- Author Jason Gerald gerald@how-what-advice.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 10:50.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 12:04.
Are you having a toothache? If so, maybe you are currently looking for a fast and effective way to get rid of it, both moderate and unbearable toothaches. You should consult your dentist if the pain doesn't go away or gets worse, but in the meantime, you can try some of the first steps and alternative home remedies to relieve the pain.
Step
Part 1 of 4: Taking Quick Action

Step 1. Clean the food residue
One of the first things you can try-even before trying home remedies-is to get your teeth cleaned as soon as possible. Try cleaning your teeth of food debris that is trapped between your teeth and that may be causing pain.
- Use dental floss carefully to remove food debris between the teeth.
- Then, rinse thoroughly. Gargle in quick motions using warm water to remove any remaining food residue. Spit out the mouthwash when you're done.

Step 2. Do not use the sore tooth to chew
Before getting treatment, find easy ways to control the pain. Avoid chewing in the mouth where the sore tooth is, and especially don't chew with the sore tooth.
- Maybe you could try using a temporary patch. If a tooth is damaged or cavities, you can temporarily fill it with softened gum or dental wax until a more permanent solution is found.
- In pharmacies, temporary dental fillings are also available. Dental fillings that are sold are made of zinc oxide or a similar material, and will relieve pressure and last up to two weeks.
Step 3. Take painkillers
Use over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen/paracetamol or ibuprofen to reduce pain before going to the dentist. Follow the directions for use on the packaging to find out the right dose
- Generally you will need to take one or two pain relief pills every four or six hours. The exact dose is different for each brand and type of drug.
- You can buy painkillers at any pharmacy or drug store.
- Do not apply aspirin or other painkillers directly to the gum tissue, as this can cause damage.

Step 4. Use a topical pain reliever
Another option is an over-the-counter pain reliever ointment. The way it works is by numbing the area around the tooth or by applying it directly to the cavities. The active ingredient is benzocaine. Follow the instructions for use to find out the right amount and how to apply.
- Pain relief ointments such as Orajel are available at many pharmacies.
- Use only pain-relieving ointments specifically for teeth. Other types of ointments can be dangerous if swallowed.
- In some cases, benzocaine can cause a rare but dangerous condition called methemoglobinemia which reduces the amount of oxygen in the blood. Children younger than 2 years of age should not be given drugs containing benzocaine, and adults should not exceed the recommended dose.

Step 5. Use a cold compress
Another quick way to reduce toothache is to numb it with cold temperatures. Cold temperatures will reduce blood flow to the area. The pain you experience will decrease when blood flow decreases.
- Wrap a piece of ice in a plastic bag or cheesecloth and place it on the jaw where the tooth hurts for 10 to 15 minutes.
- Then, take a break of 10 to 15 minutes. After that, reapply the compress on the affected area for as long as needed
- Make sure the affected area feels "normal" again before applying the compress again. If it still feels numb, the tissue around the tooth will be damaged.
Part 2 of 4: Using Temporary Home Remedies

Step 1. Clean the affected area with a clove
Cloves are an old treatment for toothaches, because naturally cloves can cause a numbing effect and are also effective at killing bacteria. You can use whole cloves, ground cloves, or clove oil.
- If using ground cloves, clean your hands first, then place a pinch of ground cloves between the sore gum and the inner cheek. Numbness will arise after the cloves are mixed with saliva.
- If using whole cloves, clean your hands first and place two or three whole cloves in your mouth near the affected area. Once the cloves are softened by the saliva, chew them slowly to get the oil out.
- Alternatively, mix a few drops of clove oil with 1/2 tsp (2.5 ml) of olive oil. Then, dip a sterile cotton ball in it and hold it on the painful part of the tooth or gum.

Step 2. Gargle with salt water
Another way to reduce pain and kill bacteria is to gargle with salt water. Salt can't cure, but it can cleanse the mouth of bacteria and remove moisture from the inflamed gums around the sore tooth, thereby relieving the pain.
- Mix 1 tsp salt (5 ml molten salt) with 250 ml warm water. Allow the salt to dissolve in the water before use.
- Gargle with this solution for 30 seconds and then spit it out. Repeat if necessary.
- After gargling with salt water, you may want to gargle again with plain water. Please rinse again with tap water for 30 seconds.

Step 3. Try garlic or onion
Both are traditional remedies for toothache and are believed to contain antibacterial properties. Onions may cause bad breath, but they will help kill harmful germs in your mouth and reduce pain.
- Squeeze one white bottom clove between the sore tooth or gum and the inner cheek. Hold until the pain subsides.
- Or, slice an onion and place it on the aching tooth.
Step 4. Make the bayberry paste
Bayberry root bark is believed to be a natural antibiotic and contains tannins and flavonoids that function as conditioning. A paste made from a mixture of bayberry and vinegar can relieve toothaches, reduce swelling, and strengthen gums.
- Mash 2.5 cm pieces of bayberry root bark with 1/4 tsp (1.25 ml) vinegar. Increase the amount of bayberry root bark and vinegar as needed to make a paste.
- Apply the paste directly to the affected area and leave it on until the pain goes away. Then rinse with warm water.

Step 5. Make a paste of ginger and cayenne pepper
If your teeth are sore and sensitive, a paste made of ground ginger, chili powder, and water can be applied directly to sensitive teeth to relieve pain. Both of these spices can relieve pain. The effect is stronger when used together.
- Mix a pinch of ground ginger and a pinch of chili powder in a bowl. Add a few drops of water to taste and stir until it forms a paste.
- Dip a sterile cotton ball in the paste. Place the cotton swab directly on the tooth and hold it until the pain subsides or as long as you can-the ginger and chili paste may be uncomfortable.
- Use this paste only on the aching tooth. Do not apply to the gum tissue as it may cause irritation or a burning sensation.

Step 6. Use the myrrh fluid
Myrrh is a resin from a type of thorn tree, and is used in perfumes, incense, and medicine. Myrrh has a refreshing effect that reduces inflammation and also kills bacteria. Therefore, myrrh liquid has long been used as a home remedy for toothaches.
- In a small saucepan, heat 1 tsp (5 ml) ground nuts in 2 cups (500 ml) water for 30 minutes. Strain the liquid and let it cool.
- Mix 1 tsp (5 ml) of filtered myrrh liquid with 1/2 cup (125 ml) water and gargle with the solution five or six times a day.
Step 7. Place the wet tea bag on the affected area
Like bayberry root bark, black or red tea contains conditioning tannins that can reduce inflammation. Peppermint tea also provides a mild numbing effect and can reduce pain. Tea bags are widely used in home remedies for toothache.
- To use tea as a pain reliever, microwave a tea bag in a small container of water for 30 seconds until it's warm. Then, squeeze out the water.
- Press the tea bag against the sore tooth or gum and bite a bit until the pain goes away.

Step 8. Use alcoholic beverages
Let's be clear, we do not recommend that you drink to forget the pain. On the other hand, alcoholic beverages such as vodka, brandy, whiskey, or gin have the ability to numb a toothache when applied directly to it.
- Dip a sterile cotton ball in an alcoholic beverage, such as brandy or vodka, and place it on the aching tooth. You may also need to take a sip of whiskey and soak the liquid in your mouth near the affected area.
- The pain that goes away is only temporary. Also, do not try this technique with pure alcohol as it is not safe to swallow.
Part 3 of 4: Undergoing Professional Treatment from a Dentist

Step 1. Make an appointment with the dentist
Home remedies are not a permanent solution, just to relieve the pain. If your toothache doesn't go away or gets worse, you should seek professional treatment with a dentist.
- Behind the toothache you feel there may be serious problems, including eroded tooth enamel, damaged and cavities, or infection.
- See a dentist if the pain does not go away with home remedies, is accompanied by swelling, fever, or pus, is caused by an injury, or is making it difficult for you to swallow. Also, seek medical attention if you experience jaw pain along with chest pain-the latter may be a sign of a heart attack.
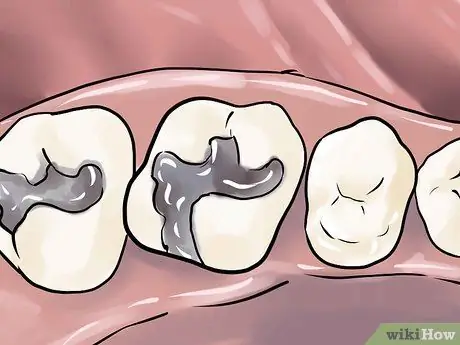
Step 2. Fill your teeth at the dentist
The dentist will examine your tooth and may decide that the pain is due to decaying teeth, meaning that bacterial acids have eroded the tooth enamel and exposed the roots. Or, the current patch may become loose. In either case, your tooth will need to be filled.
- After anesthetizing the tooth and gums, the dentist will first drill and remove the decayed part of the tooth. Then, the hole will be filled with a composite or amalgam filling.
- You can choose the filling material. Composite fillings are usually made of plastic, glass, or porcelain resin and match the color of the teeth. Amalgam fillings are usually made of silver and are stronger, but do not match the color of the teeth.
- Over time, the patch will break or loosen. The dentist will remove the old filling, drill out any newly formed decay if there is one, and apply a new filling.
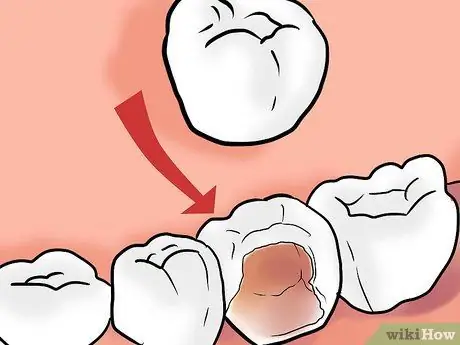
Step 3. Undergo dental crown treatment
Dental crowns, also called caps, are used when a tooth is damaged but can still be saved. Basically a dental crown is an artificial tooth blank that will restore the shape and function of the tooth, and protect it from further damage. Dental crowns are needed in cases of severe damage such as pulpitis (inflammation of the dental pulp), abrasion (eroded tooth), tooth fracture, or severe infection.
- If the decay has spread, or in the case of a root canal, the filling is no longer sufficient and the dentist will use a dental cap or crown.
- Usually the dentist will give you a local anesthetic. Then the tooth will be aligned and replaced with a crown made from your dental impression. Dental crowns are made of the same restorative material as regular fillings.
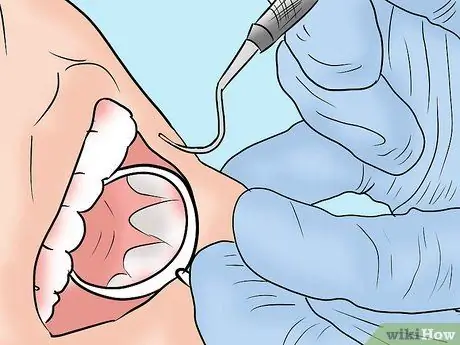
Step 4. Undergo gum tissue grafting
It could be that the pain you feel is actually not caused by the teeth, but the gums. Some people experience gum recession, which means the gums recede from the teeth, exposing the enamel and nerves of the teeth, and the teeth become very sensitive.
- If the pain is caused by gum recession, your dentist may suggest preventive measures. Sometimes gum recession is caused by inadequate oral and dental hygiene. Your dentist may recommend flossing regularly, brushing your teeth with a soft-bristled brush, and using a toothpaste such as Sensodyne.
- In severe cases, your dentist may refer you to an oral surgeon or periodontist for a gum graft. In this procedure, the doctor will take tissue from the roof of the mouth and graft it onto the damaged gums. After that, the tissue will recover and can protect the tooth as it should.

Step 5. Begin the desensitizer treatment
If your toothache isn't caused by cavities, decay, or injury, it's possible that your teeth are simply sensitive due to the loss of enamel. This condition can be treated, among other things, by gradually reducing tooth sensitivity, called a desensitizer.
A desensitizer is a topical treatment from a doctor that gradually reduces tooth nerve sensitivity. If the sensitivity of the nerves is reduced, the tooth pain will also be reduced

Step 6. Treat a tooth infection
Toothache can also be caused by infection of the dental pulp or even the root of the tooth. If so, you should seek treatment as soon as possible so that the infection doesn't damage your teeth or spread.
- Antibiotics are only needed if there is an infection in the mouth.
- Infection occurs due to purulent inflammation (abscess) caused by decay or injury.
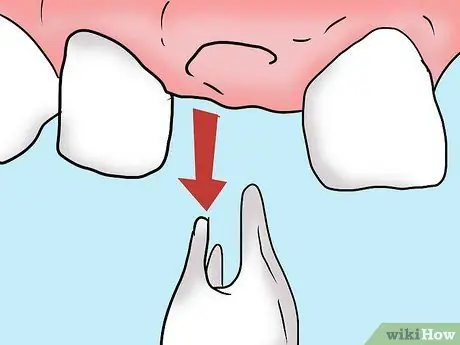
Step 7. Extract the aching tooth
If the pain in the tooth is caused by damage or severe infection, or due to the growth of wisdom teeth, then the tooth needs to be extracted. This is the last option. Extracted teeth are lost forever.
Wisdom teeth are usually extracted because it can cause the teeth to be too close together. Teeth that are too close together cause a lot of pressure in the mouth, causing pain or possible infection
Part 4 of 4: Preventing Toothache From Coming Again

Step 1. Brush your teeth and floss regularly
To avoid new damage or worsening existing damage, you must apply good oral health care. This is done so that your teeth are healthy, strong, and free of pain.
- Brush your teeth twice a day and floss once a day. Visit the dentist for regular checkups at least once a year or every six months. This way, the dentist can know if there is a problem.
- While brushing and flossing can't repair damage that has already occurred, it can prevent new damage and heal pre-decaying calcifications.
- Try to carry a toothbrush in your bag with you wherever you go so you can brush your teeth when you are outside. If you can't brush your teeth, at least rinse your mouth with water.

Step 2. Adopt a good diet for dental and oral health
What you eat determines the health of your teeth. For example, the sugar you eat will react with bacteria to form acids that can erode tooth enamel. So, reduce your sugar intake for better and healthier teeth.
- Cut down on soda, sweetened fruit juices, sweetened tea, or sweetened coffee. Add more water in the daily menu.
- Cut down on fast food, including sweets and cakes.
- Also avoid acidic foods and juices, such as orange juice, cola, and grapes. Choose a "basic" or non-acidic snack, such as yogurt, cheese, or milk.
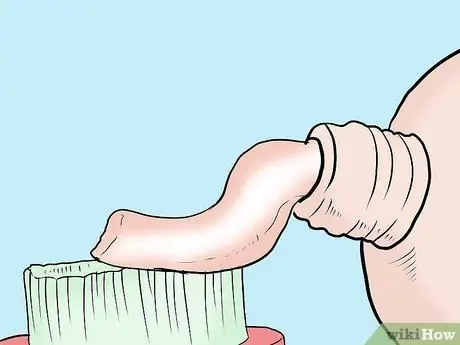
Step 3. Use a special toothbrush and toothpaste
If your toothache is caused by sensitive teeth, switch to a toothbrush and toothpaste specially formulated for sensitive teeth. You can find them easily at supermarkets or drugstores.
- Sensitive teeth are usually caused by receding gums. When the gums recede, the dentin below the enamel surface will be exposed. Toothpaste for sensitive teeth is formulated to clean these areas using gentler ingredients.
- Choose a soft-bristled toothbrush. If the toothache is related to gum damage, you can use a soft-bristled toothbrush to preserve the natural gum tissue.
- Hard and medium-bristled toothbrushes are usually effective at brushing off decay, but soft-bristled toothbrushes are a better choice for gum-related pain and the like.






