- Author Jason Gerald gerald@how-what-advice.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 10:50.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 12:04.
If you are using a large USB drive, you may want to partition it into sections, to make it easier for you to organize your files. In addition to making file management easier, you can also store multiple operating systems on one drive, as well as separate the operating system from other programs and/or files. To partition a USB drive in Windows, you must use a third-party program. Meanwhile, Linux and OS X provide built-in programs for partitioning drives.
Step
Method 1 of 3: Windows
Step 1. Know the limitations of the Windows operating system
While you can partition a drive in Windows through third-party programs, Windows can only read one of the partitions. You can't beat this limit. To change the visible partition, you can use the program that creates the partition.
- Disk Management does not allow you to partition a USB drive. Therefore, you should use a third-party partition manager program.
- If you connect the USB drive to a Linux or Mac computer, all the partitions you create will be accessible.
Step 2. Back up the files on the USB drive
When partitioning a drive, all data on the drive will be deleted. Therefore, you should back up the data on the drive before starting.
Step 3. Download Bootice
Bootice allows you to partition a USB drive, and enable specific partitions in Windows.
You can download Bootice from majorgeeks.com/files/details/bootice.html
Step 4. Extract the Bootice file with an archive manager program that supports RAR format
- One free archive manager program that supports the RAR format is 7-Zip, which you can download from 7-zip.org. After installing 7-Zip, right-click the Bootice file and select 7-Zip > Extract Here.
- You can also use the trial version of WinRAR to open Bootice files. However, this application that you can download from rarlabs.com requires you to purchase a license after the trial period ends.
Step 5. Run Bootice from the folder where you extracted the files
After double clicking Bootice, Windows may ask you to confirm the action.
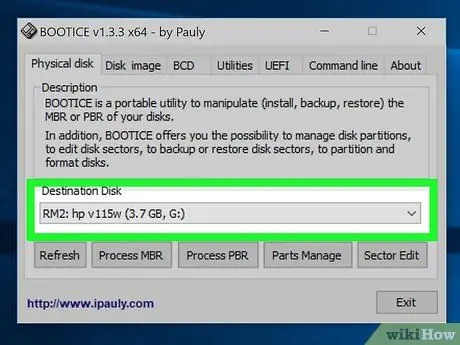
Step 6. Click the Destination Disk menu, then select your USB drive
Choose the right drive because all data on the selected drive will be erased. Pay attention to the size and letter of the drive before choosing.
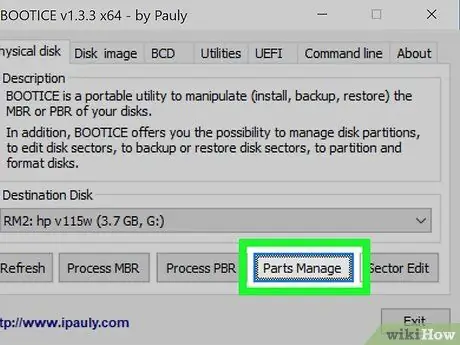
Step 7. Click the Parts Manage button in the Bootice window to open the Partition Manager feature
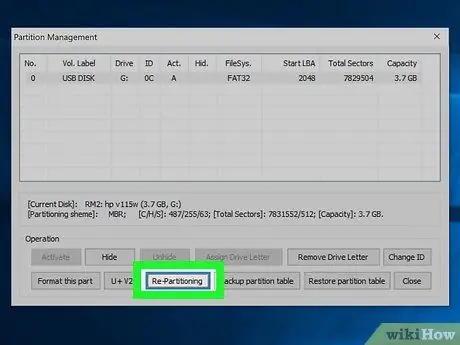
Step 8. Click the Re-Partitioning button to open the Removable disk repartitioning window.
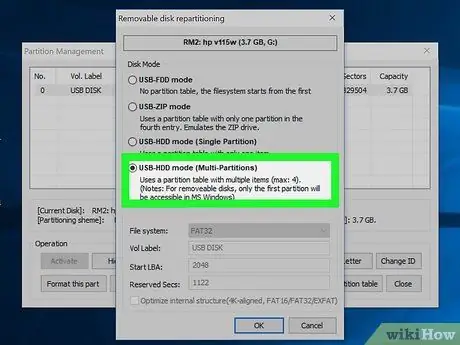
Step 9. Select the USB-HDD Mode (Multi-Partitions) option then click OK to open the Partition Settings window
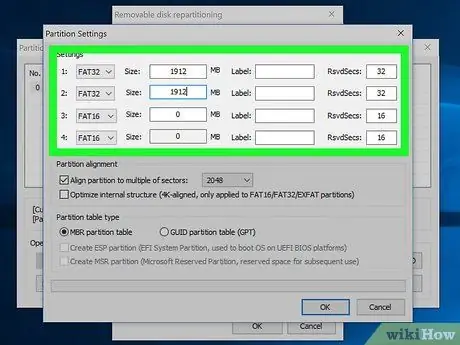
Step 10. Set the partition size you want
Generally, the available space on the drive will be divided equally into 4 partitions. You can adjust the size of each partition as needed. If you want to create less than 4 partitions, set the storage space on the unwanted partition to "0".
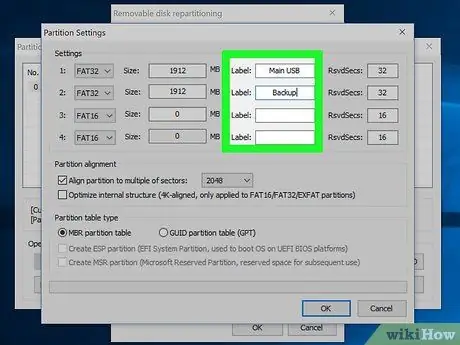
Step 11. Label the partitions to make it easier for you to distinguish the partitions on the drive
Since Windows can only display one partition at a time, it is highly recommended that you label each partition.
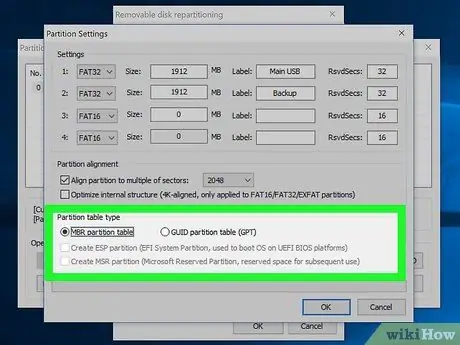
Step 12. Select the partition table
At the bottom of the window, you can select MBR or GPT options. If you will only use the drive to save data or start up an old computer, select MBR. On the other hand, if you want to use the drive to start a new computer, or if you want to use a more advanced partition table, select the GPT option.
Check the Create ESP Partition option so that your GPT drive can be used to start a computer with UEFI system
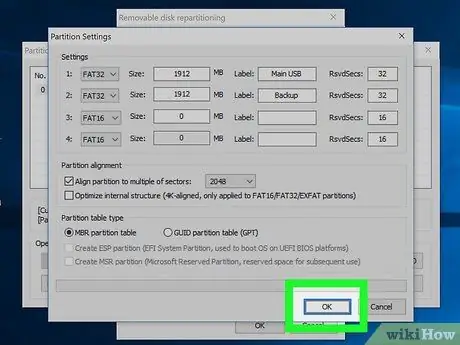
Step 13. Click OK to format the drive
You will receive a warning that all data on the drive will be erased. The formatting process will only take a few moments.
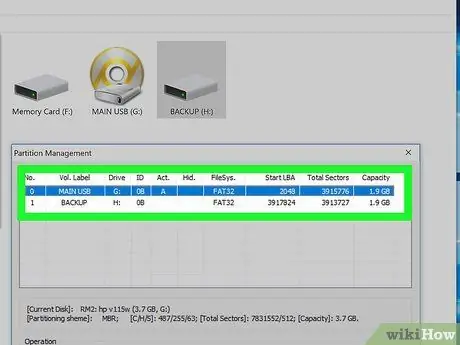
Step 14. After the format process is complete, the first partition will appear like a normal drive in Windows Explorer
Use the drive as usual.
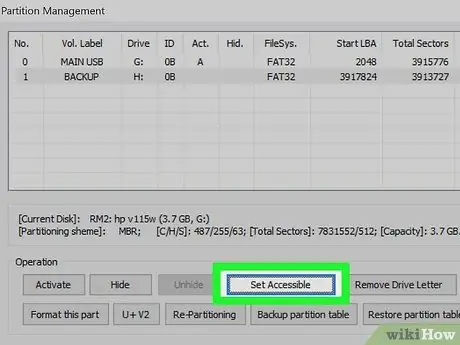
Step 15. Select the active partition with Bootice
Windows can only display one USB drive partition at a time. Therefore, to display other partitions, you must activate the partition via Bootice. You can select the partition you want to activate at any time.
- Open Bootice, then select the partition you want to activate in the Partition Manager window.
- Click the Set Accessible button. After a while, the partition you selected will be active, and Windows will display the partition.
Method 2 of 3: Mac
Step 1. Back up the files on the USB drive
When partitioning a drive, all data on the drive will be deleted. Therefore, you should back up the data on the drive before starting.

Step 2. Open the Utilities subfolder in the Applications folder and select Disk Utility
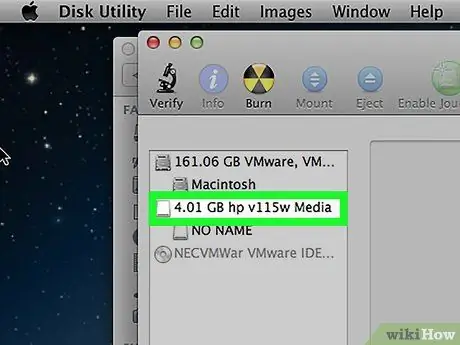
Step 3. Select the USB drive on the left side of the Disk Utility window
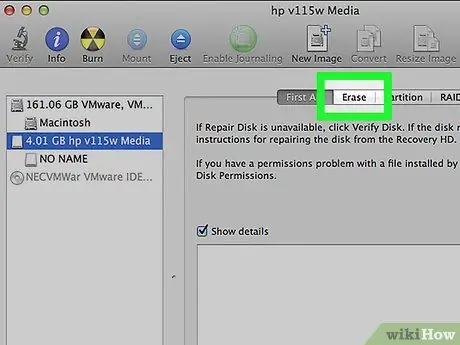
Step 4. Click the Erase button
A new window will open.
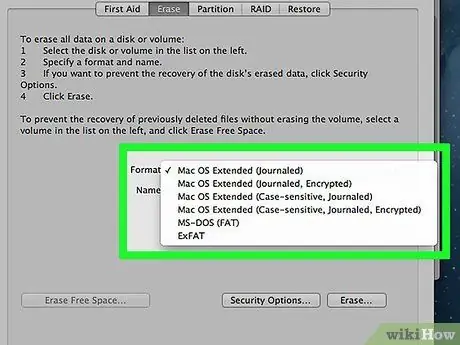
Step 5. To enable partitioning capabilities, select the GUID Partition Map option from the Scheme menu
To make it easier for you to resize the partition, select the OS X Extended (Journaled) file system in the Format option. However, this HFS/OS X Extended file system is only compatible with Mac computers
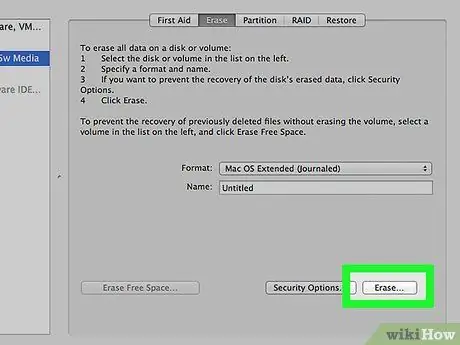
Step 6. Click Erase
The drive formatting process will begin. The new partition table will be written to the drive, and you will be able to click the Partition button in the Disk Utility window.
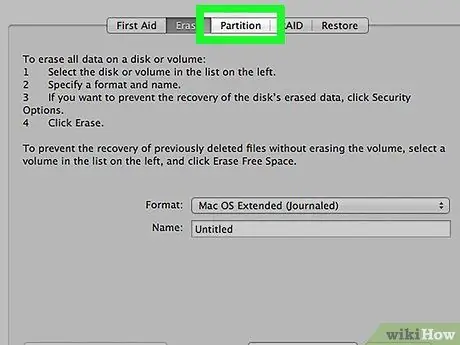
Step 7. Click the Partition button at the top of the Disk Utility window
The Partition window will open.
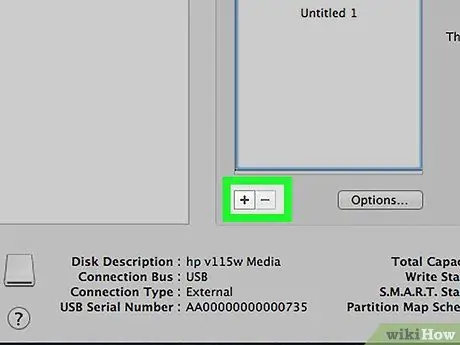
Step 8. To create a new partition, click the "+" button
You can create as many partitions as you need.
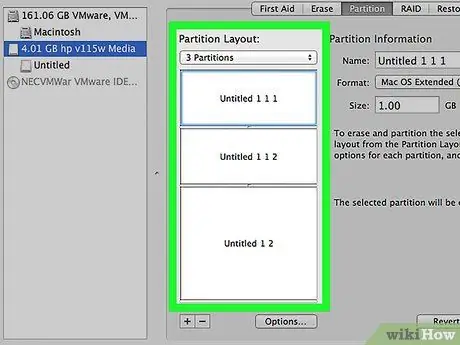
Step 9. Drag the edge of the circle graph to adjust the size of the partition
After determining the size of the new partition, the size of the old partition will also be adjusted.
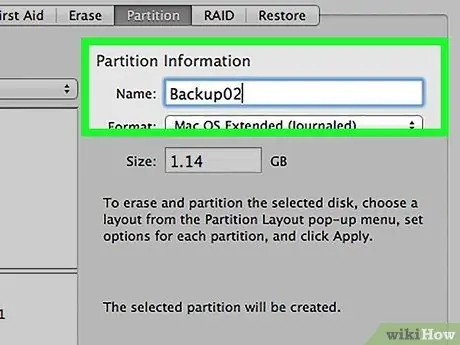
Step 10. Select a partition to label the partition
The partition label will make it easier for you to distinguish the partitions on the drive.
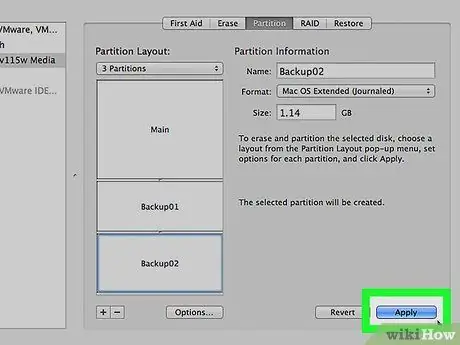
Step 11. Click OK to apply changes to the partition table
The formatting process will take a few moments.
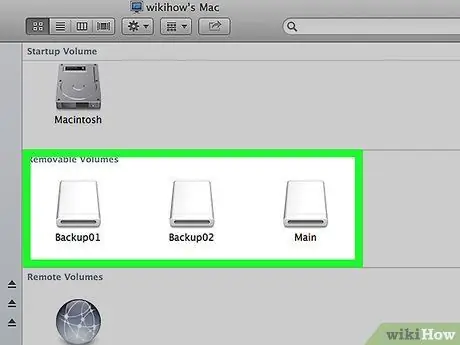
Step 12. Start using your new partition
Once formatted, all partitions on the USB drive will appear as separate drives.
The HFS/OS X Extended file system is supported only by computers with the OS X operating system. Windows does not support more than one partition in a USB drive without the help of third-party programs
Method 3 of 3: Linux
Step 1. Back up the files on the USB drive
When partitioning a drive, all data on the drive will be deleted. Therefore, you should back up the data on the drive before starting.
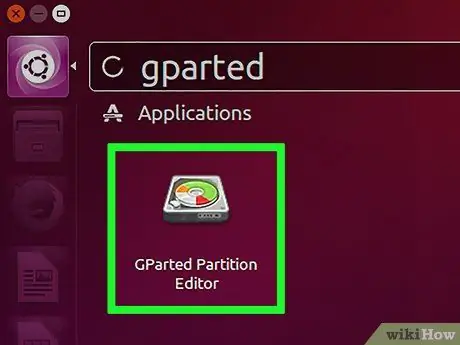
Step 2. Open GParted Partition Editor
This guide is based on the Ubuntu Linux distribution, which includes GParted by default. If your Linux distribution doesn't include GParted, you can download GParted via gparted.org/ or your distribution's package manager (such as yum or apt-get).
In Ubuntu, open the Dash and enter "gparted," or click "System" → "Administration" → "GParted Partition Editor."
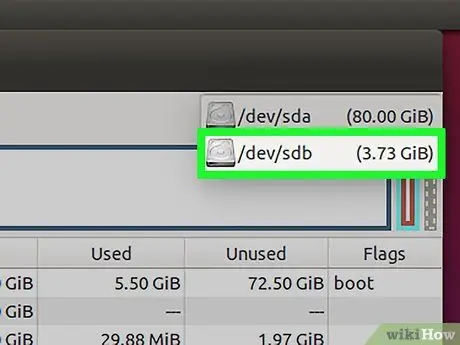
Step 3. Select your USB drive from the menu in the upper right corner of the window
Be careful when selecting a drive because if you choose the wrong drive, you may lose all the data on that drive. Pay attention to the size of the drive to help you identify the USB drive.
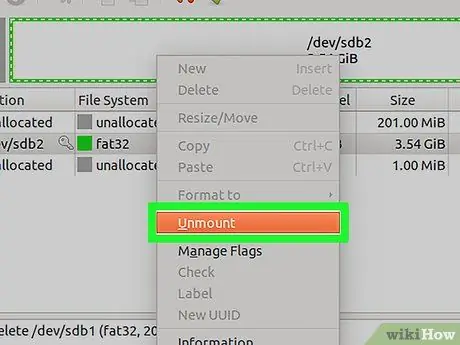
Step 4. Right-click on the drive and select Unmount to remove the drive from the operating system and prepare it for partitioning
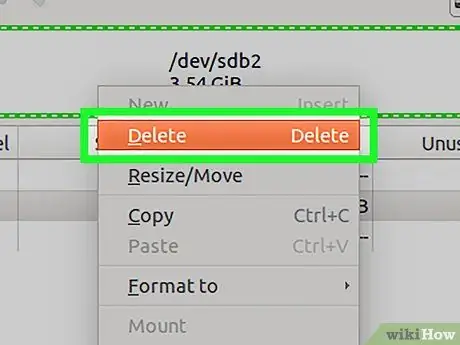
Step 5. Right-click the drive partition, then click Delete to delete it
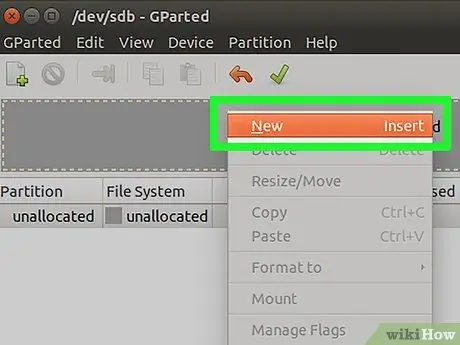
Step 6. Right-click on the Unallocated view, then select New
The Create new Partition window will open.
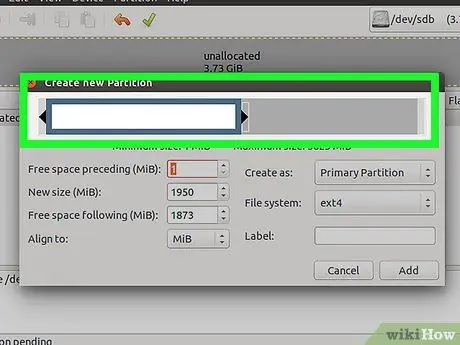
Step 7. Set the size of the new partition by sliding the button or entering the partition size (in MB) in the text box provided
Make sure you leave enough space for the second partition.
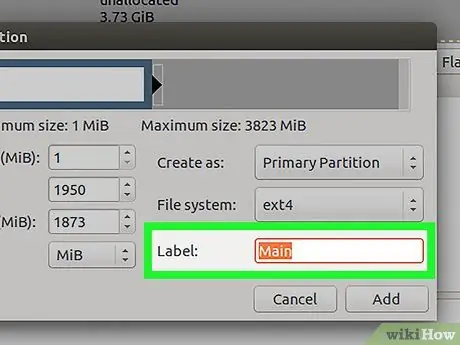
Step 8. Label the partitions to make it easier for you to distinguish them
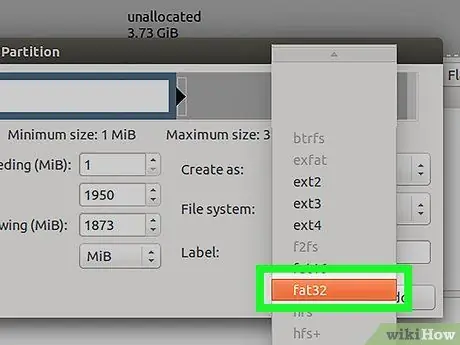
Step 9. Select the file system for the new partition
If you only want to use the partition on Linux, select EXT2. If you want to use a partition to start Windows, select NTFS. However, you can only start Windows from the first partition of the drive. To use a partition as a storage medium between operating systems, select the FAT32 or EXFAT file system.
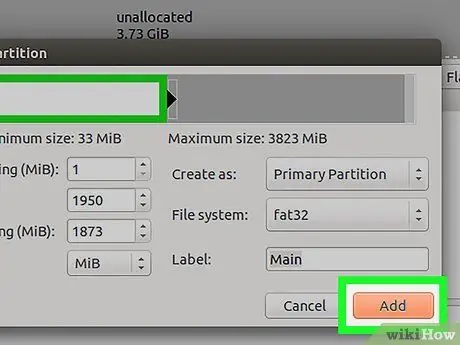
Step 10. To create a partition, click Add
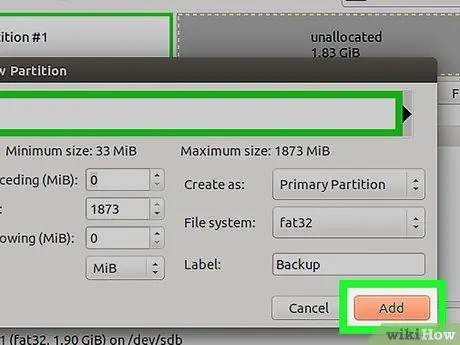
Step 11. Repeat the above process to create additional partitions
You can create additional partitions as long as there is free space on the drive.
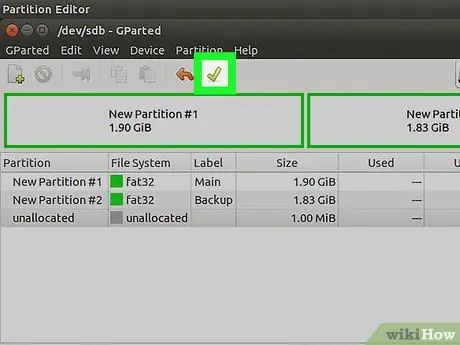
Step 12. When finished creating the partition, click the green check button in GParted, then click Apply to write the partition table on the drive
All changes you make will take effect. The partition creation process will take a while.
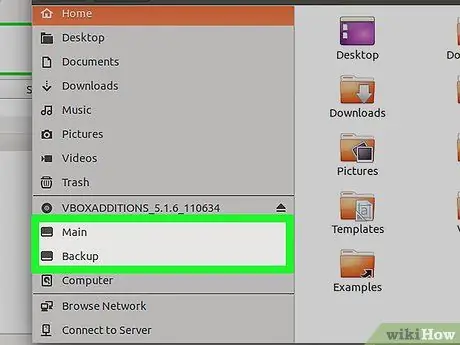
Step 13. Start using your new partition
Once formatted, all partitions on the USB drive will appear as separate drives.






