- Author Jason Gerald gerald@how-what-advice.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 10:50.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 12:04.
To move a list or table of data from Word to Excel, you do not need to move individual pieces of data into the cells of an Excel spreadsheet (worksheet). You can simply format your document properly in Word, then the entire document can be imported into Excel with just a few clicks.
Step
Method 1 of 2: Converting Lists
Step 1. Understand how the Word document will be converted
To import a document into Excel, certain characters are used to determine what data will enter the cells in the Excel worksheet. By performing a few formatting steps before importing, you can control the appearance of the worksheet and minimize the amount of manual formatting that has to be done. This is especially useful if you are importing a long list from a Word document into Excel.
This method works best when there are several entries in the list, each with a similar format (a list of addresses, phone numbers, email addresses, etc.)
Step 2. Make sure there are no formatting errors in the document
Before starting the conversion process, make sure that each entry is formatted the same way. You must correct any punctuation errors or rearrange any entries that do not match. This is to ensure the data transfer process runs smoothly.
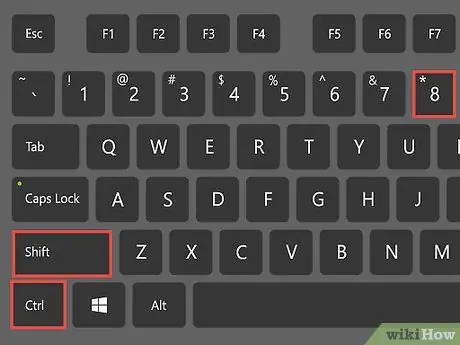
Step 3. Display the formatting characters in the Word document
By displaying normally hidden format characters, you can determine the best way to separate each entry. You can display formatting characters by clicking the Show/Hide Paragraph Marks button on the Home tab, or by pressing Ctrl+⇧ Shift+*.
Most lists have one paragraph mark at the end of each line, or at the end of a line, or in a blank line between entries. You will use this sign to enter the distinguishing character of the cells in Excel
Step 4. Replace the paragraph marks between entries to remove extra spaces
Excel will use spaces between entries to define rows, but you should remove them at this time to help with the formatting process. Don't worry, you'll be adding it back soon. This step works best if you have one paragraph mark at the end of the entry and one space between entries (two consecutive spaces).
- Press Ctrl+H to open the Find and Replace window.
- Type ^p ^p into the Find field. This is the code for two consecutive paragraph marks. If each entry is a single line and there are no blank lines in between, use only one ^p.
- Enter the delimiter character into the Replace field. Make sure that this character is not a character in the document, such as ~.
- Click Replace All. You'll notice that these entries combine themselves, but leave it alone as long as the delimiter character is in the right place (between each entry)
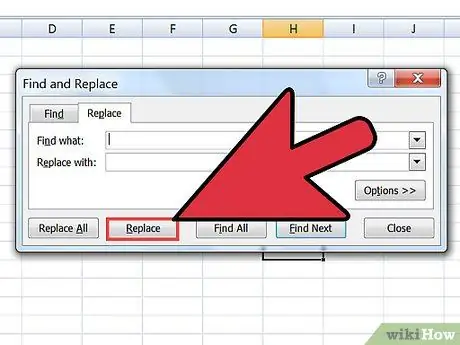
Step 5. Separate each entry into separate columns
Now the entries appear in separate lines. You must specify the data that will appear in each column. For example, if each entry in the first line is a name, in the second line is a street address, and in the third line is a country and postal code, do the following:
- Press Ctrl+H to open the Find and Replace window.
- Remove one of the ^p marks in the Find field.
- Replace the character in the Replace field with a comma,.
- Click Replace All. This will replace the remaining paragraph symbols with a comma separator, which will separate each line into a column.
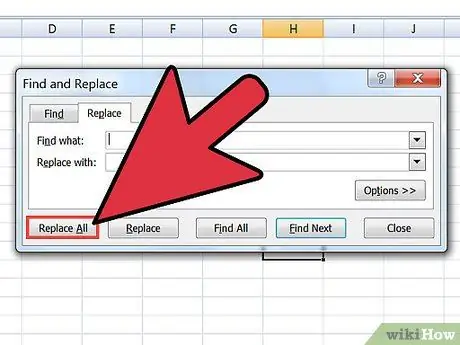
Step 6. Change the delimiter character to complete the formatting process
After you've completed the two Find and Replace steps above, the list will no longer look like a list. They will all be on the same line and have a comma between each piece of data. The Find and Replace step will return the data back into a list form but still have commas that define the columns.
- Press Ctrl+H to open the Find and Replace window.
- Enter ~ (or whatever character you chose at the beginning) into the Find field.
- Enter ^p into the Replace field.
- Click Replace All. This will make all entries back into individual groups separated by commas.
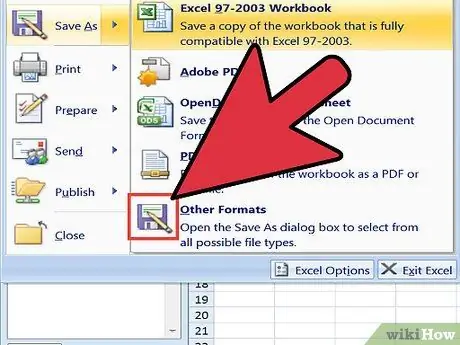
Step 7. Save the file as a plain text file
The entry format is complete and you can save this document as a text file. This is done so that Excel can read and parse your data so that it appears in the correct columns.
- Click the File tab and select Save As.
- Click the Save as type drop-down menu and select Plain Text.
- Name the file and then click Save.
- If the File Conversion window appears, click   OK;.
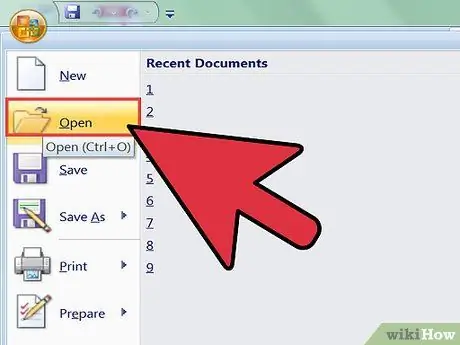
Step 8. Open the file in Excel
Since the file is saved in plain text, you can open it in Excel.
- Click the File tab and select Open.
- Click the Excel All Files drop-down menu and select Text Files.
- Click Next > in the Text Import Wizard window.
- Select Comma in the Delimiter list. You can see how the entries will be separated in the preview at the bottom. Click Next >.
- Select the data format for each column, then click Finish.
Method 2 of 2: Converting Tables
Step 1. Create a table in Word and then enter data into it
For a list of data in Word, you can convert it to a table format and then copy the table to Excel. If your data is already in table format, skip to the next step.
- Select all the text to be converted into a table.
- Click the Insert tab and then click the Table button.
- Select Convert Text to Table.
- Enter the number of rows per row of data in the Number of columns column. If there are blank rows between each row of data, add one to the column total.
- Click   OK;.
Step 2. Check the table format
Word will create a table based on your settings. Check to make sure the table is correct.
Step 3. Click the small + button that appears in the top left corner of the table
This button will appear when you hover your mouse over the table. Clicking this button will select all the data in the table.
Step 4. Press
Ctrl+C to copy data. You can also click the Copy button on the Home tab.
Step 5. Open Excel
Once the data is copied, you can open Excel. If you want to place the data in an existing worksheet, open the worksheet. Place the cursor in the cell you want to make the top-left cell of the table.
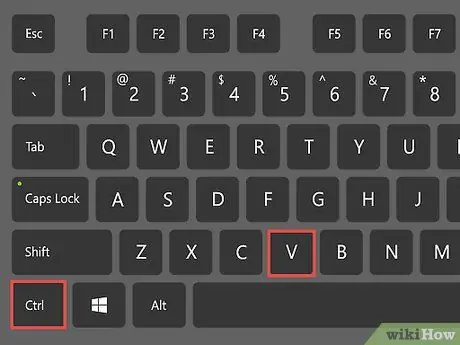
Step 6. Press
Ctrl+V to paste data.
Each of the cells from the Word table will be placed into a separate cell in the Excel worksheet.
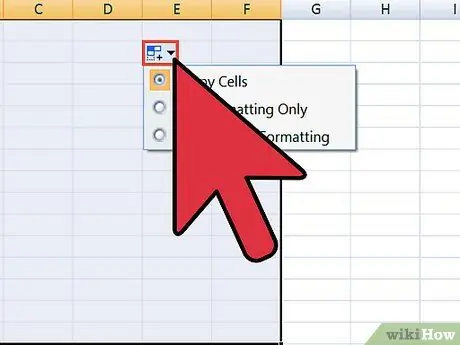
Step 7. Separate any remaining columns
Depending on the type of data you are importing, there may be some additional formatting that you need to do. For example, if you import city addresses, country codes, and postal codes that are in one cell, you can auto-split them in Excel.
- Click the column headings that you want to split. This step will select the entire column.
- Select the Data tab and click the Text to Columns button.
- Click Next > then select Comma in the Delimiters column. If you use the example above, this step will separate the city from the country code and postal code.
- Click Finish to save changes.
- Select the columns that still need to be divided, then repeat this process. Select Space and not Comma as the delimiter. This step will separate the country code from the postal code.






