- Author Jason Gerald gerald@how-what-advice.com.
- Public 2024-01-19 22:11.
- Last modified 2025-06-01 06:05.
Globulins are simple proteins that exist in the body and their levels in the blood can be measured with the help of medical technology. If the levels in the body are too high or not in balance with the levels of albumin (another type of protein), the threat of several health problems is waiting in sight. Therefore, if you think you have high globulin levels or have received the diagnosis, immediately consult a doctor for recommendations for appropriate treatment. Fortunately, there are several methods that can be used to reduce globulin levels in the body, such as by changing your diet or lifestyle. In many cases, the best way to lower globulin levels is to treat the underlying medical disorder.
Step
Method 1 of 3: Changing Your Diet
Step 1. Cut down on high-protein foods to lower globulin levels in the body
If your doctor asks you to reduce your globulin levels, try to limit your intake of high-protein foods to start the process. Because protein contains very high levels of globulins, eating high-protein foods will undoubtedly increase the levels of globulins in your body. In particular, the ideal daily protein intake is 0.08 g/kg so you need to eat slightly below this amount of protein each day. Remember, changing your daily protein intake probably won't change the total protein number in your A/G ratio test, but it can significantly affect your globulin levels. Some examples of protein-dense foods that should be avoided are:
- Red meat and eggs
- Milk, cheese and yogurt
- Hemp seeds and soybeans

Step 2. Eat more fruits and vegetables to lower globulin levels
Both fruits and vegetables are low in protein. That is, you can consume as much as possible without worrying about the globulin levels in the body increasing. However, try not to eat fruits and vegetables that have been processed and/or packaged in cans because apart from being unnatural, such products are also unhealthy. Instead, consume more:
- Apples, pears and berries
- Oranges, grapefruit and other citrus fruits
- Tubers such as beetroot, turnips, and carrots
- Broccoli, cauliflower and peas
Step 3. Eat more nuts and healthy fats
If you only eat fruits and vegetables, your body will not receive complete and essential nutrition. Therefore, to keep your nutritional intake healthy and balanced without the need to consume large amounts of protein, try eating foods rich in healthy fats. In addition, eating nuts is also a perfect way to increase calories without consuming too many protein sources rich in globulins. In particular, consume more:
- Foods with healthy fats such as olive oil, safflower oil, sunflower oil, and soybean oil
- Nuts like walnuts, cashews and almonds

Step 4. Stop taking protein powders or protein supplements aimed at increasing globulin levels in the body
Like other protein sources, protein supplements and protein powders are also rich in globulins. Therefore, to suppress globulin levels in the body, stop using protein supplements! If you still want to increase muscle mass at the same time, try consulting the right and healthy way to do it.
Protein supplements are very popular consumed by people who do weight training regularly and want to increase their muscle mass
Method 2 of 3: Changing Your Lifestyle
Step 1. Do strength training and aerobic exercise to lower globulin levels in the body
In fact, exercising every day is one of the most effective ways to lower globulin levels. Therefore, if your doctor asks you to lower your globulin levels, try to exercise for at least 30 minutes every day. If you want, you can do one 30-minute weight training session or 3 10-minute jogging sessions at certain intervals.
- Aerobic exercise or cardiovascular exercise that can stimulate heart performance, such as running, swimming, jumping rope, or cycling
- Strength training generally involves weights, such as doing bench presses, lifting barbells, and doing squats

Step 2. Reduce stress to lower the globulin levels in your body.
In addition to having a negative impact on mental health, living side by side with excess stress can also increase the levels of globulins in your body. Therefore, focus on eliminating the stress you are feeling while trying to eliminate one by one the stressors that often interfere with your life. Some effective ways to reduce stress and calm yourself are:
- Try practicing meditation or yoga
- Make time for outdoor activities or leisurely walks
- Listen to relaxing music

Step 3. Keep your body hydrated by consuming as much water as possible every day
Dehydration can make globulin levels in the body increase. If left unchecked, this condition can make globulin levels too high and endanger your health. Therefore, drink plenty of water and other clear fluids (such as fruit juices or herbal teas) throughout the day to keep the body well hydrated.
Adult men should consume about 4 liters of water per day, while adult women should consume at least 3 liters of water per day
Method 3 of 3: Checking Globulin Levels in the Body

Step 1. See a doctor if you think you have chronic inflammation
Although high levels of globulins can be caused by many things, the accompanying symptoms are minimal. One of the most common symptoms is inflammation, which is often caused by fluid buildup in the feet and hands. Make sure you also see a doctor if you experience symptoms of liver disorders (which are generally caused by high levels of globulins in the body). Some of the symptoms of liver disorders are:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Body feels itchy
- Fatigue that doesn't go away and loss of appetite
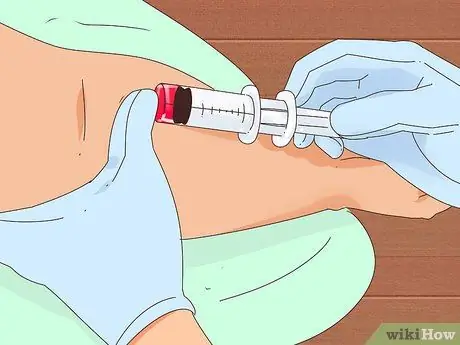
Step 2. Be prepared to have your A/G ratio checked by providing a sample of your blood
For those who are unfamiliar with the term, understand that the A/G ratio is a procedure that allows your doctor to measure the ratio of the amount of albumin to globulin in your body. In the procedure, the doctor will take a blood sample from the arm and send the results to a laboratory for analysis. After about 1-2 weeks, call the doctor again if the results of your examination have not come out.
- Low albumin levels can indicate liver disorders, kidney disorders, and disorders caused by poor absorption or digestion of protein in the body. In addition, low albumin may also be a symptom of acute malnutrition, celiac disease, or inflammation of the intestines.
- Total protein levels that are too high may indicate a chronic inflammatory problem, infection, or even multiple myeloma.
- If a blood-blocking device has been in place for too long, or if you are taking estrogen pills/oral contraceptive pills, the A/G ratio may not be accurate.

Step 3. Consult the possibility of performing serum protein electrophoresis
In particular, it is another type of blood test. In this procedure, the doctor will take a blood sample from the hand or arm with the help of a syringe, then send the results to a laboratory for analysis. Unlike the A/G ratio, which measures all types of globulins, serum protein electrophoresis will only measure the levels of gamma globulins in the body. Your doctor may recommend this test if you suspect an immune system disorder in your body.
Chances are, this test is also necessary if your doctor suspects multiple myeloma (a type of cancer) in your body
Step 4. Discuss the results of the examination with the doctor
In general, a globulin level that is too high indicates the presence of cancer cells in your body (such as Hodgkin's syndrome or malignant lymphoma), while a globulin level that is too low indicates a liver or kidney disorder. Don't worry, the doctor will be happy to explain the results to you.
High globulin levels can also be caused by dehydration or certain medications. To eliminate this possibility, don't forget to inform your doctor about the medicines you are taking
Tips
- A globulin imbalance can indicate a serious medical problem in the body, such as infection, immune disorders, inflammation, Hodgkin's syndrome, lymphoma, or some types of cancer.
- Actually, there are 4 types of globulins in your blood, namely alpha 1, alpha 2, beta, and gamma.
- Healthy levels of albumin and globulin in the body of each person does vary. However, in general, adults should have about 39-59 g/L albumin in their blood.
- Although the level of globulin that is considered normal in each person's body varies, ideally, an adult should have about 23-35 g/L of globulin in their blood.






