- Author Jason Gerald gerald@how-what-advice.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 10:50.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 12:04.
Epididymitis is a disease caused by infection of the epididymis. This disease occurs in about 600,000 men per year, most of whom are aged 18-35 years. The most common causes of epididymitis are sexually transmitted infections or STIs, particularly gonorrhea and chlamydia. However, because the epididymis is connected to the urethra, epididymitis can also be caused by other things, such as E. coli. When epididymitis occurs, the scrotum swells so that it looks like a hernia. However, because it is painless, the condition is not caused by a hernia. To recognize the symptoms of epididymitis (and how to treat it), start reading Step 1.
Step
Part 1 of 3: Identifying the Symptoms of Epididymitis
Epididymitis is generally classified into two types: acute and chronic. In acute epididymitis, symptoms last less than six weeks. In contrast, in chronic epididymitis, symptoms last longer than six weeks. Symptoms of epididymitis in each patient are different, depending on the cause.
Early Symptoms

Step 1. Watch for pain in one of the testicles
Pain in the testicles is the most common symptom of epididymitis. At first, the pain may only be felt in one testicle. However, over time, the pain can spread and eventually be felt in both testicles. At the onset of inflammation, the pain usually occurs only at the bottom of the testicle, then gradually extends throughout, and even to both, testicles.
- The type of pain varies, depending on how long the inflammation has lasted. The pain can be sharp or burning.
- Pain sensation is a complicated process caused by increased blood flow, immune system components, and nerve sensitivity due to damage caused by infection.
Step 2. Watch for swelling and redness of the infected testicle
As with pain, swelling and redness may initially occur in only one testicle, then gradually spread to both testicles. Swelling of the testicles can cause the patient to feel pain when sitting.
Infected testicles may become reddish in color and feel hot due to increased blood flow. The increase in fluid also causes the testicles to swell. All of these symptoms usually occur within 3-4 hours of the first signs of infection appearing

Step 3. Watch for symptoms that arise in the urinary system
Symptoms of epididymitis that can be noticed when urinating include:
- Burning pain when urinating
- Feeling the urge to urinate more often than usual
-
Urine contains blood
Most cases of epididymitis caused by infection start as an infection in the urethra which then spreads up along the tract until it reaches the epididymis. Any type of infection that occurs in the urethra can cause the bladder to become irritated, become overactive or damage the walls
Advanced Symptoms

Step 1. Be aware of pain when urinating
As the inflammation gets worse and spreads to surrounding tissues, pain when urinating will begin. In severe cases, there is blood in the urine due to minor bleeding in the urinary tract through which urine passes when you urinate. This of course is not good and feels painful.

Step 2. Watch for urethral discharge
White, yellowish, or clear discharge sometimes appears at the tip of the penis due to inflammation and infection of the urinary tract, especially if caused by an STI.

Step 3. Take body temperature
Inflammation and infection that spreads throughout the body can trigger fever, the body's defense mechanism. Epididymitis that causes fever is a chronic condition, not an acute one.
Fever is the body's way of fighting infection. If the body temperature is more than 38°C, consult a doctor as soon as possible
Part 2 of 3: Studying the Causes and Risk Factors of Epididymitis

Step 1. Consider age, health, and living habits
Epididymitis is most common in young, sexually active men with multiple partners. Other groups that are also at risk for epididymitis are:
- Men who ride motorcycles or who usually sit for long periods of time (eg having a passive job) are at increased risk of developing epididymitis.
- Patients with low/impaired immune systems, such as HIV patients, are prone to infection and inflammation.
- Epididymitis that occurs in men older than 35 years or boys younger than 18 years is more often caused by E. coli than STIs.

Step 2. Patients who have recently had surgery or urethral procedures are also at risk of developing epididymitis
Any surgical operation or procedure (eg the use of a catheter) on the urethra is prone to causing inflammation. The inflammation may extend to the surrounding area; for example, if it spreads to the epididymis, it can cause epididymitis.

Step 3. Congenital abnormalities are also a risk factor for epididymitis
Congenital abnormalities in the urinary tract can make the area and surrounding tissues susceptible to inflammation and infection. The slightest change in the size or position of the urinary tract can cause a variety of problems, including epididymitis.
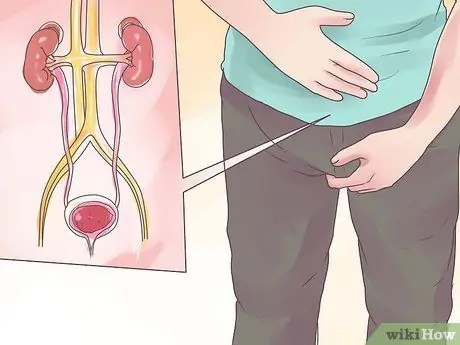
Step 4. Urinary tract infection increases the risk of epididymitis
Urinary tract infections can cause surrounding tissues, including the epididymis, to become inflamed. Urinary tract infections are the perfect breeding environment for organisms that cause epididymitis.
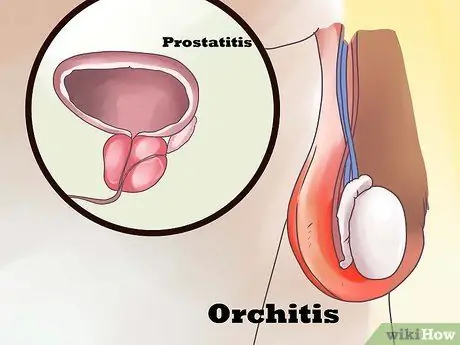
Step 5. Orchitis and prostatitis increase the risk of epididymitis
Prostatitis is inflammation of the prostate gland. The inflammation can extend to the ejaculatory ducts and the epididymis, causing epididymitis.
Orchitis is inflammation of the testicles. As described above, inflammation can extend to surrounding tissues, such as the epididymis
Part 3 of 3: Treating Epididymitis

Step 1. Use antibiotics
Treatment of epididymitis depends on the cause. Since most cases of epididymitis are caused by infection, your doctor may prescribe antibiotics. The type and dose of antibiotics prescribed depends on whether the infection is a sexually transmitted disease or another disease.
- If you have a gonorrhea or chlamydial infection, your doctor may prescribe a single dose of ceftriaxone 100 mg injected intramuscularly, then doxycycline 100 mg, in pill form, taken twice daily for ten days.
- In some cases, the doctor may replace doxycycline with a single dose of azithromycin 1 g.
- Epididymitis caused by E. coli may be treated with ofloxacin 300 mg taken twice daily for ten days.

Step 2. Use anti-inflammatory drugs
Anti-inflammatory drugs can relieve pain from epididymitis. This method is practical because anti-inflammatory drugs, such as ibuprofen, are often available at home and are relatively effective. However, over-the-counter analgesics, such as ibuprofen, should not be taken for more than ten days.
Taking ibuprofen 200 mg every 4-6 hours is effective in relieving pain and inflammation associated with epididymitis in adults. Increase the dose of ibuprofen to 400 mg if necessary
Step 3. Rest
Resting in bed for a few days helps relieve pain from epididymitis. Lying in bed minimizes pressure on the genital area thereby relieving pain. As much as possible, keep the testicles elevated to relieve the symptoms of epididymitis.
When lying down or sitting, place a rolled up towel or T-shirt under the scrotum to minimize pain

Step 4. Use a cold compress
Applying a cold compress to the scrotum effectively reduces blood flow so that inflammation subsides. Wrap a cold compress with a towel, then apply it to the scrotum for 30 minutes. Cold compresses should not be applied for more than 30 minutes to prevent damage to the skin.
Ice cubes should not be placed directly on the skin. Putting ice cubes directly on the skin will only cause problems

Step 5. Use the sitz bath method
To do this method, fill the tub with warm water to a height of 30-35 cm. Sit in the tub for about 30 minutes. The warm water temperature helps the body fight infection because it causes an increase in blood flow. This method can be done as often as needed.

Step 6. Use herbal remedies
Three types of herbs that have been proven to be effective in treating epididymitis are:
- Echinacea. Echinacea is effective for reducing inflammation and fighting infection. Consume this herb in the form of tea. Boil 1 tbsp dried Echinacea flowers and 1/4 tbsp dried peppermint in a pot of water. Drink Echinacea tea daily for pain relief.
- Pulsatilla. Pulsatilla is available in two forms: liquid extract and tea. Pulsatilla has anti-inflammatory properties. Use 1-2 ml of Pulsatilla extract three times daily. To make Pulsatilla tea, prepare 1 tsp of dry Pulsatilla and 240 ml of boiling water. Steep the dried Pulsatilla in boiling water for 10-15 minutes.
- Equisetum. Equisetum is also effective for treating epididymitis. This herb has antimicrobial properties and can help reduce inflammation. Brew 1-3 tablespoons of dried or fresh Equisetum leaves in 240 ml of boiling water for 5-10 minutes. Strain and discard the Equisetum leaves. Drink the brewed water.
Tips
- Wear the proper jockstrap. The jockstrap supports the scrotum well, thereby relieving pain. Briefs can support the scrotum better than boxers.
- Symptoms suspected to be caused by epididymitis should be consulted with a doctor as soon as possible. If not treated immediately, epididymitis can cause severe disorders, such as infertility.
- Symptoms of chronic epididymitis vary. In some cases of chronic epididymitis, pain in the testicles is the only symptom. Pain caused by chronic epididymitis is often gradual and milder than if caused by acute epididymitis.
Warning
- Do not have sex while symptoms of epididymitis persist. Having sex while having epididymitis can make the infection worse and the pain worse.
- Testicular torsion may initially be mistaken for epididymitis. However, in testicular torsion, blood flow is cut off and the testicle may eventually die. Since the symptoms of the two conditions are very similar, consult a doctor as soon as possible to confirm a diagnosis.






