clearing the cache will delete these files from the computer. Browsers save web page elements to speed up page load times the next time you visit the respective page. Therefore, when you clear your cache, the websites you normally visit may take a little longer than usual to load.
Step 6. Delete saved passwords
If you perform a deletion, all recorded usernames and passwords will be deleted from the browser. If you are using a Mac computer, the recorded password will also be removed from Keychain access. If you wish to delete your password, make sure you have recorded it elsewhere or logged into your account via another browser/device. Don't get locked out of important accounts because you forget your username or password, which are usually auto-filled.
Step 7. Clear the auto form filling data
This delete option will clear any autofill entries, as well as any history or recorded text that you entered on the web form. This deletion itself can “tidy up” forms on certain services or sites. For example, if your shipping address form is autofilling with addresses that are no longer active, you can delete the autofill entry. However, keep in mind that you will need to re-enter the information that must be provided manually, such as your name, address, credit card number, and contact information. It might be inconvenient when you delete this data, unless the autofill entries are annoying.
Step 8. Clear data from installed apps
When the box is selected, the app data you added to Chrome from the Chrome Web Store will be deleted. This data includes content on local storage space used by Gmail Offline.
Step 9. Deauthorize content license
With this cancellation, Flash Player will not play protected content that you have previously enjoyed, such as movies or music that you have purchased. The Google Chrome support team recommends deauthorizing content licenses before you sell or donate your computer.
Method 3 of 3: Removing Specific Content from Search Data
Step 1. Delete certain sites from browsing history
Step 2. Visit the “History” tab via Chrome
Press “Ctrl”+”H” or use the menu in the upper right corner of the browser window.
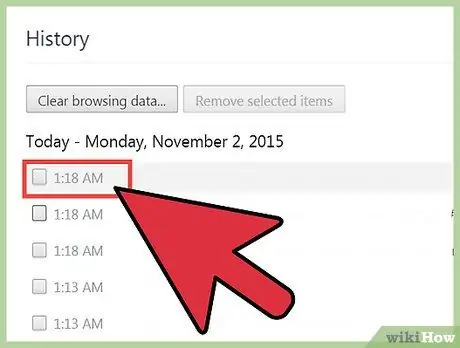
Step 3. Select the browsing data entry you want to delete
Click the box next to each entry that you want to delete. You can select as many entries as you need. In addition, you can also select some site data by holding down the " Shift " key while clicking a box, then clicking the box at the bottom of the list. Use the search field at the top of the “History” tab to search for the link or keyword entry you want to remove.
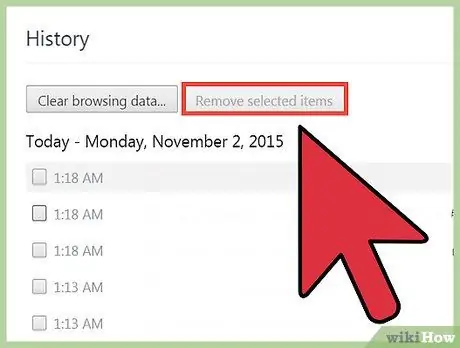
Step 4. Press "Remove selected items" button
This button can only be clicked if you have selected at least one website to delete.
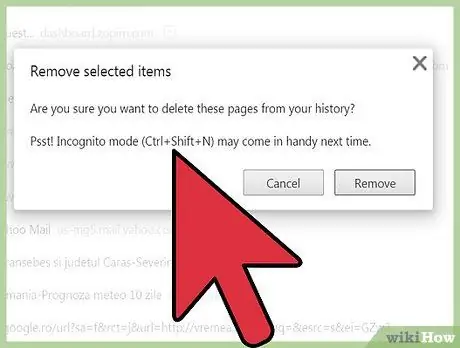
Step 5. Make sure you really want to delete the selected page from your browser history
You will see a pop-up dialog box with the message “Are you sure you want to delete these pages from your history?”. Feel free to deselect and recheck the selection so you don't delete important entries or data. Once you are sure, you can continue with the deletion process.
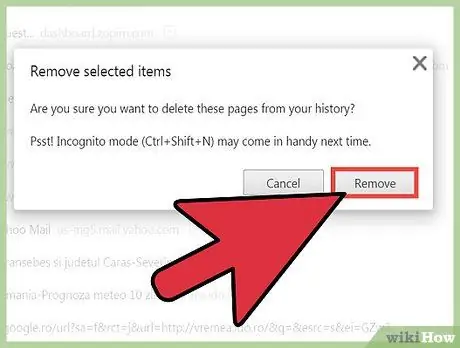
Step 6. Click "Remove"
Chrome will permanently delete the selected sites from your browsing history.
Tips
- Use incognito mode (incognito mode via shortcut “Ctrl”+” Shift”+”N”) when you want to browse sensitive sites. When using inkognito mode, Chrome will not save browsing history. This means that you can visit the website you want in secret. However, keep in mind that if someone can access your IP address, they will still be able to see the sites you visit, regardless of the browsing history entries you delete from your computer.
- If you can't find the link you want to remove, type the keyword for the link (or the link itself if you can remember) into the search field.






