- Author Jason Gerald gerald@how-what-advice.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 10:50.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 12:04.
If there is a suspicion that you have diabetes, immediately consult a doctor. Type 1 diabetes develops when the islet cells in the pancreas no longer produce insulin. This type of diabetes is an autoimmune disease that makes these cells no longer function. Type 2 diabetes is more related to lifestyle (due to lack of exercise and excessive sugar consumption). It is very important for you to know the signs and symptoms of diabetes and the diagnosis so that it can be treated as soon as possible.
Step
Part 1 of 2: Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms of Diabetes
Step 1. Be aware of the signs and symptoms
If you experience one or two things from the list below, we recommend seeing your doctor for further evaluation. Common signs and symptoms of Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes are:
- Excessive thirst
- Excessive hunger
- Blurred vision
- Frequent urination (waking up 3 or more times at night to go to the bathroom)
- Fatigue (especially after eating)
- Quick to feel irritated or irritable
- Wounds don't heal or are slow to heal
Step 2. Pay attention to your lifestyle
People who are inactive (less or never exercise) have a high risk of Type 2 diabetes. People who are overweight or obese, or eat more sugary foods and refined carbohydrates than the ideal amount are also at increased risk of developing Type 2 diabetes.
Be aware that the development of Type 2 diabetes is related to an unhealthy lifestyle, while Type 1 diabetes is a congenital condition that is usually seen in childhood

Step 3. See a doctor
The only way to confirm whether you have diabetes or not is to have a diagnostic test with a doctor (through a blood test). Blood test results determine whether you are "normal," "prediabetic" (have a high risk of developing diabetes in the near future if you don't make significant lifestyle changes), or "diabetic."
- The sooner you know for sure, the better because diabetes requires early treatment.
- The damage to the body associated with diabetes is usually the result of long-term "uncontrolled sugar levels". This means that if you receive treatment that helps control your blood sugar, you can prevent or at least "delay" many of the long-term health consequences of diabetes. Therefore, you should get a diagnosis and treatment as soon as possible.
Part 2 of 2: Undergoing Diagnostic Tests for Diabetes
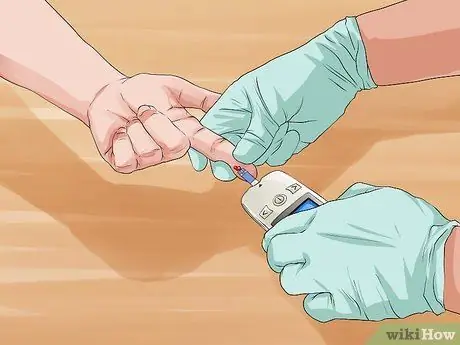
Step 1. Run the test
Doctors can do 2 tests to check blood glucose. Normally, diabetes checks are done with a fasting blood test, but it can also be done with a urine test.
- Normal blood glucose levels range from 70 to 100.
- The threshold for diabetes ("prediabetes") blood sugar levels is between 100 and 125.
- A blood sugar level above 126 is considered diabetes.

Step 2. Measure HbA1c (hemoglobin A1c) levels
This test is newer than the usual test, and is used by some doctors to diagnose diabetes. This test checks for hemoglobin (a protein) in red blood cells and measures how much protein is stuck to it. A large amount means there is a lot of sugar attached, and it is directly correlated with diabetes risk.
- To explain the normal correlation between HbA1c and mean blood sugar levels are as follows: HbA1c 6 equals blood glucose level of 135. HbA1c 7 = 170, HbA1c 8 = 205, HbA1c 9 = 240, HbA1c 10 = 275, HbA1c 11 = 301, and HbA1c 12 = 345.
- In most labs, the normal range for HbA1c is between 4.0-5.9%. In cases of uncontrolled diabetes, the value is 8.0% and above, and in controlled patients it is less than 7.0%.
- The benefit of measuring HbA1c is that it provides an overview of what is happening over time. The HbA1c value reflects the average sugar level in the last 3 months, unlike the simple glucose test which is a one-time measurement of sugar levels.

Step 3. Undergo treatment
In diabetes treatment, you will need insulin in the form of injections or pills every day, and will be asked to pay attention to diet and exercise.
- Sometimes, in milder cases of Type 2 diabetes, all you need is diet and exercise. Adequate lifestyle changes can tackle diabetes and return you to "normal" sugar levels. The motivation is certainly enough to change the lifestyle.
- You will be asked to reduce the consumption of sugar and carbohydrates, and exercise for about 30 minutes a day. By complying with these changes, you will see a significant reduction in blood sugar levels.
- On the other hand, Type 1 diabetes always requires insulin injections because this condition is an autoimmune disease caused by the body's inability to produce insulin.
- Diabetes must be treated properly. If left untreated, high blood sugar can lead to more serious health problems, such as nerve damage (neuropathy), kidney damage or failure, blindness, and blood circulation problems that can lead to infections that are difficult to cure and progress to gangrene requiring amputation (especially in the extremities). lower).
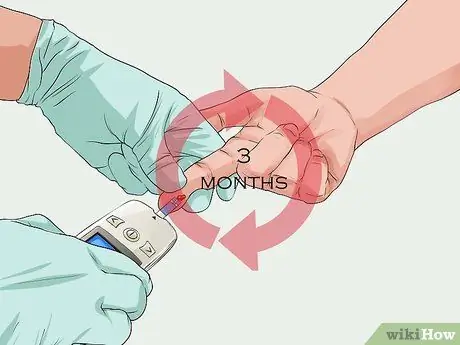
Step 4. Run a follow-up test
Blood tests should be repeated every 3 months for people who fall into the "prediabetes" or "diabetic" categories. The point is to monitor improvement (for those who make positive lifestyle changes) or condition decline.
- Repeated blood tests also help doctors determine insulin and medication doses. Doctors try to "target" blood sugar levels to fall within a certain range. So, the results of follow-up blood tests are very important.
- Repetition can also be a motivation to exercise more often and change your diet because you can see real results on your next blood test.






