- Author Jason Gerald gerald@how-what-advice.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 10:50.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 12:04.
This wikiHow teaches you how to install a program from a DEB package file on a Debian, Ubuntu, or Mint Linux operating system. Files with.deb extension can be installed using the GDebi Package Installer, Ubuntu Software Manager (Ubuntu only), Apt, and Dpgk.
Step
Method 1 of 4: Using Ubuntu Software Manager

Step 1. Double-click the. DEB file
If you are using Ubuntu with a graphical user interface (GUI), this method will walk you through one of the most convenient ways to install DEB package files.
If you experience problems with programs/support elements (dependencies) while using this method, try using the GDebi Package Installer or Dpkg
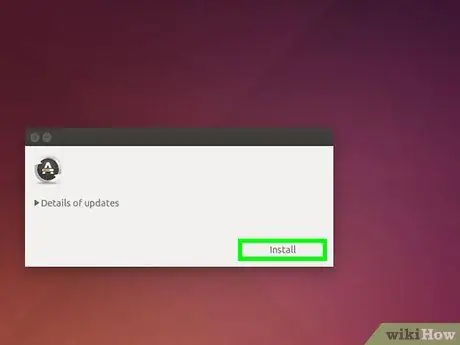
Step 2. Click the Install button
The authentication window will be displayed.
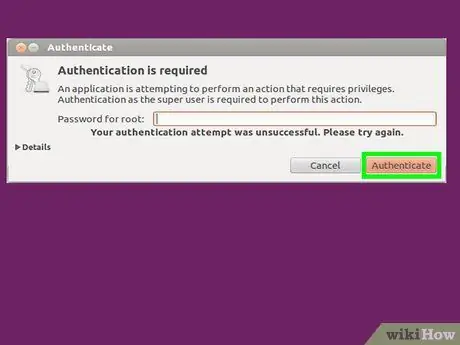
Step 3. Enter the password and click Authenticate
The installation process will begin. Once done, you can see a confirmation message.
Method 2 of 4: Using the GDebi Package Installer
Step 1. Install GDebi if you haven't already
GDebi is one of the most trusted programs for installing DEB package files due to its ability to manage programs/support elements. If you're using Linux Mint, GDebi is already installed and set up as your computer's main package manager. If you are using Ubuntu or Debian, you will need to install it yourself (or follow another method). To install GDebi:
- Press Ctrl+Alt+T to open a Terminal window.
- Type in sudo apt-get update and press Enter or Return.
- Enter the password when prompted.
- Type in sudo apt install gdebi-core and press Enter or Return.

Step 2. Open a Terminal window
If you are logged into a shell account, move on to the next step. Otherwise, you can press Ctrl+Alt+T to open a Terminal window (in most window managers).
- If you are using Linux Mint, you can install the DEB file at this point by double-clicking the file in the file manager window and selecting “ Install Packages ”.
- If your computer is running Ubuntu or Debian and you want to use the GDebi GUI, open a file manager window, right-click the DEB file, and select “ Open With Other Application " Click " GDebi ” when prompted and select “ Install Packages ” to complete the installation.
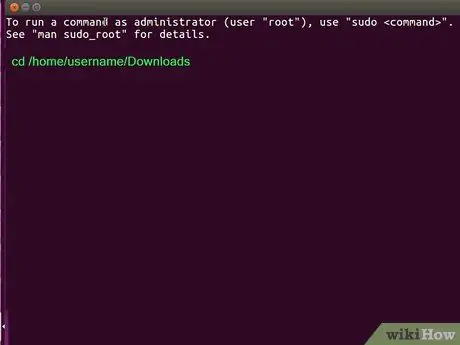
Step 3. Use cd to access the DEB file storage directory
For example, if you saved the file to the /home/username/Downloads directory, type cd /home/username/Downloads and press Enter or Return.
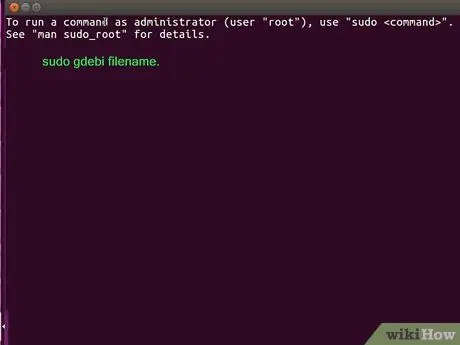
Step 4. Type in sudo gdebi filename.deb and press Enter or Returns.
Replacename.deb file with the name of your DEB file. The DEB package and all associated supporting elements will be installed.
Method 3 of 4: Using Dpkg

Step 1. Open a Terminal window
If you are logged into a shell account, move on to the next step. Otherwise, you can press Ctrl+Alt+T to open a Terminal window (in most window managers).
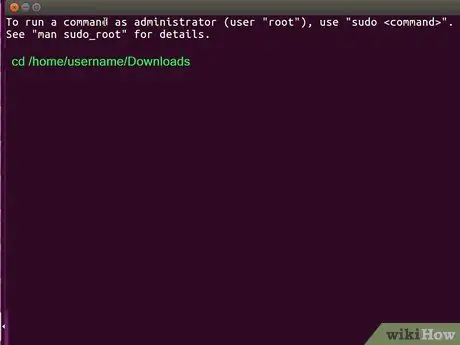
Step 2. Use cd to access the DEB file storage directory
For example, if you saved the file to the /home/username/Downloads directory, type cd /home/username/Downloads and press Enter or Return.
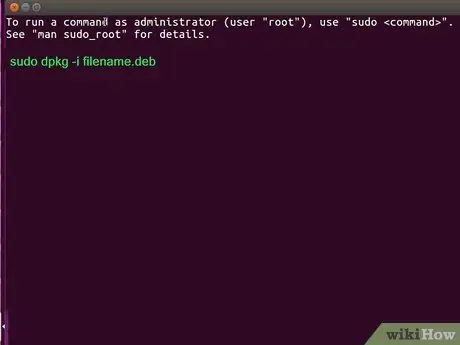
Step 3. Type in sudo gdebi filename.deb and press Enter or Returns.
Replacename.deb file with the name of your DEB file. This command works to install DEB packages.
If this is your first time running a command using sudo in Terminal, you will need to enter your password when prompted before you can continue
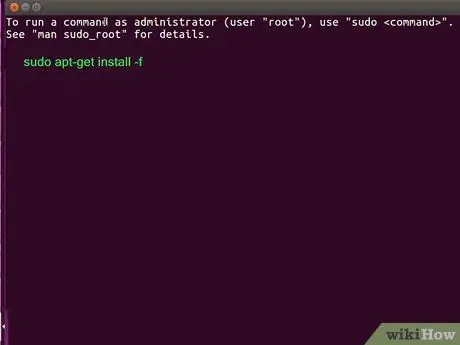
Step 4. Resolve errors in programs/supporting elements or dependencies (optional)
If the previous command returned an error regarding the program/supporting element, run the command sudo apt-get install -f to resolve it.
Method 4 of 4: Using Apt

Step 1. Open a Terminal window
If you are logged into a shell account, move on to the next step. Otherwise, you can press Ctrl+Alt+T to open a Terminal window (in most window managers.
Apt is usually used to download and install programs from outside sources, but you can use it to install local DEB packages using a special syntax
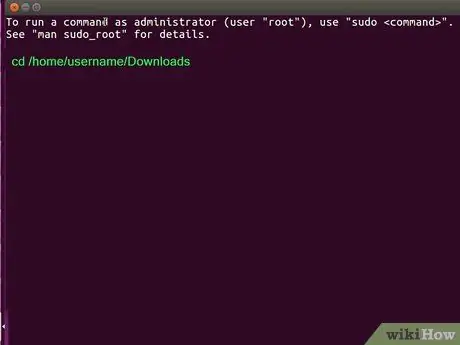
Step 2. Use cd to access the DEB file storage directory
For example, if you saved the file to the /home/username/Downloads directory, type cd /home/username/Downloads and press Enter or Return.
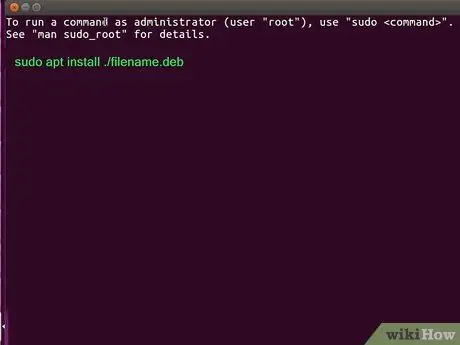
Step 3. Run the install command
Type sudo apt install./filename.deb and press Enter or Return. The program will be installed afterwards.
- Make sure you replace filename.deb with the filename and pay attention to the./ symbol that comes before it. If you don't add it, the Apt tool will look for packages on outside sources.
- If this is your first time running a command using sudo in Terminal, you will need to enter your password when prompted before continuing.






