- Author Jason Gerald gerald@how-what-advice.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 10:50.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 12:04.
Maybe you've experienced this. When you try to delete a file, an error message appears that says: Cannot delete: Access is denied.' Make sure the disk is not full or write-protected and that the file is not currently in use.' You can use several methods to permanently delete the file. However, before you go through all the steps in this article, it's important that you first make sure that the file is really not in use at this point. If this is not the cause, you can use a free third-party application, or use a simple command line tool to forcefully delete the file or folder.
Step
Method 1 of 3: Closing Files Still Open
Step 1. Close any programs that are still open
The most common cause of this error message is that a program is currently accessing the file that you want to delete. An example is when you try to delete a document that is currently open in Microsoft Word, or delete a song that is currently playing.
Step 2. Open "Task Manager"
Press Ctrl+Alt+Del, then select "Task Manager" from the menu that appears. Click the " User Name " tab, then look for the entry under your username. Most programs can be closed without crashing the computer system.
Step 3. Close any programs you recognize
This can be done by selecting the program and clicking "End Process".
If you close a program that makes the computer system unstable, restart the computer to restore it
Step 4. Restart your computer
Restarting the computer can often resolve failures when deleting certain files because the file is being accessed by a program. Try deleting files after you restart your computer and before you open any programs. If the file still displays an error message when you try to delete it, continue to the next method.
Method 2 of 3: Using Third Party Programs
Step 1. Look for a program to unlock
Some of the popular programs include Process Explorer, Unlocker, and LockHunter. For Mac computers, you can use Lock-UnMatic and Mac OS File Unlocker. All of these programs are available for free and can be integrated into the Windows interface. If you use Unlocker, be careful when browsing their website as there are many misleading advertisements that can introduce malware into your computer.
Step 2. Install the program
All of these programs are quite easy to install. Extract the installation file if needed and run the Install or Setup file. The installation setup usually works fine for most users.
Some programs may try to install a web browser toolbar during the installation process. Make sure you've deselected this option if you don't want to install a new toolbar
Step 3. Right-click the file you want to delete
From the menu that appears, select the tool you just installed. A new window will open showing a list of the programs currently accessing the file.
Step 4. Close the program
Select the program you want to close, then click the "Kill Process" button. When all programs that are locking files have been closed, you can easily delete the files.
Method 3 of 3: Using Command Prompt
Step 1. Find the files on your hard disk (hard drive)
If you're having trouble finding it, try using the Search option. Click the "Start" menu and type the file name into the Search field. If you're using Windows 8, start typing the file name when you're at the Start screen.
Step 2. Right-click the file, then select "Properties"
Remove (uncheck) all attributes of the file or folder.
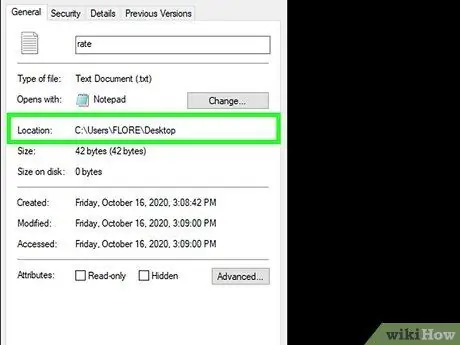
Step 3. Note the location of the file
You will need the location of this file later when you force delete it using the Command Prompt.
Step 4. Run Command Prompt
This can be done by clicking Start and typing "cmd" into the Search field (without the quotes).
Step 5. Close all open programs
Close all other open programs, but keep Command Prompt open.
Step 6. Open Task Manager
This can be done by pressing Ctrl+Alt+Del, then selecting "Task Manager" from the menu that appears. You can also do this by pressing Start, then " Run ", and typing "TASKMGR. EXE".
Step 7. Click the "Processes" tab present in the Task Manager
Look for a process named "explorer.exe". Select the process and click the "End Process" option. Shrink the Task Manager window, but dont close.
Step 8. Return to Command Prompt
Here you can forcibly delete files or folders using a simple command line tool. Although files and folders can be deleted in the same way, there are slight differences in the commands that must be used.
Step 9. Look for this path:
C:\Documents and Settings\Your Username>. It will be in your command prompt.
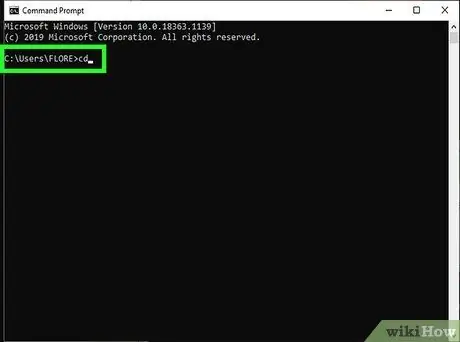
Step 10. Execute the command
In the Command Prompt window, enter cd My Documents after your Username.
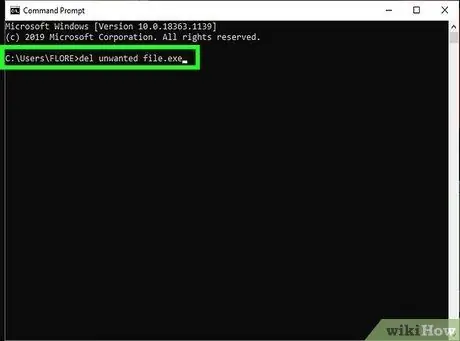
Step 11. Delete the file
After "My documents", enter the Delete command followed by the name of the file you want to delete. For example, "del unwanted file.exe".
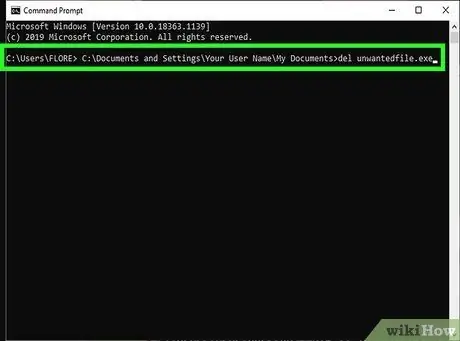
Step 12. Use the DEL command to delete stubborn files in the Command Prompt window
The final command should look like this: C:\Documents and Settings\Your Username\My Documents>del unwanted file.exe.
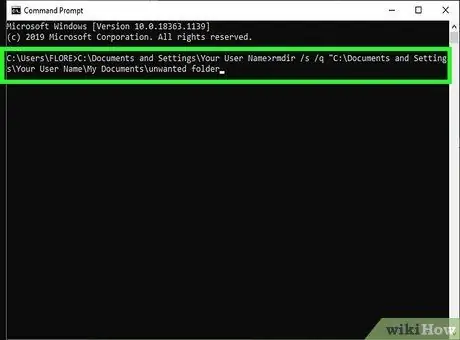
Step 13. Delete a folder
Use the "RMDIR /S /Q" command instead of the "del" command if you want to delete folders, not files. The command line should look like this: C:\Documents and Settings\Your Username>rmdir /s /q "C:\Documents and Settings\Your Username\My Documents\unwanted folder".

Step 14. Press ALT+TAB key
The Task Manager window will be displayed again. Next, restart the windows interface by clicking File, selecting New Task, and typing "EXPLORER. EXE".
Step 15. Close Task Manager
By now the file must have been deleted. You can check it by doing a search. Press Start and enter the name of the file into the search field.
Tips
- To get more information about the DOS Command, type HELP into the Command Prompt window, or search the internet for information.
-
To return to the previous directory in the Command Prompt window, use the following command:
CD..
Warning
- This trick will not work if the file you want to delete is being used by another program. Like when you want to delete an mp3 file that is currently playing. If this happens, close the media player program you used to play the file and delete the file.
- Don't end any other process except "EXPLORER. EXE". If you do, this action can cause something unwanted, such as loss of data, system becomes unstable, and operating system crashes or crashes.






