- Author Jason Gerald [email protected].
- Public 2024-01-19 22:11.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 12:04.
This wikiHow teaches you how to remove write protection from a file or removable storage device so you can edit the file or device content. You must use an administrator account to remove protection. Some types of removable storage spaces, such as CD-Rs have built-in write protection that cannot be erased.
Step
Method 1 of 5: Performing Basic Repairs

Step 1. Check the physical lock on the storage device
Most SD cards and USB fast drives have a small lever or switch on the cover that determines whether the device is writable or read-only. Therefore, look for such a lever or switch and slide it if necessary.
- Physical locks, especially on SD card covers often provide write protection that cannot be hacked or tricked until the lock is unlocked.
- If the lock mechanism is broken, you might be able to try to repair it.

Step 2. Make sure you are using the appropriate file system
Windows and Mac computers use different file systems by default (Windows uses the NTFS system which Macs don't support), and many fast drives, external hard drives, and SD cards are formatted for use on Windows computers. If you have difficulty using the drive on a Mac computer after using it on a Windows computer, you can reformat the drive by following these steps:
- Back up the contents of the drive on a Windows computer (the reformatting process will erase the contents of the drive).
- Attach the drive to the Mac computer.
- Change the drive format to " Mac OS Extended (Journaled) ".
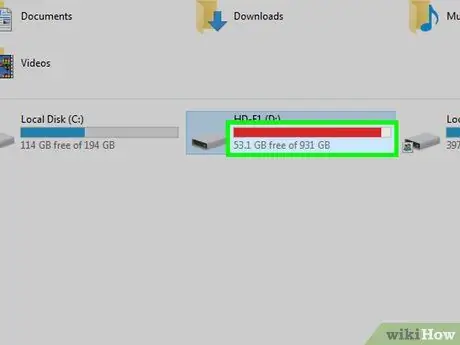
Step 3. Check if the memory on the drive is fully occupied
You may encounter a protection error when there is no more free space on the drive that you want to use/write to. You can check this by selecting the drive in question in the This PC (Windows) or Finder (Mac) program and looking at the amount of space left on the drive.
Step 4. Scan the computer for viruses
A computer virus can change the computer's response to removable storage space, or even make all USB devices read-only. A virus scan can solve any virus-related problems you are experiencing on your computer.
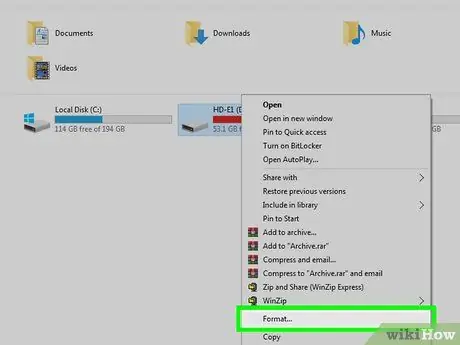
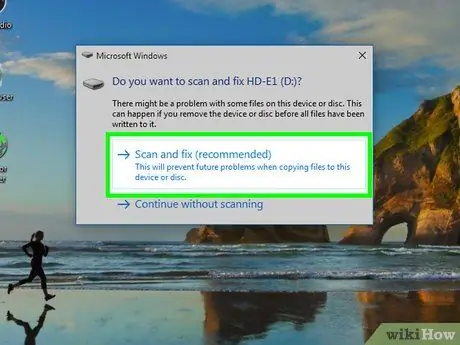
Step 5. Format the fast drive or CD.
The reformatting process will erase the contents of the removable device and change the file system according to the selected format option. Since this process will reset the device, make this the last step.
Method 2 of 5: Removing Protection from Files on a Windows Computer
Step 1. Open the “Start” menu
Click the Windows logo in the lower-left corner of the screen.
Step 2. Open File Explorer
Click the folder icon in the lower-left corner of the Start menu.
Step 3. Visit the file location
Click the desired file storage folder on the left side of the File Explorer window.
You may need to browse or browse some additional files or directories afterwards to find the files
Step 4. Select the file
Click the write-protected file that you want to delete.
Step 5. Click the Home menu option
It's in the upper-left corner of the window. After that, a toolbar will appear at the top of the window.
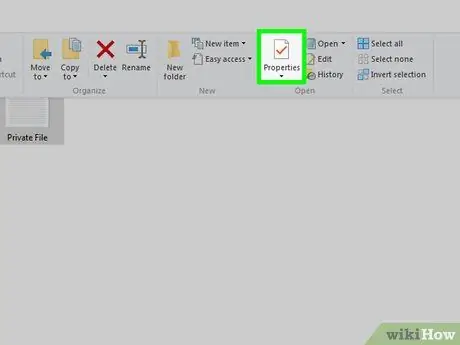
Step 6. Click the “Properties” icon
It's a red checkmark icon in the "Open" section of the toolbar. After that, the "Properties" window will be displayed.
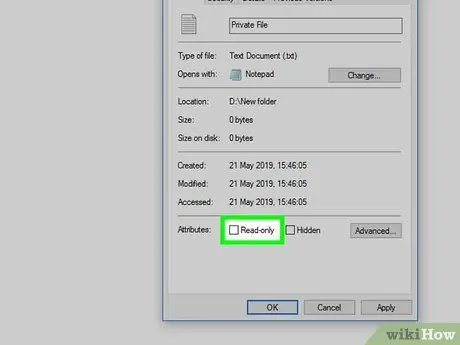
Step 7. Uncheck the "Read-only" box
This box is at the bottom of the “Properties” window.
If you don't see this option, make sure you're on the “ General ” in the “Properties” window.
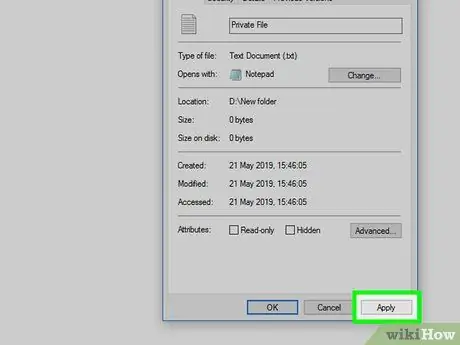
Step 8. Click Apply, then click OK.
These two buttons are at the bottom of the window. The changes will be saved to the file and the “Properties” window will be closed. Now, you can edit the file.
Method 3 of 5: Removing Protection from Files on Mac Computers
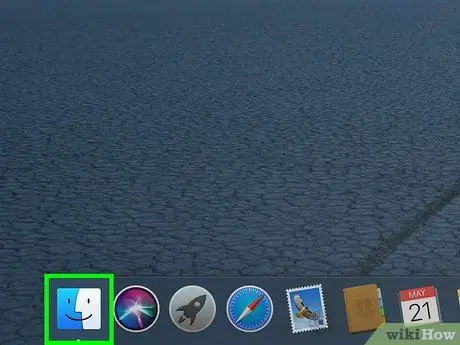
Step 1. Open Finder
Click the blue face icon in your computer's Dock. After that, a new window will open.
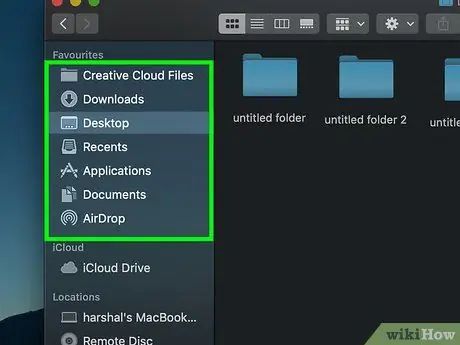
Step 2. Visit the location where the file is saved
Click the file storage folder on the left side of the Finder window.
You may need to go into a few additional folders afterwards to find the file you want
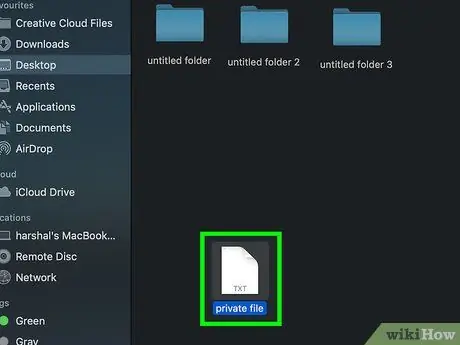
Step 3. Select the file
Click the file to select it.
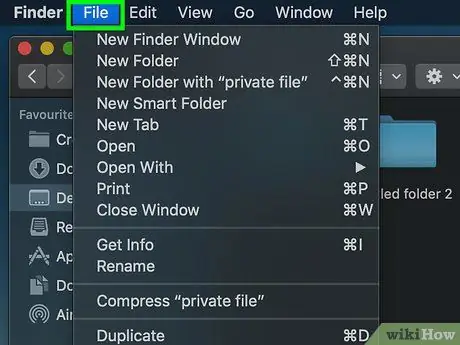
Step 4. Click File
This menu option is in the upper-left corner of the screen. After that, a drop-down menu will be displayed.
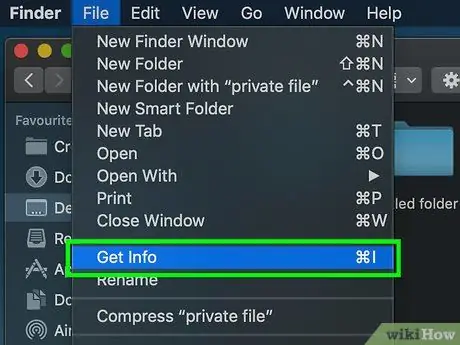
Step 5. Click Get Info
This option is in the drop-down menu “ File " Once clicked, the " Get Info " window for the selected file will be displayed.
Step 6. Unlock on “Get Info” menu
If the lock icon in the lower-right corner of the window is closed, click the icon, then enter the administrator password.
Step 7. Click the Sharing & Permissions heading
This title is at the bottom of the window. Menus " Sharing & Permissions ” will be expanded to show additional options.
If the title " Sharing & Permissions ” contains username and “Read Only” option below it, skip this step.
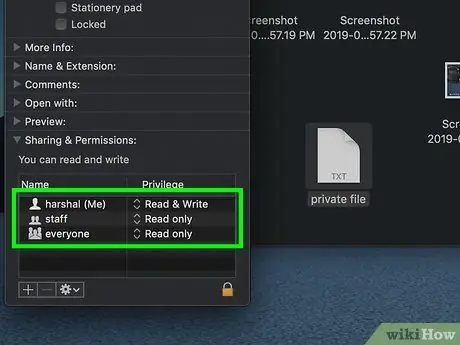
Step 8. Find your username
Under the heading " Sharing & Permissions ”, you can see the name used to log in to the computer.
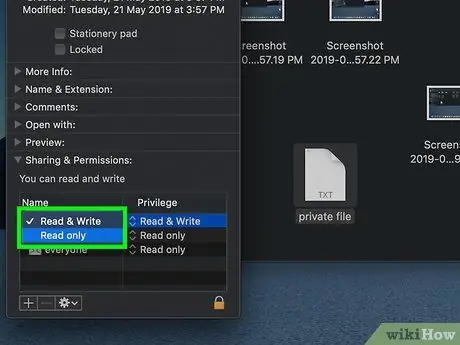
Step 9. Change file permissions
Click the " Read Only " box next to the name until the label changes to " Read & Write ", then close the " Get Info " window. You can now edit the file.
Method 4 of 5: Removing Protection from Free Storage Space on Windows

Step 1. Make sure the storage device is connected
A USB fast drive, external drive, or SD card must be installed on the Windows computer before proceeding to the next step.
Step 2. Open the “Start” menu
Click the Windows logo in the lower-left corner of the screen.
Step 3. Type regedit into the “Start” menu
The computer will look for the Registry Editor command.
Step 4. Click regedit
This blue block icon appears at the top of the “Start” window. After that, the Registry Editor program window will open.
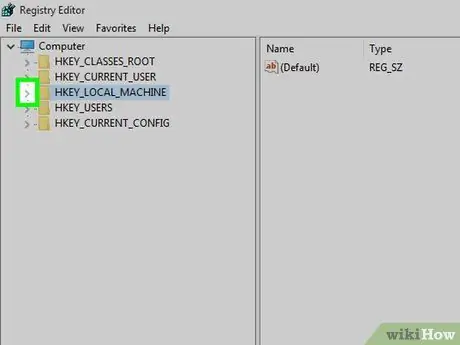
Step 5. Expand the "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE" folder
Click the down arrow on the left side of the " HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE " folder in the upper left corner of the window.
You may need to swipe up on the left pane of the window to find this folder
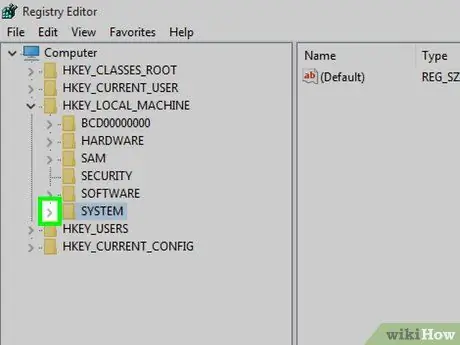
Step 6. Expand the "SYSTEM" folder
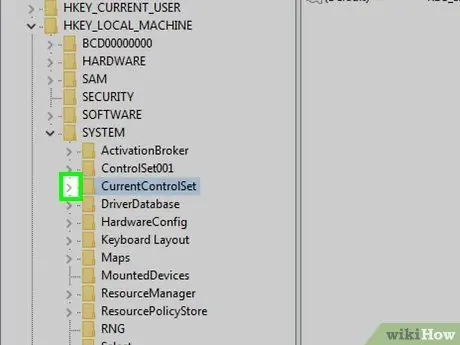
Step 7. Expand the "CurrentControlSet" folder
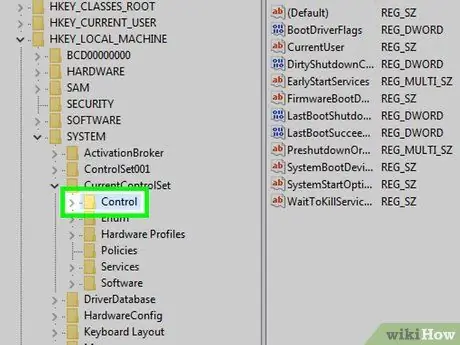
Step 8. Select the "Control" folder
Click a folder to select it.
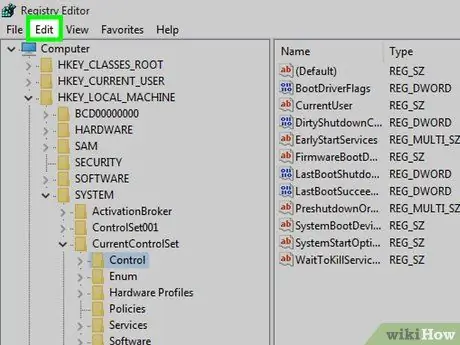
Step 9. Click Edit
It's a tab at the top of the window. Once clicked, a drop-down menu will open.
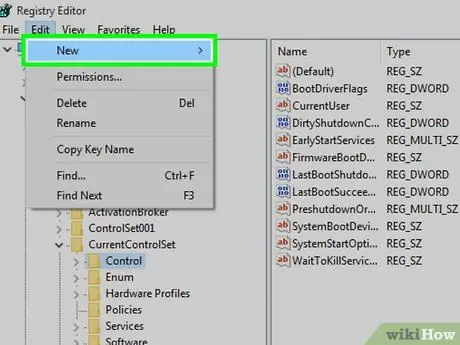
Step 10. Select New
It's at the top of the drop-down menu Edit ”.
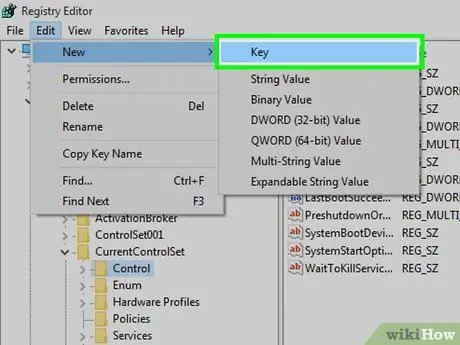
Step 11. Click Key
It's at the top of the pop-out menu " New " The new folder (also known as " Key " or keys) will be displayed in the " Control " folder.
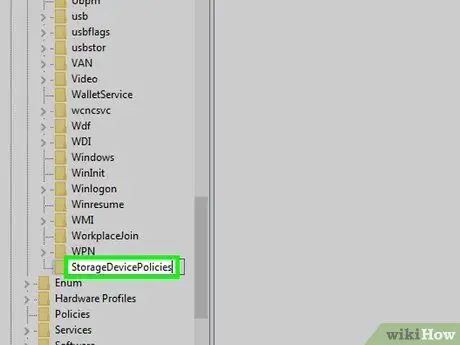
Step 12. Rename the key
Type StorageDevicePolicies and press Enter.
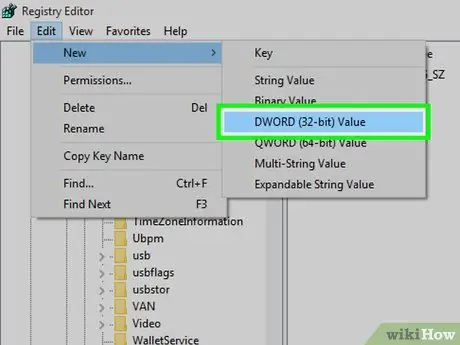
Step 13. Create a new DWORD entry in the key
To make it:
- Select the "StorageDevicePolicies" key you just created.
- Click " Edit ”.
- Choose " New ”.
- Click " DWORD (32-bit) Value ”.
- Type WriteProtect and press Enter.
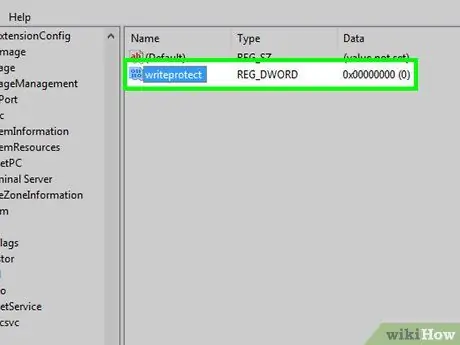
Step 14. Open the DWORD value
Double-click the value to open it. After that, a new window will be displayed.
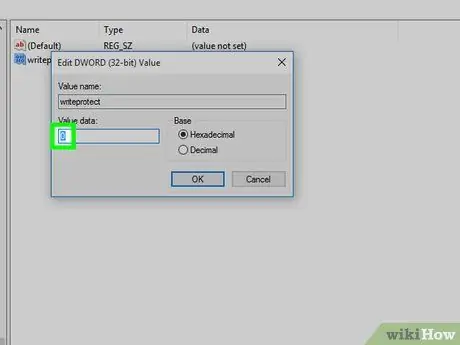
Step 15. Change the "Value" number to zero
Select a number in the " Value " column, then type 0 to replace the number.
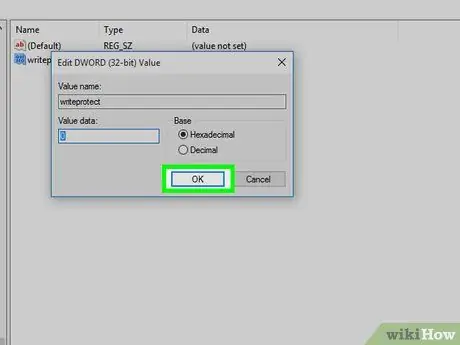
Step 16. Click OK
After that, the read-only error you're experiencing on the removable storage device will be fixed.
If the speed disc or CD is still not writable, you will need to take it to a data recovery service to save the content stored on it
Method 5 of 5: Removing Protection from Free Storage Space on Mac Computers

Step 1. Make sure the storage device is connected
A USB fast drive, external drive, or SD card must be installed on the Windows computer before proceeding to the next step.
If you're using a newer Mac computer, you may need to use an adapter for a removable storage device that plugs into one of the computer's USB-C ports
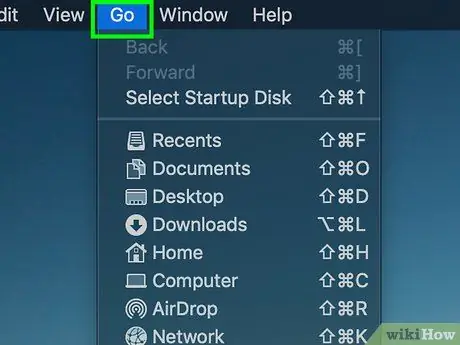
Step 2. Click Go
This menu option is at the top of the screen. After that, a drop-down menu will be displayed.
If you don't see the option " Go ” at the top of the screen, click the desktop or the blue Finder face icon in your computer's Dock to display it.
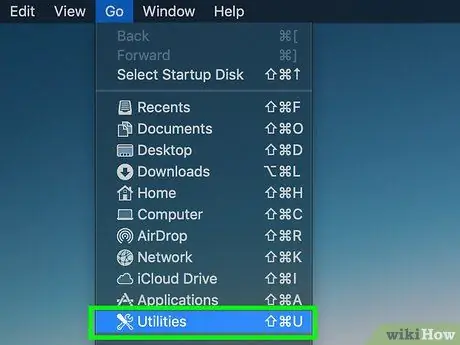
Step 3. Click Utilities
This option is at the bottom of the drop-down menu “ Go ”.
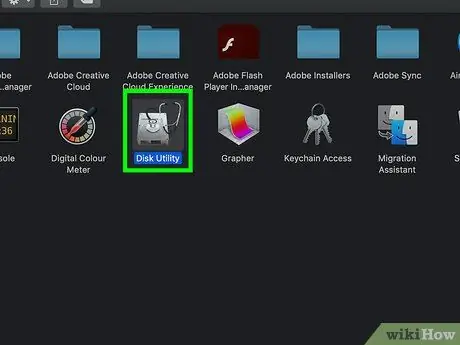
Step 4. Open Disk Utility
Double-click the hard drive-shaped " Disk Utility " icon to open it. After that, a new window will open.
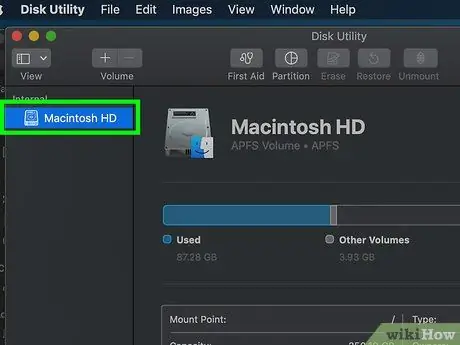
Step 5. Select a storage device
Click the storage device name in the upper-left corner of the Disk Utility window.
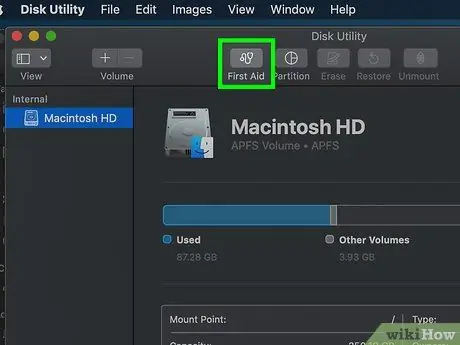
Step 6. Click on First Aid
It's a stethoscope-shaped tab at the top of the Disk Utility window.

Step 7. Wait for the computer to finish scanning
If the device write protection is enabled because of an error on the device itself, the error will be corrected and you can use the drive again as usual.






