- Author Jason Gerald gerald@how-what-advice.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 10:50.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 12:04.
A histogram is a graph that shows the frequency, or amount of something that happened in a certain time interval. Histograms are similar to bar graphs; however, the area represented by the histogram is used to graph the number of occurrences of a set of numbers. You may want to use a histogram to show continuous data such as time, measurements, and temperature. However, the problem with histograms is that it is difficult to compare the two data sets and the exact data cannot be read from the graph. Knowing how to draw a histogram will be helpful for students demonstrating the statistical findings of a project as well as for business professionals.
Step
Method 1 of 3: Drawing by Hand

Step 1. Using a ruler, draw the basic axes
These axes are the vertical and horizontal lines that form the baseline of the histogram. If you find it difficult to make a right angle where the two axes intersect, then use this trick: use the edge of a piece of paper!

Step 2. Measure the group
In a histogram, data is represented in the form of groups. These groups are evenly distributed, so you need to draw a group marking line along your x-axis.
For example: 0-4 apples, 5-9 apples, 10-14 apples, and so on at 1, 2, and 3 along the axis
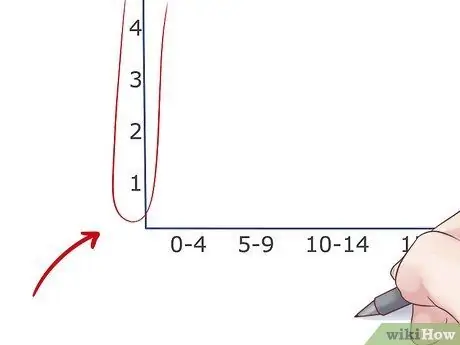
Step 3. Measure the vertical axis
The vertical axis in a histogram always shows the frequency. Time measurement is needed, but it depends on the direction of your data (but the numbers still need to be drawn the same distance). Just make sure you leave some extra space at the top to make your chart easier to read.
- If the upper bound of your histogram is 54, for example, you should set the highest value on your axis to 60.
- If the frequency doesn't start up to a high enough number, you can omit a lot of the numbers below it. For example, if the first frequency is 32, you can start the graph from 25 or 30.
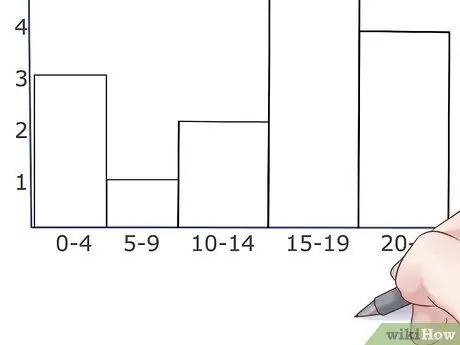
Step 4. Draw the graph
Draw a horizontal top line for each interval or group thinly, at the height of the data measurement. Then, draw the bar in the middle of the data points represented. Make sure that the bars depicted are the same size and width as each other. Usually, histogram bars touch each other, but if you don't have a result for a particular group, then don't think about it.
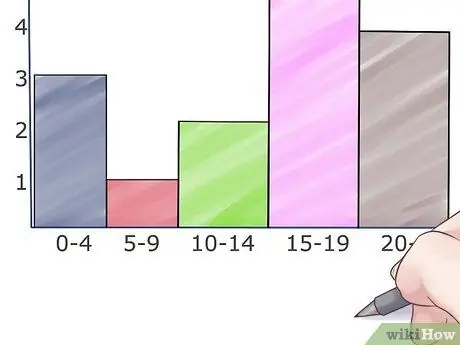
Step 5. Add some color
Add different colors to the histogram rectangle with colored pencils, markers, or crayons to distinguish the intervals from one another.
Method 2 of 3: Using Excel
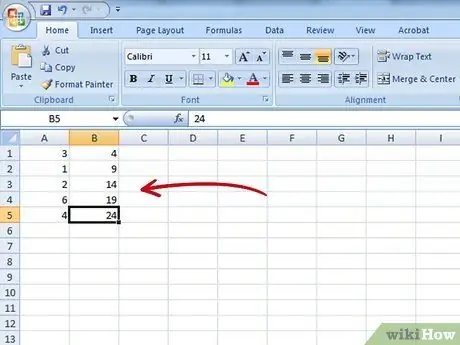
Step 1. Fill in your data
In an Excel document, fill the second column with bins, or the group of data you want (20/30/40, 0/5/10/15, etc.) with one group per box. Fill in the first column with the yield frequency of each group (which is called the level), or the height you want the bar image of each group to be.
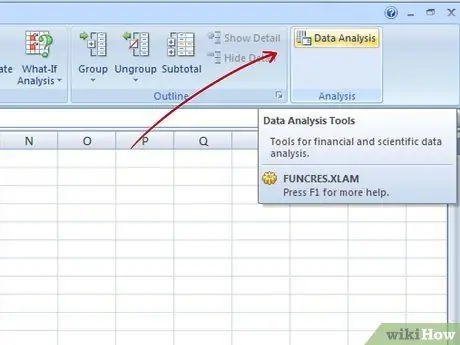
Step 2. Perform data analysis
Click Tools → Data Analysis. This feature is not always a standard feature in Excel so you may need to install it using the Add-ins option.
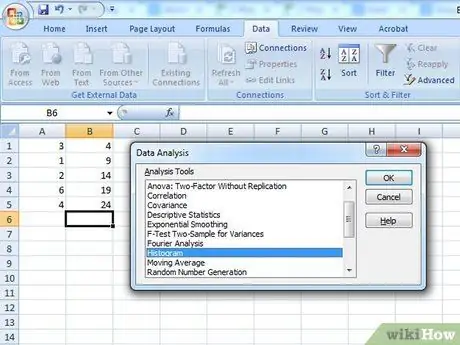
Step 3. Select the histogram
Select the histogram option in the Data Analysis menu and then click OK.
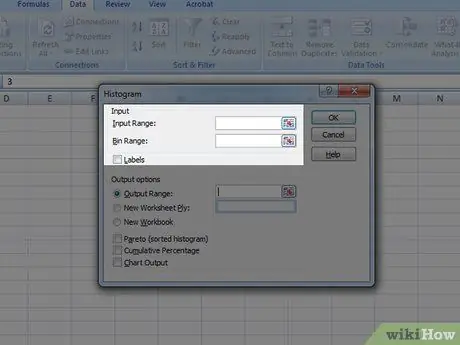
Step 4. Adjust the input data and its bin range
You need to use the menu to select which column is which section.
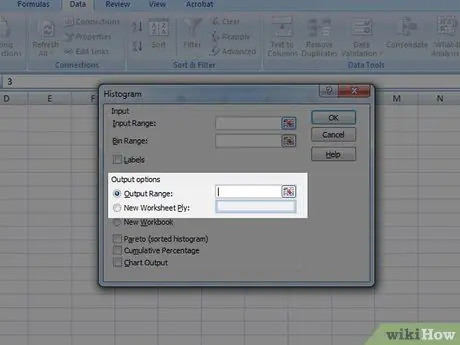
Step 5. Select the output graph
Select the output graph button and then press OK.
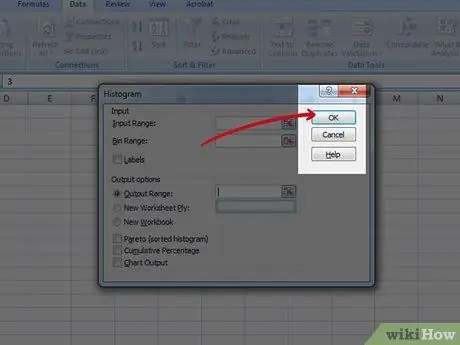
Step 6. Done
Enjoy your graphics. Don't forget to save it.
Method 3 of 3: Using Online Programs
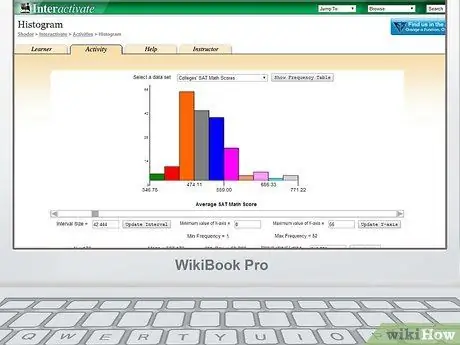
Step 1. Go to a website that can create histograms
We recommend using this one.
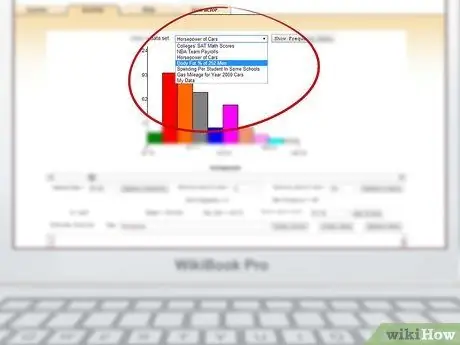
Step 2. Choose a predefined format
There is a drop down menu at the top of the chart that will give you some sample charts that you can populate with your own data. Another way is that you can create an entire chart from scratch.
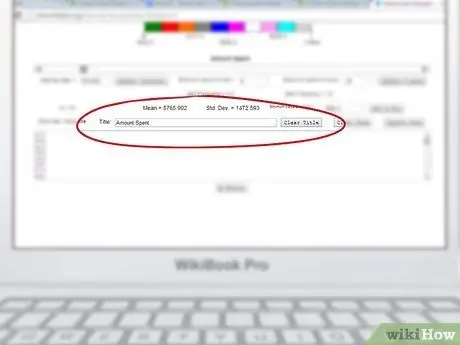
Step 3. Name the chart
You will see a box labeled Title in the middle of the page. You should name your chart in that box.
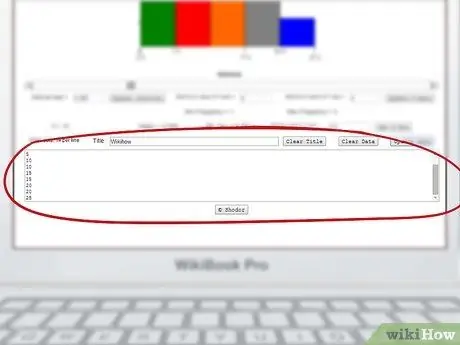
Step 4. Enter your data into the box at the bottom
You'll see a large box below the title bar, at the bottom of the page. Enter every data point you have, with one data point per line (so…5, 5, 5, 10, 10, 15, 15, 20, 20, 25, etc.).
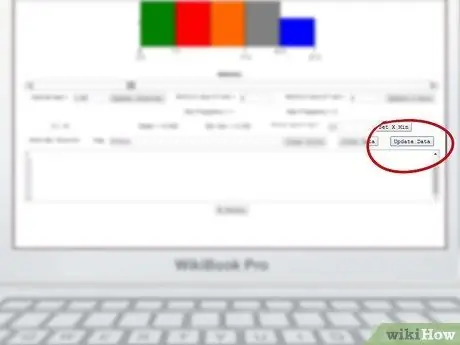
Step 5. Click Update Data
Click the Updata Data button above the data box.
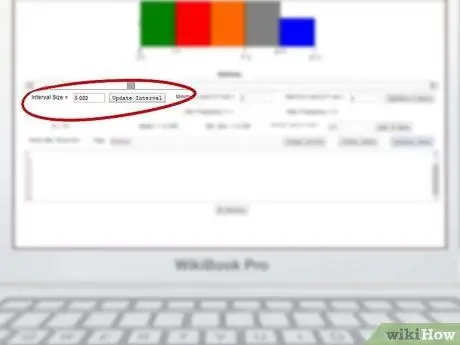
Step 6. Set the frequency
The graph should automatically adjust its frequency to your data, but you can also manually set the interval spacing and maximum and minimum values for the axes.
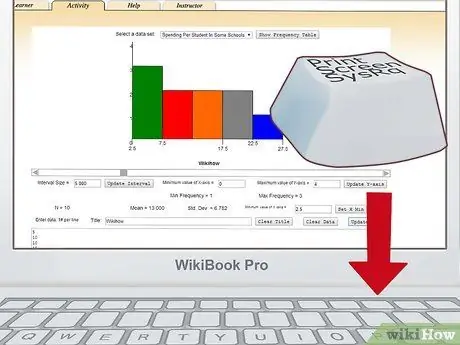
Step 7. Print or save your graphic
Use the print screen function on the keyboard to take a picture of the entire graphic. Paste and crop the image in MS Paint or any basic drawing software you have on your computer. Save this image and print it if you want.
Tips
- Don't forget to name the y and x axes to make sure the information is correct.
- When calculating the sum of each set of intervals, it helps if you cross the numbers in the data so you don't count them twice.
- When drawing a histogram, be sure to use a ruler to draw the lines so that all lines are straight and neat.






