- Author Jason Gerald gerald@how-what-advice.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 10:50.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 12:04.
Registry in Windows is a database that stores the settings and options of the Windows operating system. The Registry contains information and settings for hardware, operating system default software, most third-party software, and user settings. The Registry also lets you see how the kernel is operating, by displaying computer performance information such as performance counters and active hardware. You can use the Registry Editor to modify the registry on your computer, which can be useful when you are troubleshooting hardware problems or removing viruses.
Step
Method 1 of 3: Via the "Run" Box
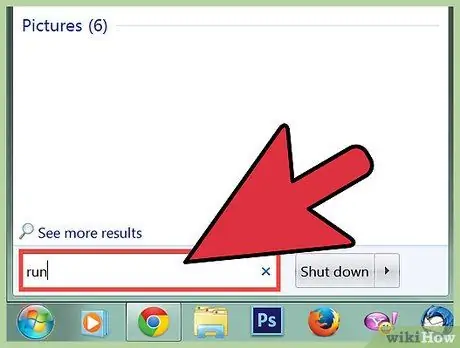
Step 1. Click the Start menu, then select "Run"
You can also press Win+R on any version of Windows. If you can't open the Start menu, read the next part of this article.
- Windows 8 - Go to the Start screen, then type run, or find "run" in the All Apps screen.
- Windows 8.1 - Right click the Start button, then select "Run".
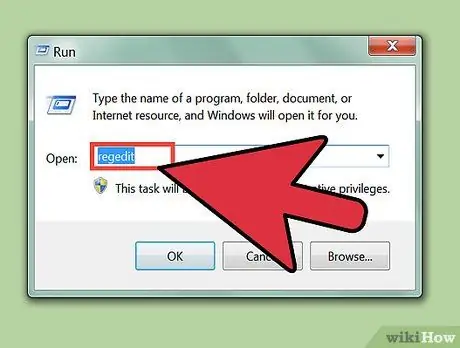
Step 2. Type regedit in the Run box, and press Enter to open the Registry Editor
- You may be asked for confirmation when you open the Registry Editor, depending on your computer's security settings.
- You need Administrator access to open Registry Editor.
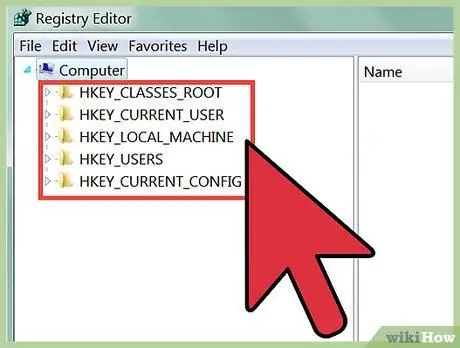
Step 3. Browse the Registry entries
Use the menu to the left of the Registry Editor to find the Registry key you want. Many directories have multiple levels of subdirectories. The keys in each directory will appear in the left frame.
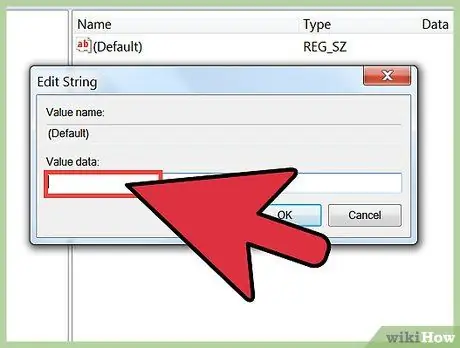
Step 4. Edit the key by double clicking on it
When you double-click a key in the right frame, a window that allows you to change the value for that key appears. You should only edit registry keys when you already know what they are used for, or when you follow trusted guidelines. Editing registry keys will affect the performance of your system, and even damage Windows.
Read security guides for editing the Registry on the internet
Method 2 of 3: Using the Command Line
Step 1. Open the command line
There are several ways to open the command line so you can keep it open even if one way is blocked. Here are the ways:
- Click Start, then select Command Prompt. If you are using Windows 8.1, right-click the Start button, then select Command Prompt. If you are using Windows 8, find Command Prompt on the All Apps screen.
- Press Win+R, type cmd, and press Enter.
- Press Ctrl+⇧ Shift+Esc to open Task Manager. Click File, hold down Ctrl, and click "Run new task".
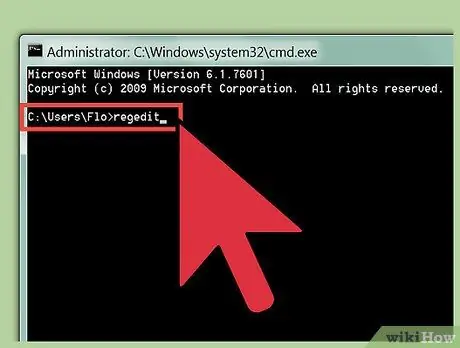
Step 2. Type regedit, and press Enter
You can enter this command at any location in the command line. You may be asked for confirmation when you open the Registry Editor.
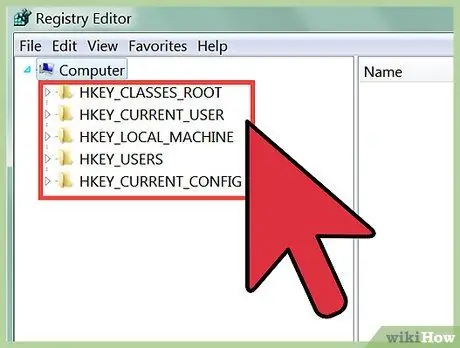
Step 3. Use the menu on the left of Registry Editor to explore Registry entries
The directory tree on the left of the screen will allow you to find the Registry key you want. Expand directory to see subdirectories. Selecting a directory displays the keys in that directory in the right frame.
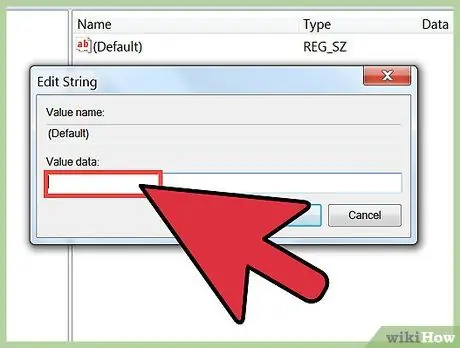
Step 4. Edit the key by double clicking on it
When you find the key you want to edit on the right side of the window, double-click on the key to edit it. Be careful when making changes -- changing the wrong key can cause Windows to crash.
Read security guides for editing the Registry on the internet
Method 3 of 3: Troubleshooting When regedit Can't Open
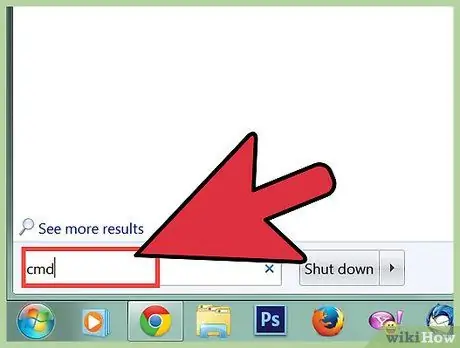
Step 1. Open the command line
If you can't open the Registry Editor, there may be a problem with your system settings, which is usually caused by a virus or malware infection. You can change the settings so that you can open the Registry Editor, but you should also remove the virus.
- Refer to step 1 in the previous section to open the command line.
- You can also open the command line in safe mode ("Safe Mode with Command Prompt") if the command line does not open in Windows. Read guides to do this on the internet.
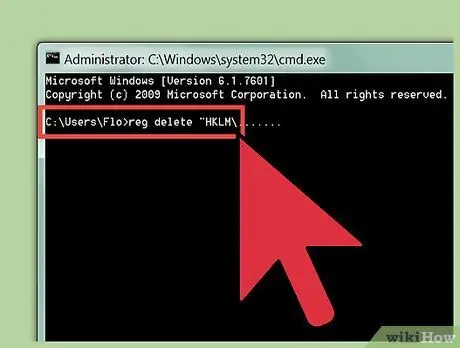
Step 2. Enter the command to unblock Registry Editor
Use a command line window to remove the key that is blocking Registry Editor. Enter the following command on the command line, then press Enter:
reg delete "HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Image File Execution Options\regedit.exe"
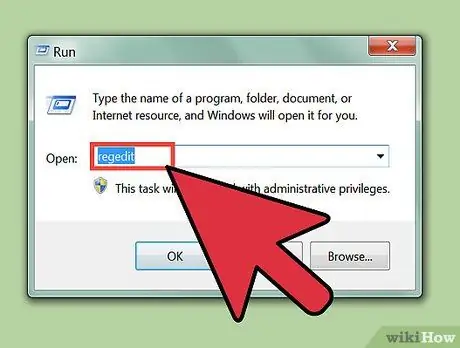
Step 3. Try opening the Registry Editor again with the two methods described earlier
Step 4. Recover system from virus or malware infection
Most likely, Registry Editor is blocked by a virus or malware, which may have come from an illegally downloaded program, an email attachment, or something else built into it. Read our guide to removing viruses and malware from the internet. If your system is in a bad state, you will most likely have to reinstall Windows.






